Decay Equations (Cambridge (CIE) AS Physics) : Revision Note
Neutrino emission
An electron neutrino is a type of subatomic particle with no charge and negligible mass which is emitted from the nucleus
The electron anti-neutrino is the antiparticle of an electron neutrino
Electron anti-neutrinos are produced during β– decay
Electron neutrinos are produced during β+ decay
Electron neutrino and anti-electron neutrino

The anti neutrino is denoted by a line above the symbol
Examiner Tips and Tricks
One way to remember which particle decays into which depends on the type of beta emission, think of beta ‘plus’ as the ‘proton’ that turns into the neutron (plus an electron neutrino)
α & β decay equations
Alpha decay
Alpha decay is common in large, unstable nuclei with too many protons
The decay involves a nucleus emitting an alpha particle and decaying into a different nucleus
An alpha particle consists of 2 protons and 2 neutrons (the nucleus of a Helium atom)
Alpha decay
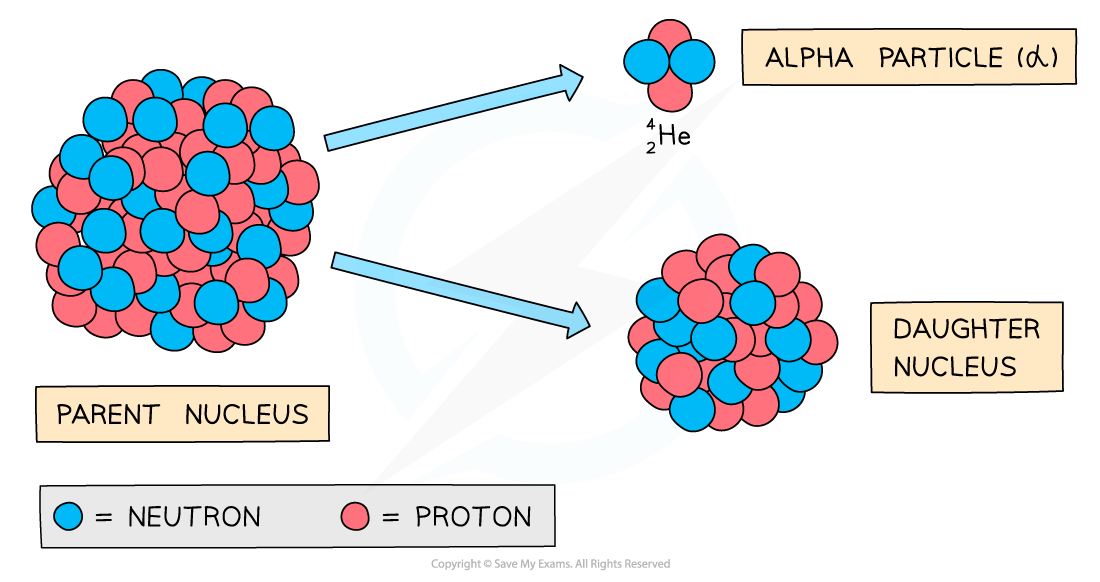
Alpha decay produces a daughter nucleus and an alpha particle (helium nucleus)
When an unstable nucleus (the parent nucleus) emits radiation, the constitution of its nucleus changes
As a result, the isotope will change into a different element (the daughter nucleus)
Alpha decay can be represented by the following radioactive decay equation:
An example would be:
When an alpha particle is emitted from a nucleus:
The nucleus loses 2 protons: proton number decreases by 2
The nucleus loses 4 nucleons: nucleon number decreases by 4
Worked Example
The radioactive nucleus undergoes alpha decay into a daughter nucleus Po.

(a) Which letter in the diagram represents the daughter product?
(b) Which is the nucleon and proton number of the final nucleus Po?
Answer:
(a)
Step 1: Determine the number of neutrons
This is alpha decay
The nucleon number of the parent nucleus decreases by 4
The proton number of the parent nucleus decreases by 2
Therefore, the number of neutrons is:
Step 2: Determine the change in the proton and neutrons
A helium nucleus has 2 protons and 2 neutrons
The proton and neutron numbers will decrease by 2
This reaches the point of the diagram marked C
(b)
Step 1: Write the equation for the alpha decay

Step 2: Determine the nucleon and proton numbers of Po
Nucleon number = 218
Proton number = 84
β- decay
A β- particle is a high energy electron emitted from the nucleus
β- decay is when a neutron turns into a proton emitting an electron and an anti-electron neutrino
Beta decay
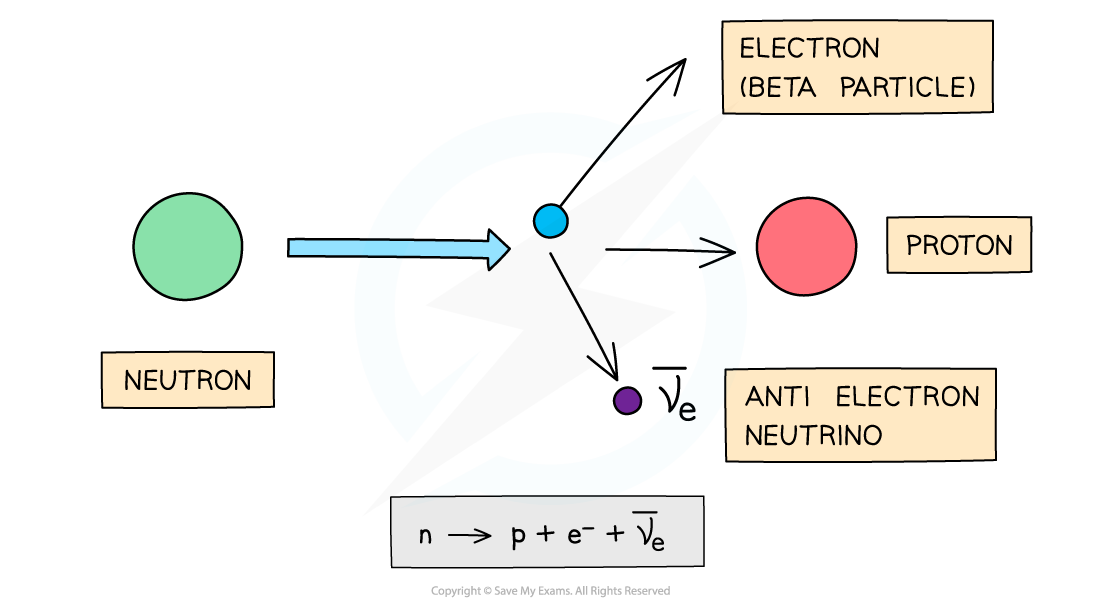
In beta-minus decay, a neutron decays into a proton, an electron and an anti-electron neutrino
When a β- is emitted from a nucleus:
The number of protons increases by 1: proton number increases by 1
The total number of nucleons stays the same: nucleon number remains the same
The decay equation for beta-minus decay is:
An example would be:
The new nucleus formed from the decay is called the “daughter” nucleus (nitrogen in the example above)
β+ decay
A β+ particle is a high energy positron emitted from the nucleus
β+ decay is when a proton turns into a neutron emitting a positron (anti-electron) and an electron neutrino
Beta-plus decay
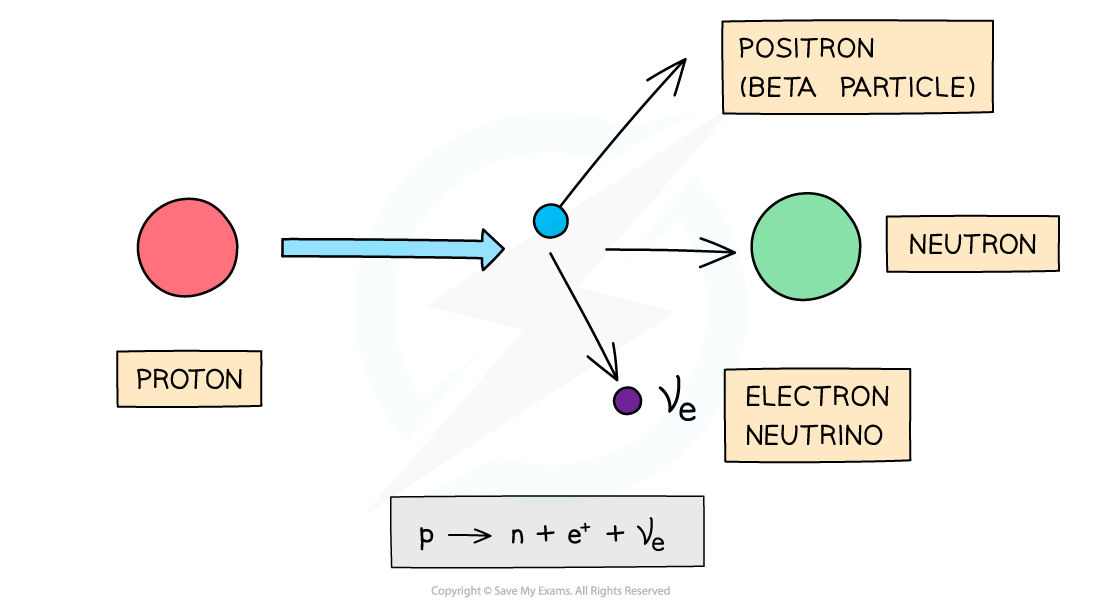
In beta plus decay, a proton decays into a neutron, a positron and an electron neutrino
When a β+ is emitted from a nucleus:
The number of protons decreases by 1: proton number decreases by 1
The total number of nucleons stays the same: nucleon number remains the same
The decay equation for beta-plus decay is:
An example of this would be:
Worked Example
A radioactive substance with a nucleon number of 212 and a proton number of 82 decays by β-plus emission into a daughter product which in turn decays by further β-plus emission into a granddaughter product.

State the letter in the diagram that represents the granddaughter product.
Answer: A
In β+ decay, a proton decays into a neutron, a positron, and an anti-electron neutrino
The number of neutrons is:
The proton number decreases by one and the number of neutrons increases by one
This happens twice, so it reaches point A on the diagram

Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember to avoid the common mistake of confusing the number of neutrons with nucleon number. In alpha decay, the nucleon (protons and neutrons) number decreases by 4 but the number of neutrons only decreases by 2.
Energy of alpha & beta decay
When the number of α particles is plotted against kinetic energy, there are clear spikes that appear on the graph
This demonstrates that α-particles have discrete energies (only certain values)
Graphs showing energy of alpha and beta particles

Alpha particles have discrete energy levels whilst beta particles have a continuous range of energies
When the number of β particles is plotted against kinetic energy, the graph shows a curve
This demonstrates that beta particles (electrons or positrons) have a continuous range of energies
This is because the energy released in beta decay is shared between the beta particles (electrons or positrons) and neutrinos (or anti-neutrinos)
This was one of the first clues of the neutrino’s existence
The principle of conservation of momentum and energy applies in both alpha and beta emission

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?
