Gradient of a Velocity-Time Graph (Cambridge (CIE) AS Physics) : Revision Note
Gradient of a velocity-time graph
Acceleration is any change in the velocity of an object in a given time
Where:
v = final velocity (m s–1)
u = initial velocity (m s–1)
Δv = change in velocity (m s–1)
Δt = change in time (s)
As velocity is a vector quantity, this means that if the speed of an object changes, or its direction changes, then it is accelerating
An object that slows down tends to be described as ‘decelerating’
The gradient of a velocity-time graph is equal to the acceleration
Acceleration on a velocity-time graph
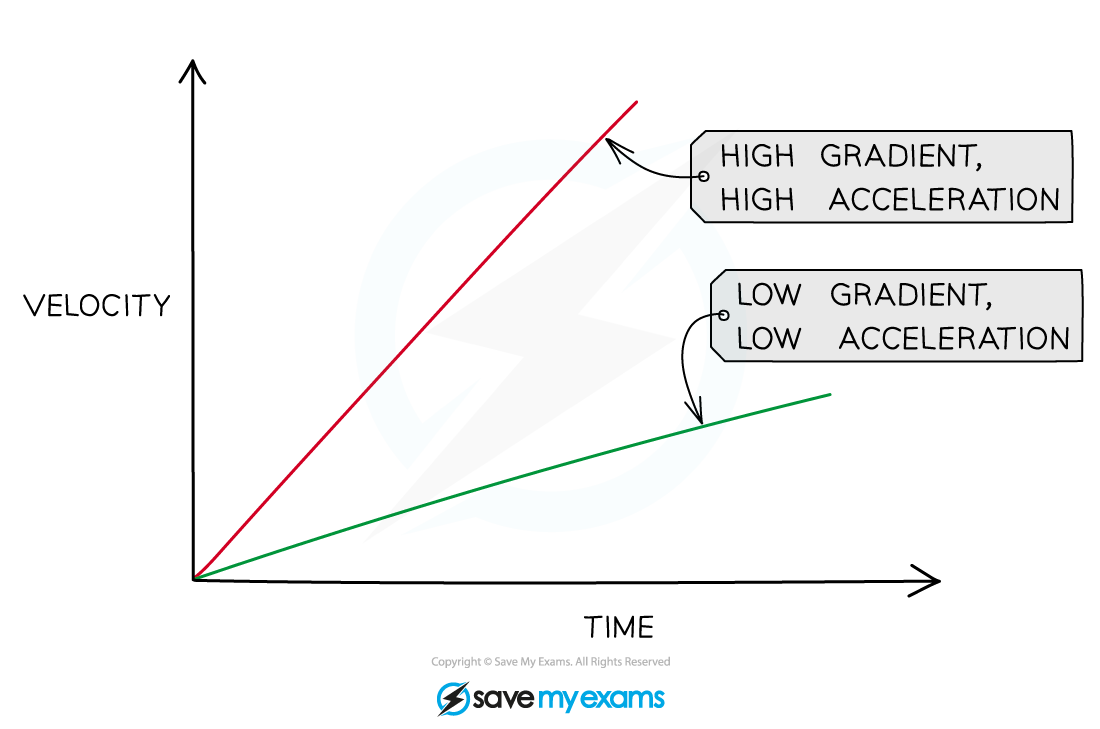
The larger the gradient, the larger the acceleration represented on a velocity-time graph
Worked Example
What does the velocity-time graph look like for this acceleration-time graph?
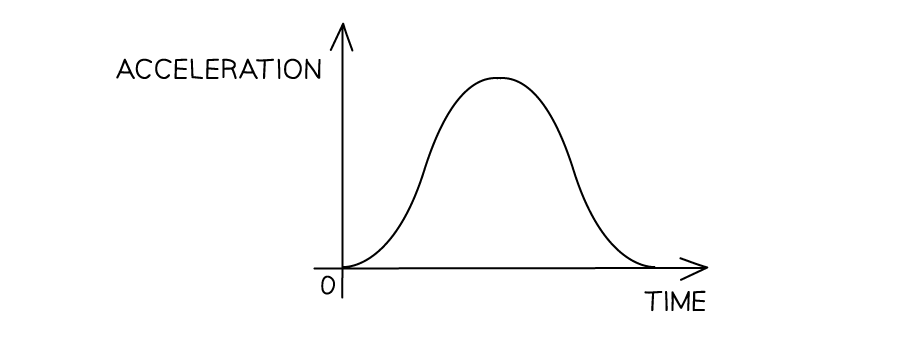
Answer:
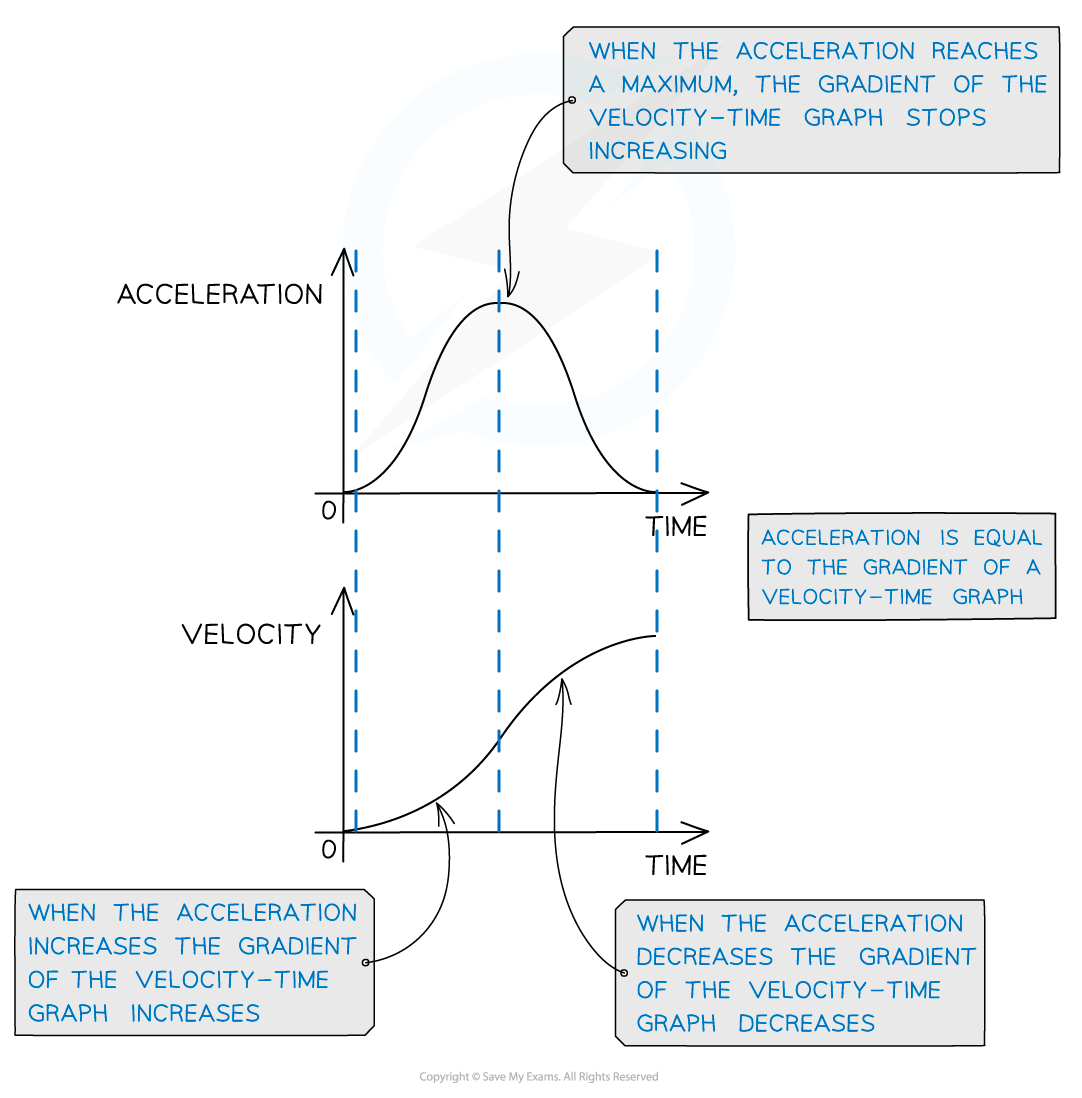
Step 1: Consider how velocity is represented on the acceleration-time graph
Acceleration is the gradient of a velocity-time graph
Step 2: Consider the velocity at each section of the acceleration-time graph
When the acceleration increases, the gradient of the velocity-time graph increases
When acceleration reaches a maximum, this is the maximum gradient of the velocity-time graph
When the acceleration decreases, the gradient of the velocity-time graph decreases
Examiner Tips and Tricks
A summary of the areas under the graph and gradients for the different motion graphs are:
Gradient:
The gradient of a displacement-time graph is the velocity
The gradient of a velocity-time graph is the acceleration
Area under the graph:
The area under a velocity-time graph is the displacement
The area under an acceleration-time graph is the velocity

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?

