Wave Intensity (Cambridge (CIE) AS Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
Wave intensity
Progressive waves transfer energy
The amount of energy passing through a unit area per unit time is the intensity of the wave
Therefore, the intensity is defined as power per unit area
Where
I is intensity in W m−2
P is power in W
A is area in m2
The area the wave passes through is perpendicular to the direction of its velocity
The intensity of a progressive wave is also proportional to its amplitude squared and frequency squared
Where
A is amplitude in m
f is frequency in Hz
Recall that ∝ means "proportional to"
This means that if the frequency or the amplitude is doubled, the intensity increases by a factor of 4 (22)
Spherical waves
A spherical wave is a wave from a point source which spreads out equally in all directions
The area the wave passes through is the surface area of a sphere: 4πr2
As the wave travels further from the source, the energy it carries passes through increasingly larger areas as shown in the diagram below:
Inverse square law for intensity
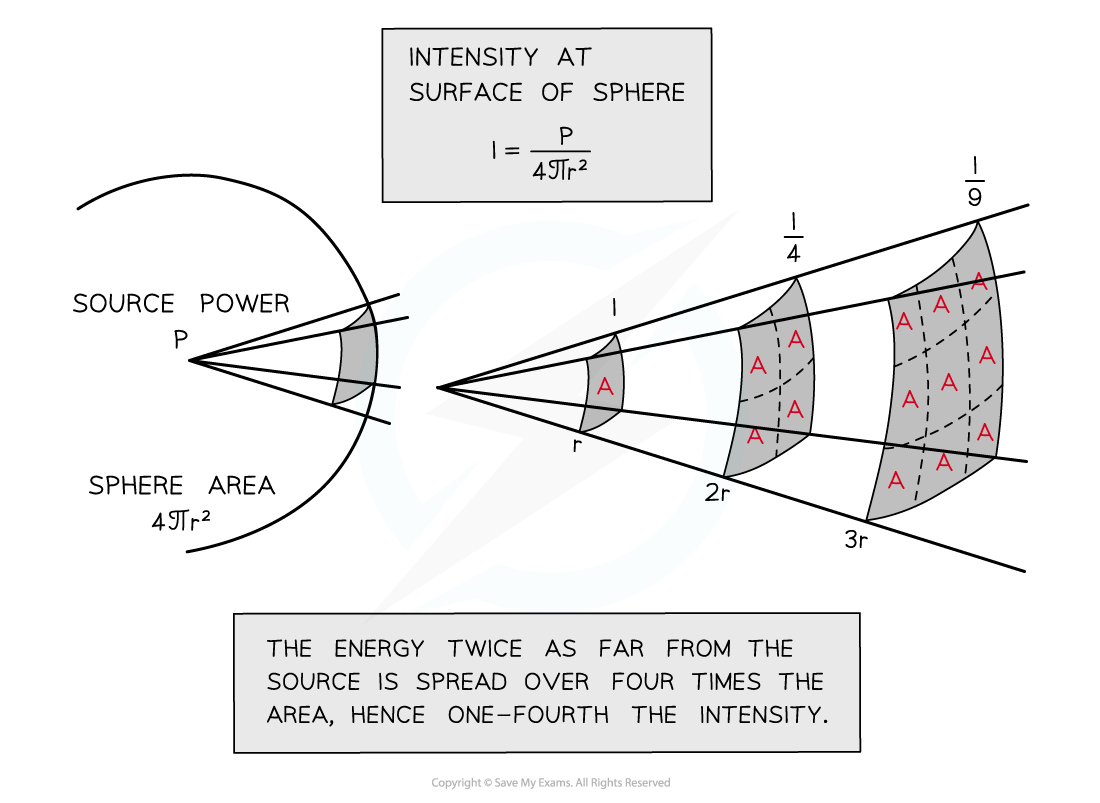
Intensity is proportional to the amplitude squared
Assuming none of the wave energy is absorbed, the intensity I decreases with increasing distance from the source
The inverse square law states that
The inverse square law means when the source is twice as far away, the intensity is 4 times smaller
Worked Example
The intensity of a progressive wave is proportional to the square of the amplitude of the wave. It is also proportional to the square of the frequency. The variation with time t of displacement x of particles when two progressive waves Q and P pass separately through a medium, are shown on the graphs.
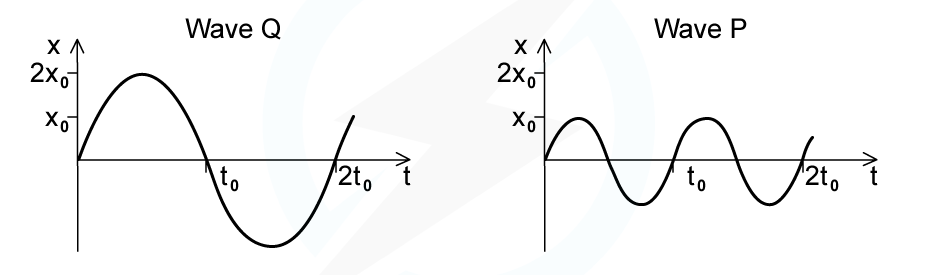
The intensity of wave Q is I0.What is the intensity of wave P?
Answer:
Step 1: Compare waves Q and P:
The amplitude of wave Q is twice the amplitude of wave P
The frequency of wave P is double the frequency of wave Q
Step 2: Evaluate how amplitude affects the intensities:
Q has twice the amplitude of P
The ratio of amplitudes squared is equal to the ratio of intensities, because intensity and amplitude squared are proportional
So Q's larger amplitude increases its intensity by a factor of 4
Step 3: Evaluate how frequency affects the intensities:
Q has half the frequency of P
The ratio of frequencies squared is equal to the ratio of intensities because intensity and frequency squared are proportional
So Q's lower frequency decreases its intensity by a factor of 4
Step 4: Determine the intensity of wave P in terms of I0 :
P has a lower amplitude which reduces its intensity by a factor of 4 compared to Q
However, P has a higher frequency which increases its intensity by a factor of 4 compared to Q
These effects cancel out, so wave P has an intensity of I0 , which is equal to that of wave Q
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The key concept with intensity is that it has an inverse square relationship with distance (not a linear one). This means the energy of a wave decreases very rapidly with increasing distance

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?