Polarisation (Cambridge (CIE) AS Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
Polarisation
Polarisation of transverse waves
Transverse waves are waves that oscillate with their displacement perpendicular to their direction of travel
These oscillations can happen in any plane perpendicular to the propagation direction
An electromagnetic wave is an example of a transverse wave that oscillates in more than one plane
A magnetic field oscillates on one plane
An electric field oscillates on a different plane
Both planes are at right angles to each other and to the direction of wave motion
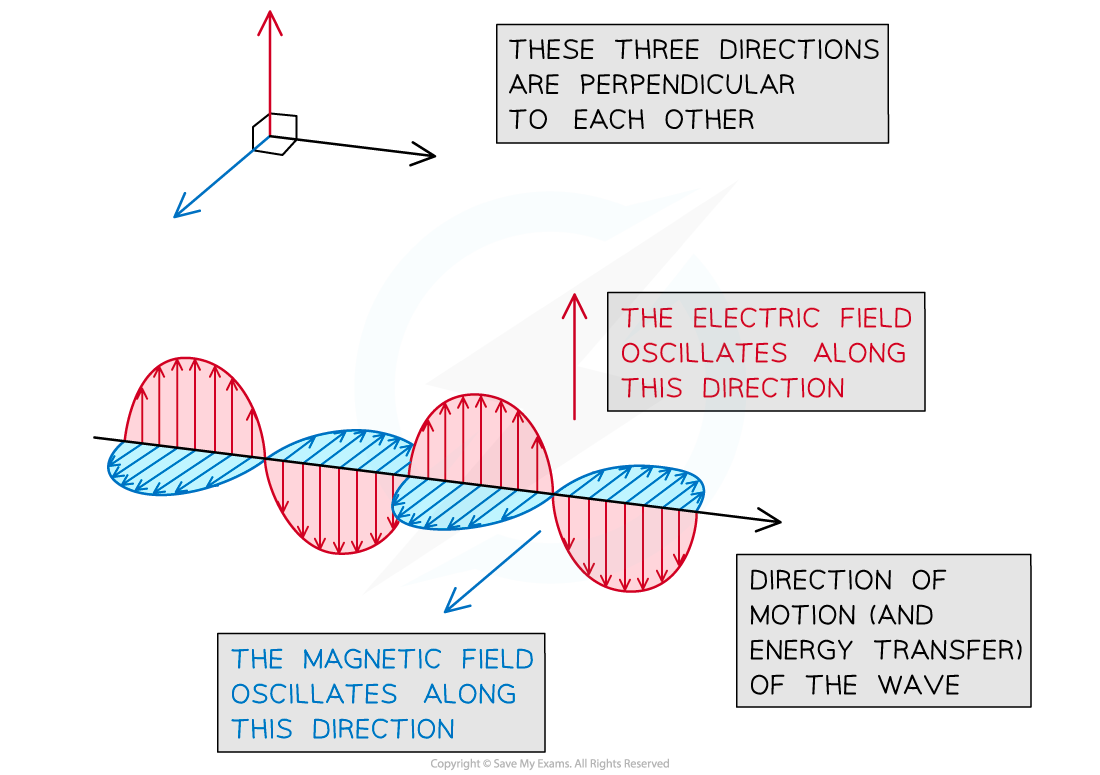
An electromagnetic wave is generated by the combined oscillation of an electric and a magnetic field
When transverse waves are polarised
vibrations are restricted to one plane of oscillation
vibrations are still perpendicular to the direction of propagation / energy transfer
The difference between unpolarised and polarised waves are shown in the diagram below
The blue arrows represent the direction of the plane of oscillation of the transverse wave
An unpolarised wave oscillates in many planes of oscillation
A vertically polarised wave oscillates only in the vertical plane
A horizontally polarised wave oscillates only in the horizontal plane
Different planes of polarisation
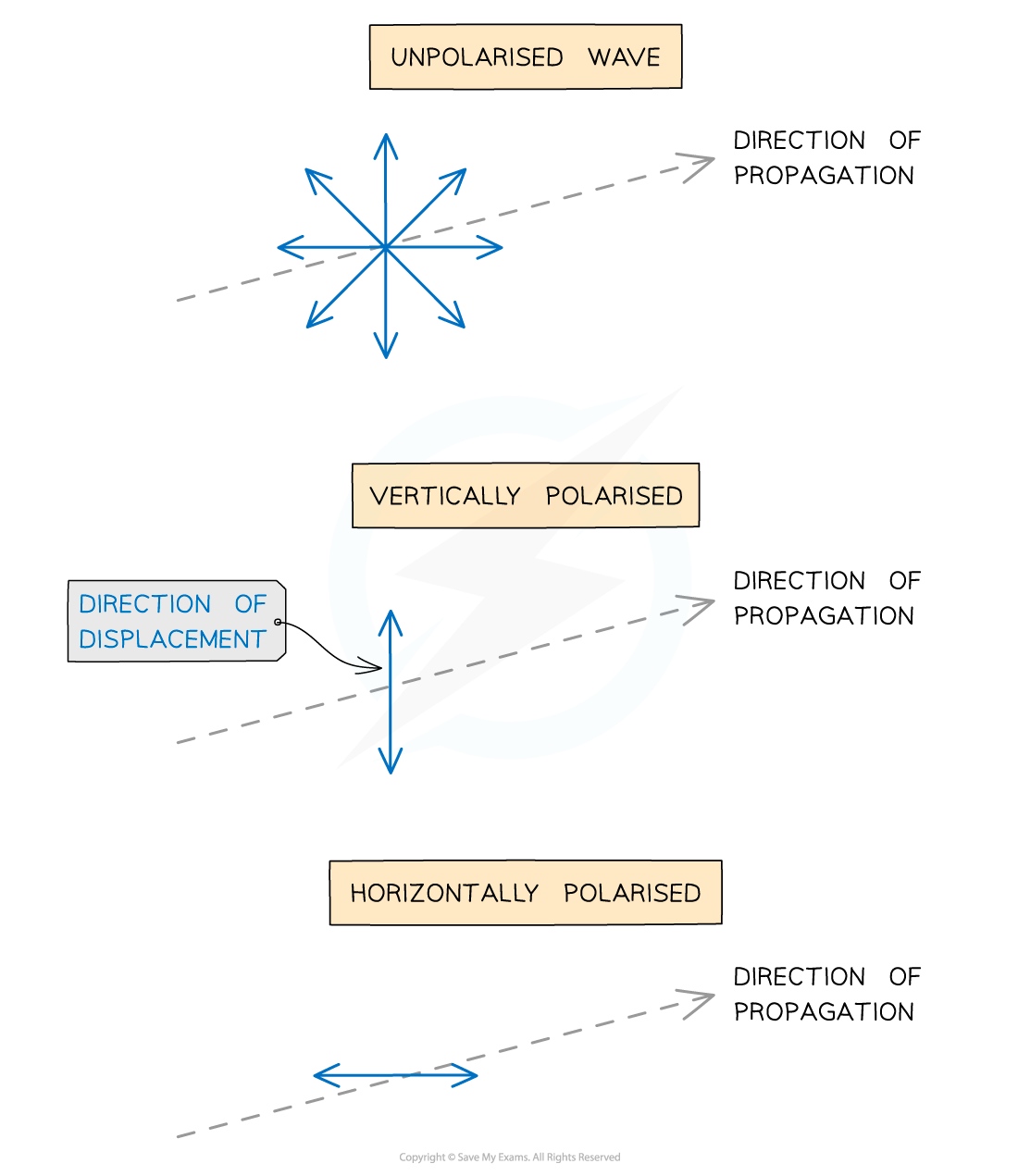
Diagram showing the displacement of unpolarised and polarised transverse waves
Polarising filters
Waves can be polarised by passing through a polariser or polarising filter.
Polarisers only allow oscillations in a certain plane to be transmitted through the filter
A polariser is an optical layer or lens that consists of many parallel tiny slits
A polariser only allows waves vibrating parallel to the direction of these slits to pass through
Waves that are not orientated in the correct plane are blocked by the filter and do not pass through
Action of a polarising filter
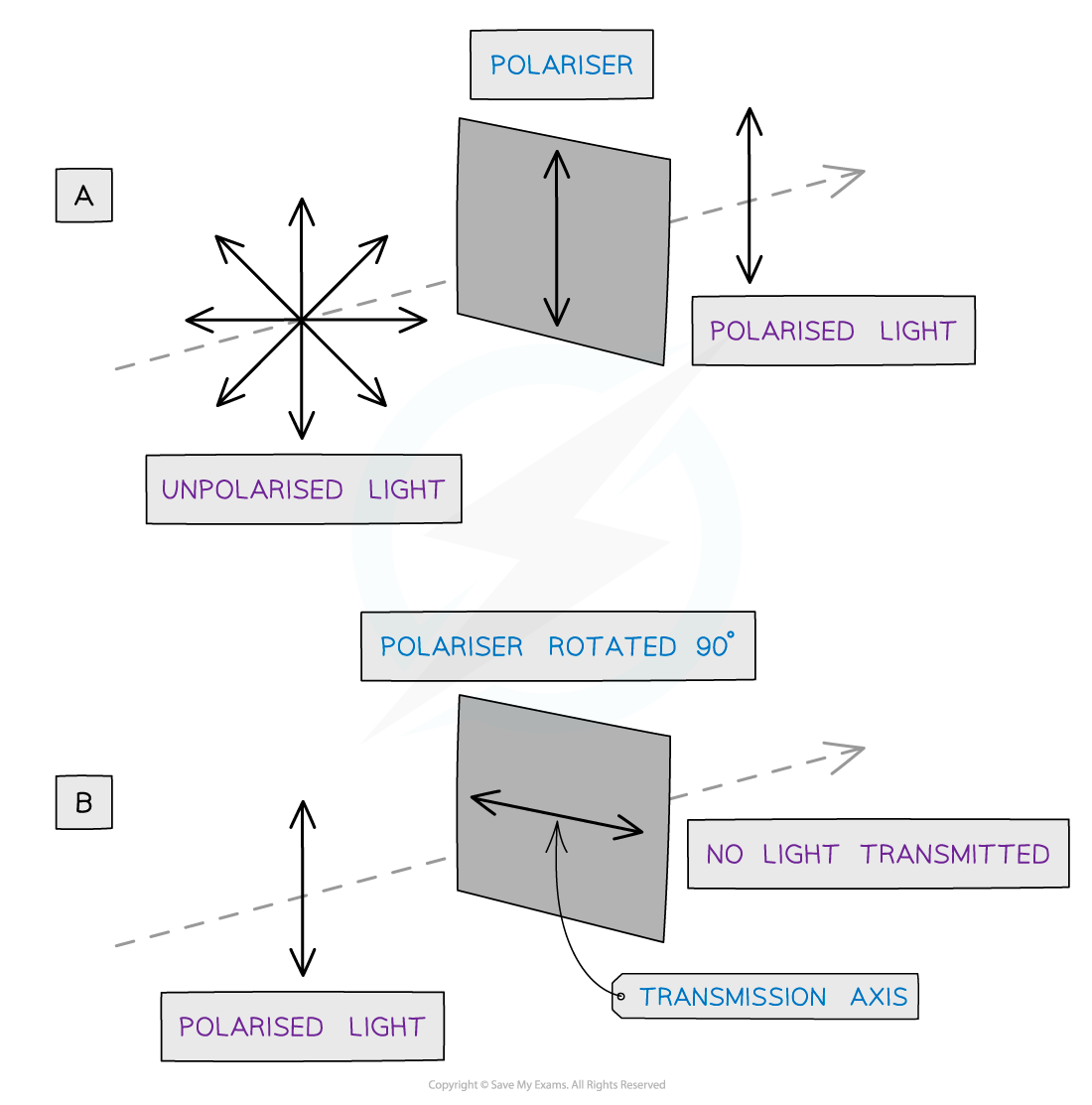
Diagram showing an unpolarised and polarised wave travelling through polarisers
Only unpolarised waves can be polarised
This is shown in diagram A
When a polarised wave passes through a filter with a transmission axis perpendicular to the wave (diagram B), none of the wave will pass through
Polaroid sunglasses
Polaroid sunglasses are an example of a polarisation
Polaroid sunglasses contain lenses with polarising filters with transmission axes that are vertically oriented
This means the glasses do not allow any horizontally polarised light to pass through
Polaroid sunglasses
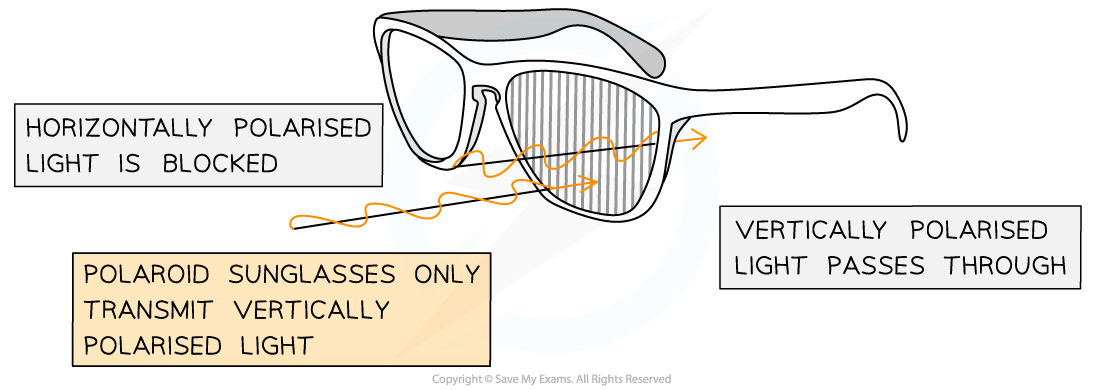
Polaroid sunglasses contain vertically oriented polarising filters which block out any horizontally polarised light
Worked Example
The following are statements about waves.
Which statement below describes a situation in which polarisation should happen?
A. Radio waves pass through a metal grid
B. Surface water waves are diffracted
C. Sound waves are reflected
D. Ultrasound waves pass through a metal grid
Answer: A
Polarisation only occurs for transverse waves, therefore, C and D can be ruled out as sound and ultrasound are both longitudinal waves
Waves are not polarised when diffracted, hence we can also rule out option B
Radio waves are transverse waves - they can be polarised by a metal grid so only the waves that fit through the grid will be transmitted, therefore, A is correct
Malus's law
Intensity of polarised electromagnetic waves
The intensity of electromagnetic waves is reduced as a result of polarisation
If unpolarised electromagnetic waves of intensity I0 pass through a polariser, the intensity of the transmitted polarised waves falls by a half
is known as the half rule
Intensity of polarised and unpolarised light
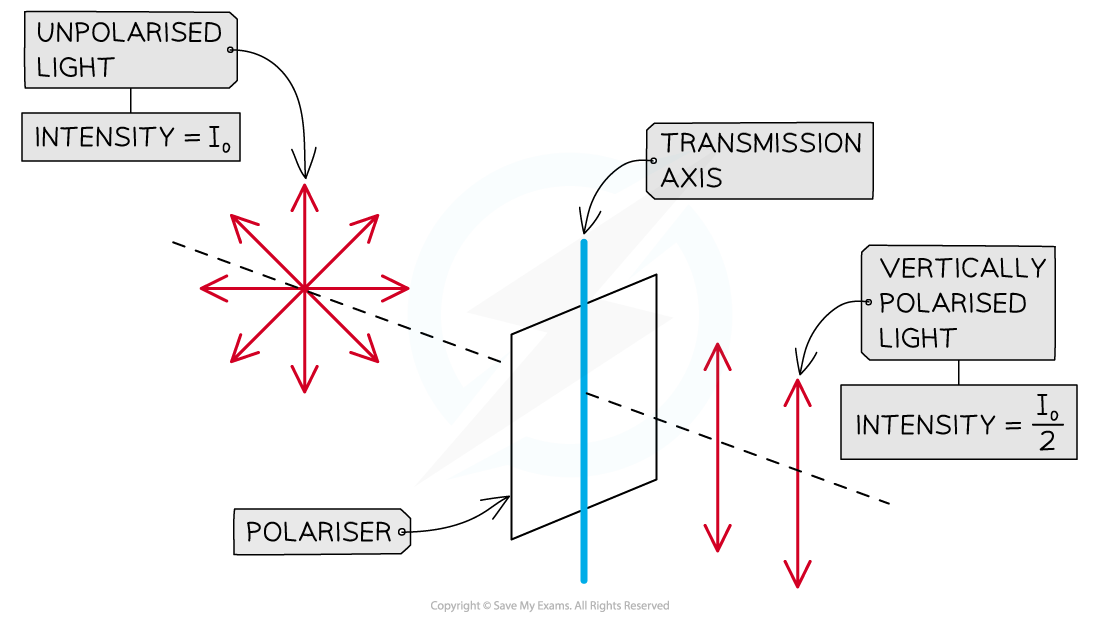
The intensity of polarised light transmitted by a polariser is half the intensity of the unpolarised light incident on it
Intensity of analysed electromagnetic waves
A second polarising filter placed after the first is known as an analyser
Intensity of waves when polariser and analyser have the same orientation
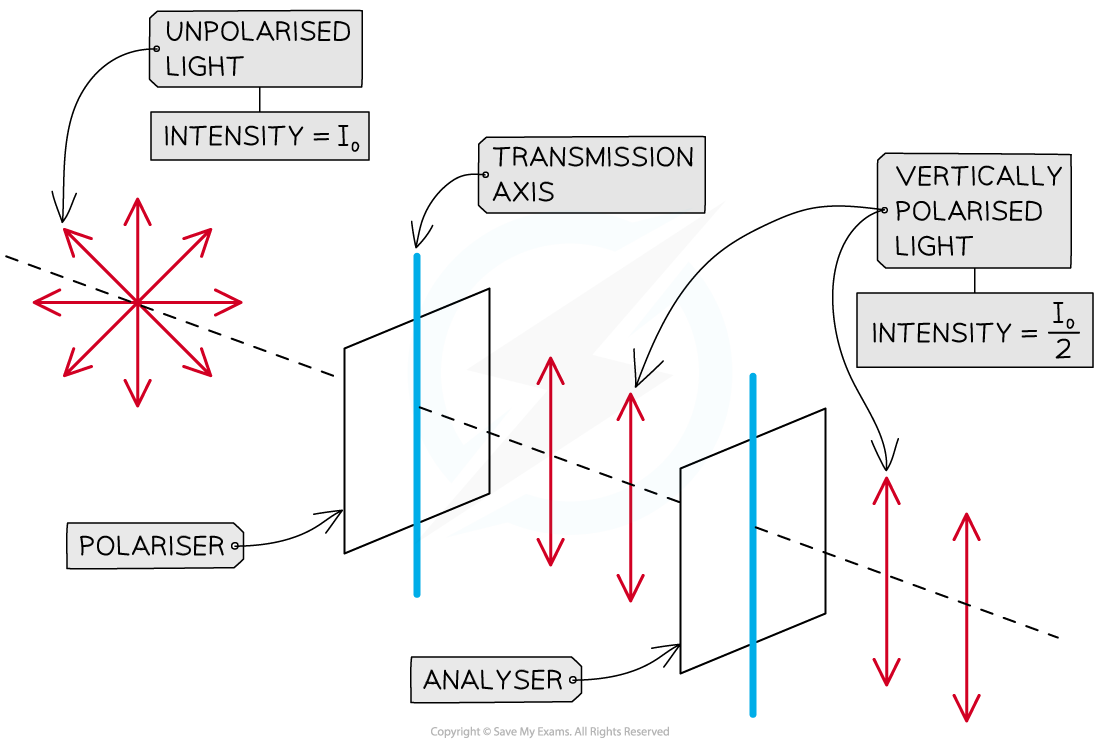
When the polariser and the analyser have the same orientation (i.e. parallel transmission axes), the intensity of analysed light is the same as the intensity of polarised light
Malus's law
Malus's law states that if the analyser is rotated by an angle θ with respect to the polariser, the intensity of the waves transmitted by the analyser is given by the equation
Where
I is intensity of transmitted light in W m−2
I0 is maximum intensity (same units)
If the polariser and the analyser have the same orientation, electromagnetic waves transmitted by the analyser have the same intensity as waves that are incident upon it, since cos(0) = 1
If vertically polarised electromagnetic waves with intensity
are incident on an analyser with a vertical transmission axis, all of the waves will be transmitted through the analyser
The intensity between the polariser and the analyser will not decrease
If the analyser is rotated by 90° with respect to the polariser (θ = 90°), the intensity of the light transmitted by the analyser will be zero, since cos(90°) = 0
If vertically polarised light is incident on an analyser with a horizontal transmission axis, none of the light will be transmitted through the analyser
In this instance, all the waves will be absorbed
Table of transmission depending on polariser orientation
Angle of transmission axis, θ / degrees | Direction of transmission axis | cos2θ | Transmitted intensity / W m−2 | Maximum or minimum light intensity transmitted |
|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | Vertical | 1 | I0 | Max |
180 | Vertical | 1 | I0 | Max |
90 | Horizontal | 0 | 0 | Min |
270 | Horizontal | 0 | 0 | Min |
Worked Example
Unpolarised light is incident on a polariser.
The light transmitted by the first polariser is then incident on a second polariser.
The polarising (or transmission) axis of the second polariser is 30° to that of the first. The intensity incident on the first polariser is I.
What is the intensity emerging from the second polariser?
A. 0.75 I
B. 0.38 I
C. 0.87 I
D. 0.43 I
Answer: B
Step 1: Apply the half rule:
When light passes through the first polariser, half its intensity is lost
Step 2: Use Malus's law:
The angle of the transmission axis is 30°
In this case, I0 in Malus's equation is I1 here, because the light has already passed through the first polariser
To 2 significant figures, this is option B
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember when using Malus’s law to square the cosine of the angle (cos2 θ)
Remember that the unpolarised light coming through will always halve in intensity when it becomes polarised through an polariser. Only then should you use Malus' law to find the intensity of the light after it has passed through the analyser. Therefore, the I and I0 in Malus' law are the intensities of light that are already polarised.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?