Stationary Waves (Cambridge (CIE) AS Physics) : Revision Note
Stationary waves
Stationary waves, or standing waves, are produced by the superposition of two waves of the same frequency and amplitude travelling in opposite directions
This is usually achieved by a travelling wave and its reflection. The superposition produces a wave pattern where the peaks and troughs do not move
Formation of a stationary wave
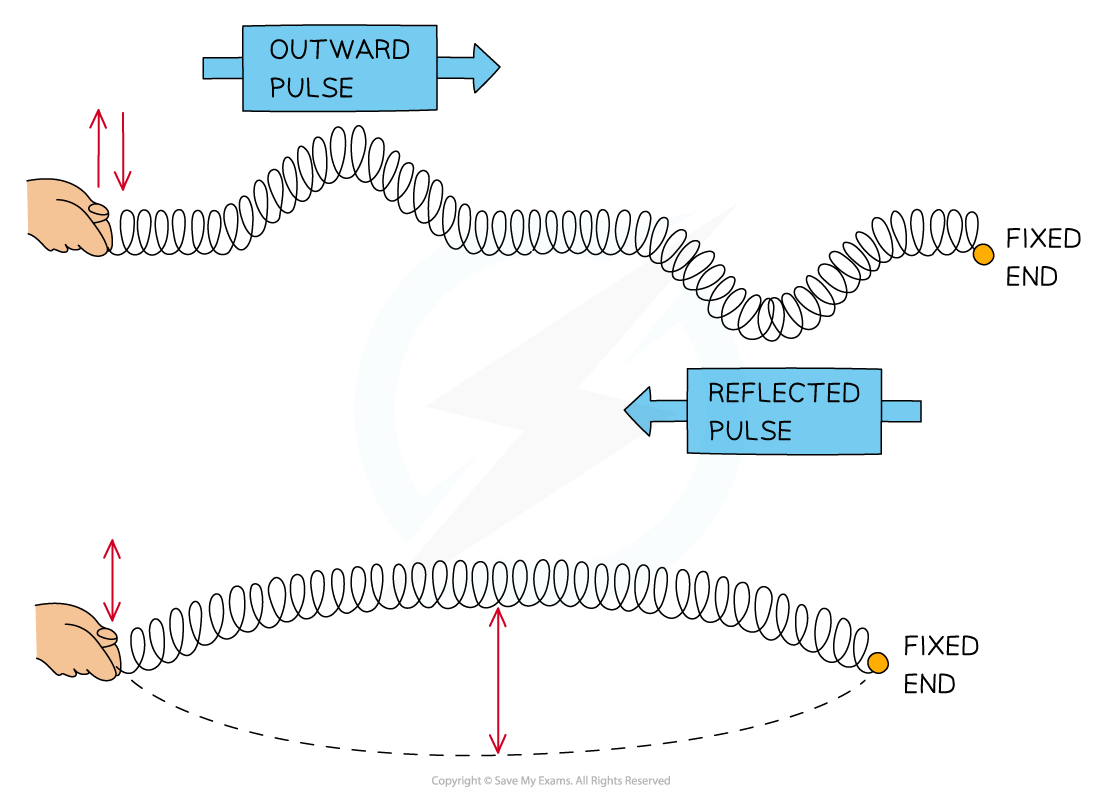
Formation of a stationary wave on a stretched spring fixed at one end
Stretched strings
Vibrations caused by stationary waves on a stretched string produce sound
This is how stringed instruments, such as guitars or violins, work
This can be demonstrated by a length of string under tension fixed at one end and forced to vibrate due to an oscillator:
Standing wave experiment
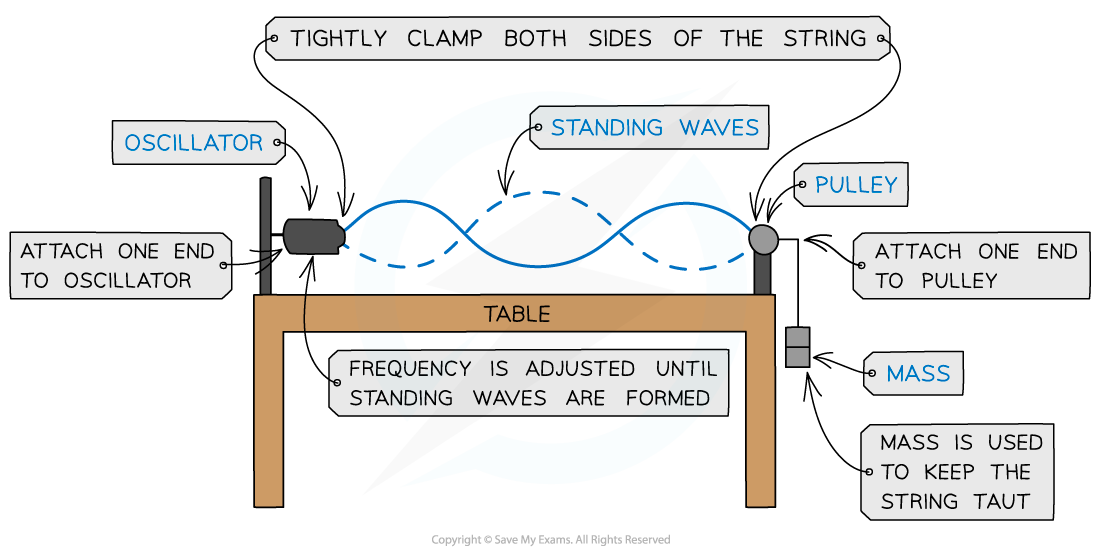
Stationary wave on a stretched string kept taut by a mass and pulley system
As the frequency of the oscillator changes, standing waves with different numbers of minima (nodes) and maxima (antinodes) form
Microwaves
A microwave source is placed in line with a reflecting plate and a small detector between the two
The reflector can be moved to and from the source to vary the stationary wave pattern formed
By moving the detector, it can pick up the minima (nodes) and maxima (antinodes) of the stationary wave pattern
Stationary microwaves
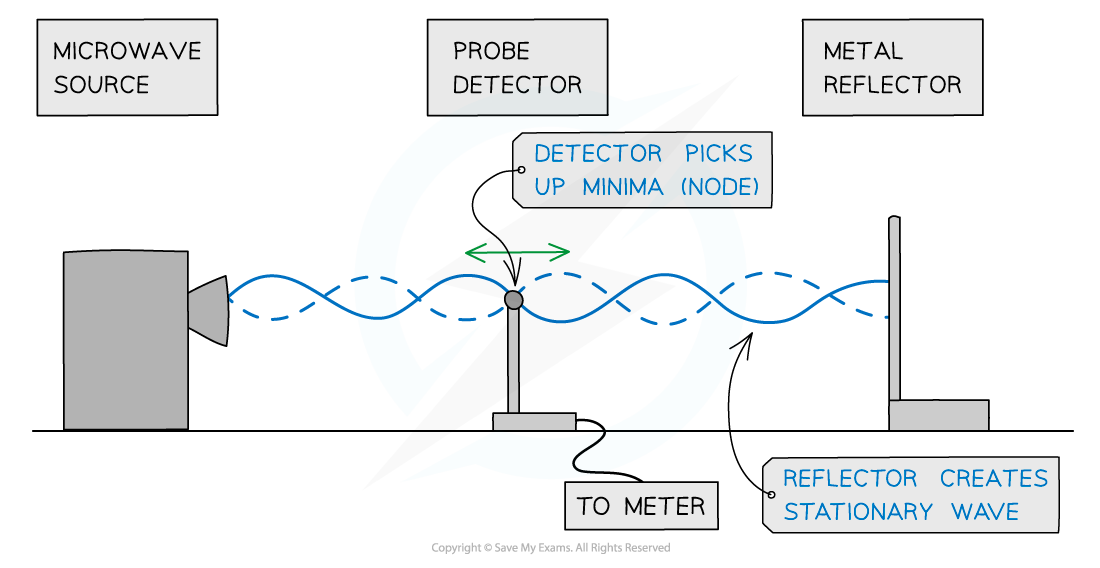
Using microwaves to demonstrate stationary waves
Air Columns
The formation of stationary waves inside an air column can be produced by sound waves
This is how musical instruments, such as clarinets and organs, work
This can be demonstrated by placing a loud speaker at the open end of an air column with fine powder inside
At certain frequencies, the powder forms evenly spaced heaps along the tube, showing where there is zero disturbance as a result of the nodes of the stationary wave
Stationary waves in an air column
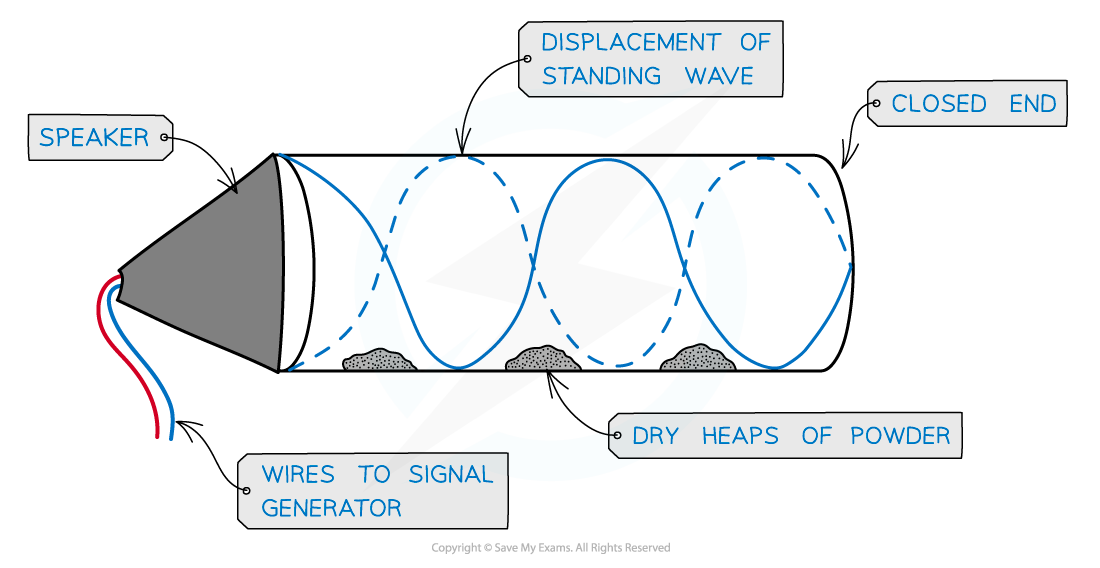
Stationary waves can be seen in air columns using dry power
In order to produce a stationary wave, there must be a minima (node) at one end and a maxima (antinode) at the end with the loudspeaker
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Always refer back to the experiment or scenario in an exam question e.g. the wave produced by a loudspeaker reflects at the end of a tube. This reflected wave, with the same frequency, overlaps the initial wave to create a stationary wave.
Formation of stationary waves
A stationary wave is made up of nodes and antinodes
Nodes are where there is no vibration
Antinodes are where the vibrations are at their maximum amplitude
The nodes and antinodes do not move along the string.
Nodes are fixed and antinodes only move in the vertical direction
Between nodes, all points on the stationary wave are in phase
The image below shows the nodes and antinodes on a snapshot of a stationary wave at a point in time
Nodes and antinodes on a stationary wave
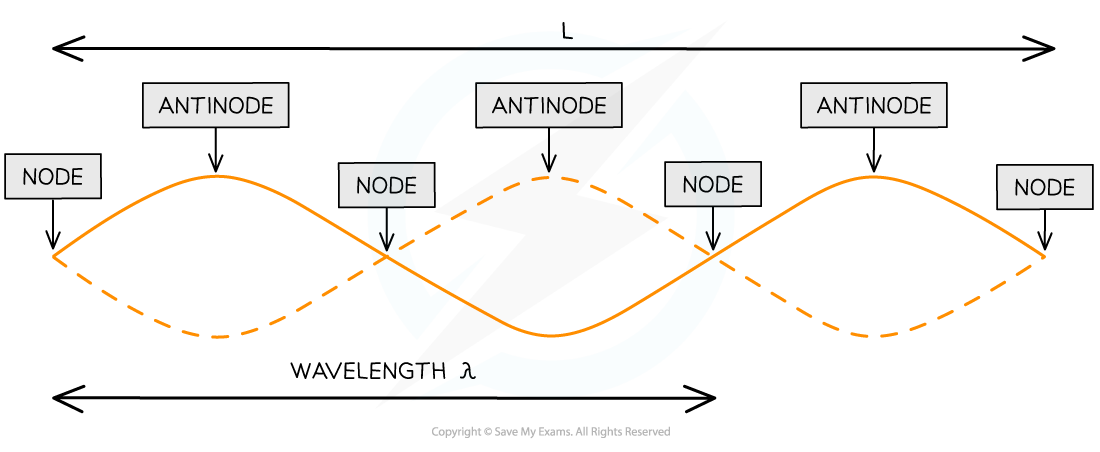
Nodes are points of zero amplitude, anti-nodes are points of maximum amplitude
L is the length of the string
1 wavelength λ is only a portion of the length of the string
Changing the frequency of the stationary wave produced will change the number of nodes and antinodes produced and consequently the wavelength
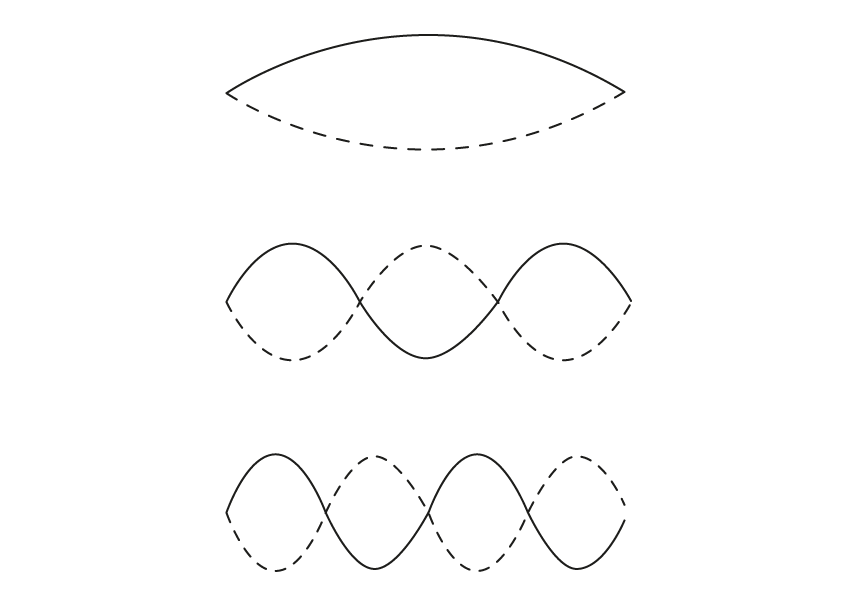
Stationary waves are produced at varying frequencies
Worked Example
A stretched string is used to demonstrate a stationary wave, as shown in the diagram.

Which row in the table correctly describes the length of L and the name of X and Y?
| Length L | Point X | Point Y |
A | 5 wavelengths | Node | Antinode |
B | 2 | Antinode | Node |
C | 2 | Node | Antinode |
D | 5 wavelengths | Antinode | Node |
Answer: C
Step 1: Determine the number of wavelengths in the length of the string
The string has 2
wavelengths
This rules out A and D
Step 2: Determine points X and Y
X is a point of 0 displacement - a node
Y is a point of maximum displacement - an antinode
Therefore, the correct row is C
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The lengths of the strings will only be in terms of whole or ½ wavelengths. For example, a wavelength could be made up of 3 nodes and 2 antinodes or 2 nodes and 3 antinodes.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?
