The Diffraction Grating (Cambridge (CIE) AS Physics) : Revision Note
The diffraction grating equation
A diffraction grating is a piece of optical equipment that creates a diffraction pattern when it diffracts monochromatic light into bright and dark fringes
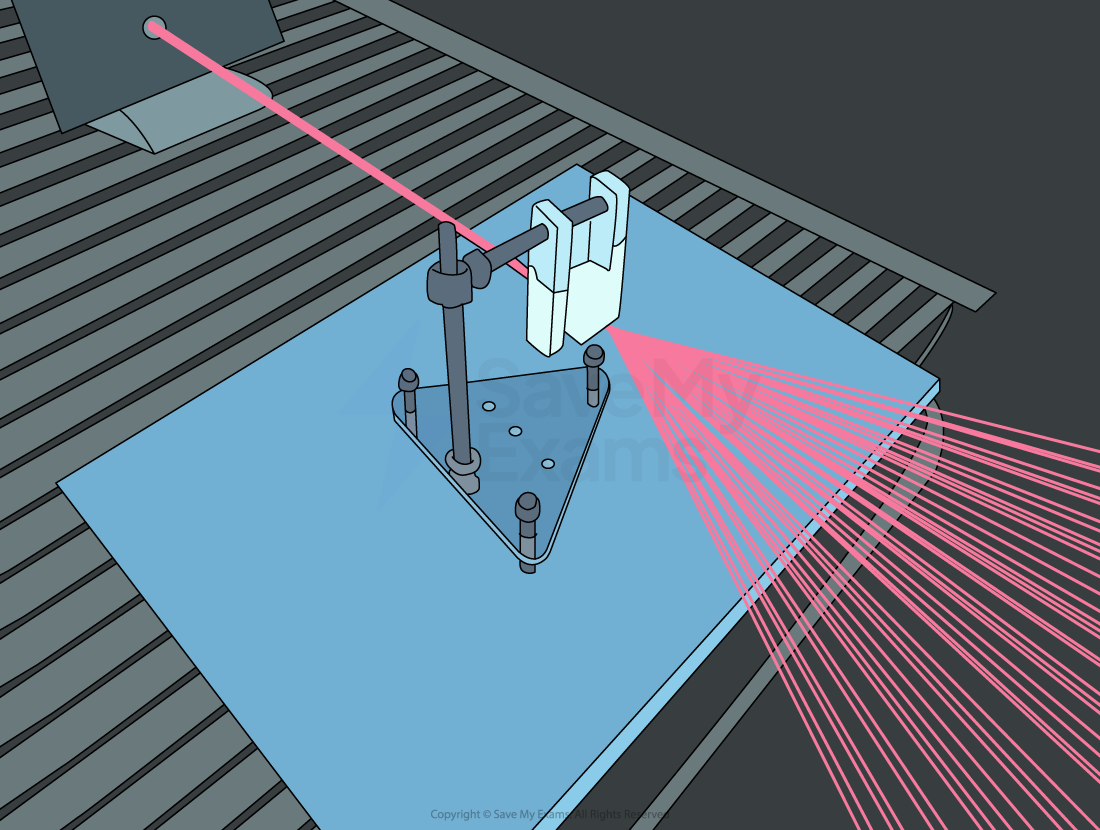
A laser light is diffracted using a diffraction grating
A diffraction grating consists of a large number of very thin, equally spaced parallel slits carved into a glass plate
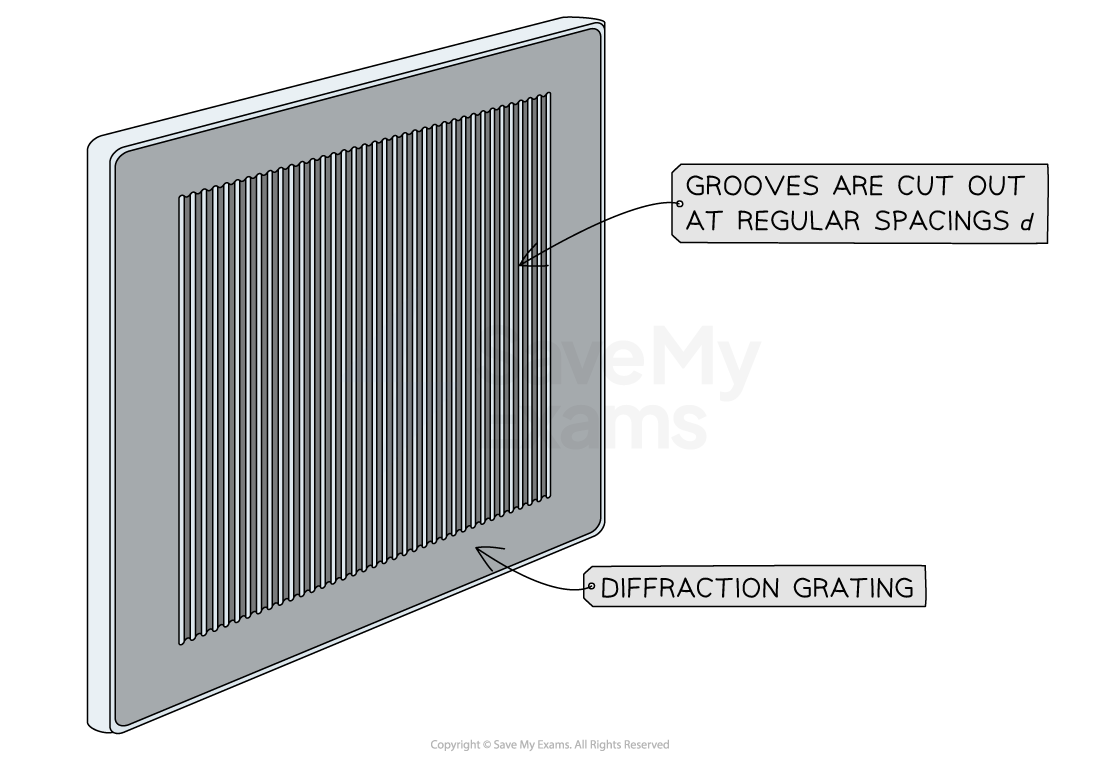
A diffraction grating consists of many parallel equally spaced slits cut into the glass plate
Just like for single and double-slit diffraction the regions where constructive interference occurs are also the regions of maximum intensity
Their location can be calculated using the diffraction grating equation
Where:
d = spacing between adjacent slits (m)
θ = angular separation between the order of maxima (degrees)
n = order of maxima (n = 0, 1, 2, 3...)
λ = wavelength of light source (m)
Slit spacing
Diffraction gratings come in different sizes
The sizes are determined by the number of lines per millimetre (lines / mm) or lines per m
This is represented by the symbol N
d can be calculated from N using the equation
If N is given in terms of lines per mm then d will be in mm
If N is given in terms of lines per m then d will be in m
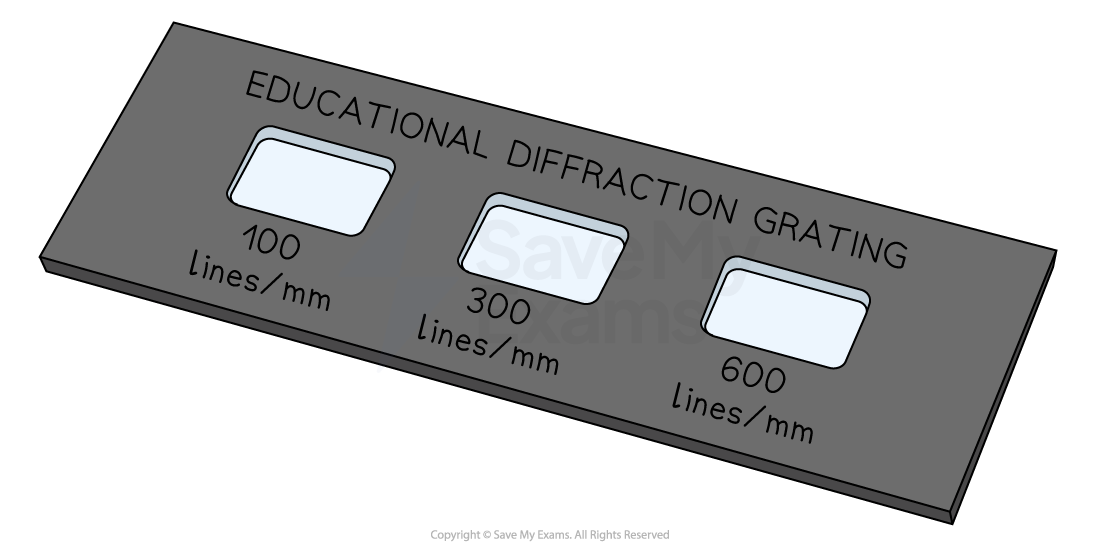
Diffraction gratings come in different sizes according to the number of lines per mm
Angular separation
The angular separation of each maxima is calculated by rearranging the grating equation to make θ the subject
The angle θ is taken from the centre meaning the higher orders of n are at greater angles
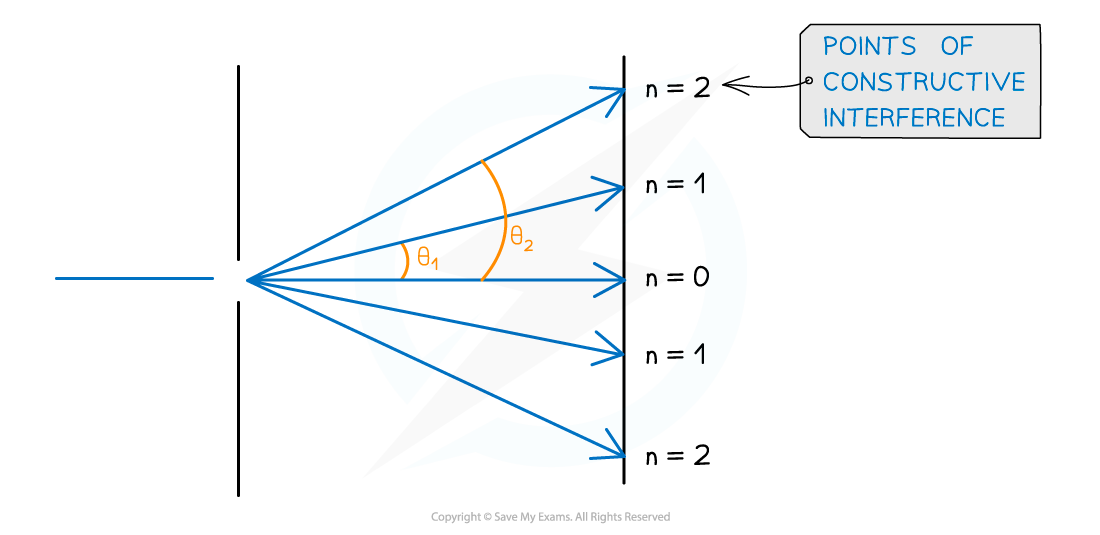
Angular separation increases as the order of maxima increases
The angular separation between two angles is found by subtracting the smaller angle from the larger one
The angular separation between the first and second maxima at n1 and n2 is θ2 – θ1
Orders of maxima
The maximum angle of diffraction with which maxima can be seen is when the beam is at right angles to the diffraction grating
This means θ = 90o and sin θ = 1
The highest order of maxima visible is therefore calculated by the equation:
Since n is an integer number of maxima, if the value obtained is a decimal it must be rounded down to determine the highest-order visible
E.g If n is calculated as 2.7 then n = 2 is the highest-order visible
Worked Example
An experiment was set up to investigate light passing through a diffraction grating with a slit spacing of 1.7 µm. The fringe pattern was observed on a screen. The wavelength of the light is 550 nm.
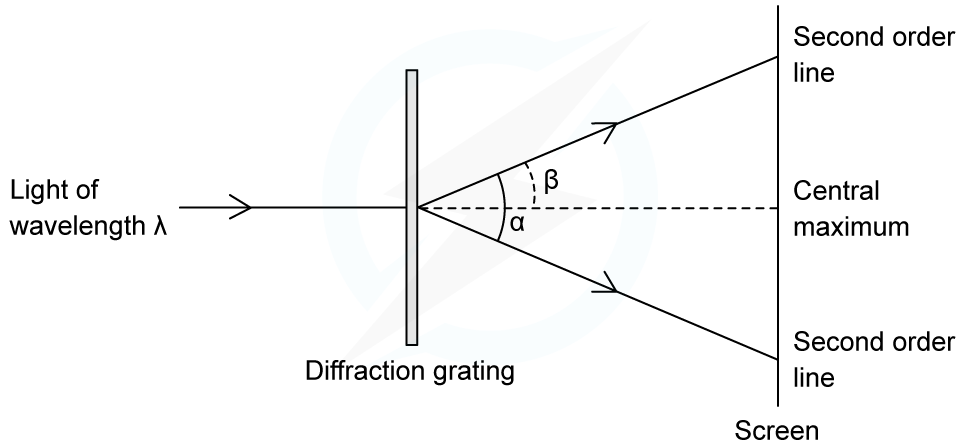
Calculate the angle α between the two second-order lines.
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities
Order of maxima, n = 2
Diffraction slit spacing, d = 1.7 µm = 1.7 × 10–6 m
Wavelength, λ = 550 nm = 550 × 10–9 m
Step 2: Rearrange for β and substitute in the values
Step 3: Calculate α
β is the angle from the centre to the second-order line
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Take care that the angle θ is the correct angle taken from the centre and not the angle taken between two orders of maxima.
Determining the wavelength of light
Method
The wavelength of light can be determined by rearranging the grating equation to make the wavelength λ the subject
The value of θ, the angle to the specific order of maximum measured from the centre, can be calculated through trigonometry
Create a right angled triangle to determine the angle of diffraction, θ
The distance from the grating to the screen is marked as D
The distance between the centre and the order of maxima (e.g. n = 2 in the diagram below) on the screen is labelled as h, the fringe spacing
Measure both of these values with a ruler
Obtain the ratio
Order of maxima and wavelength
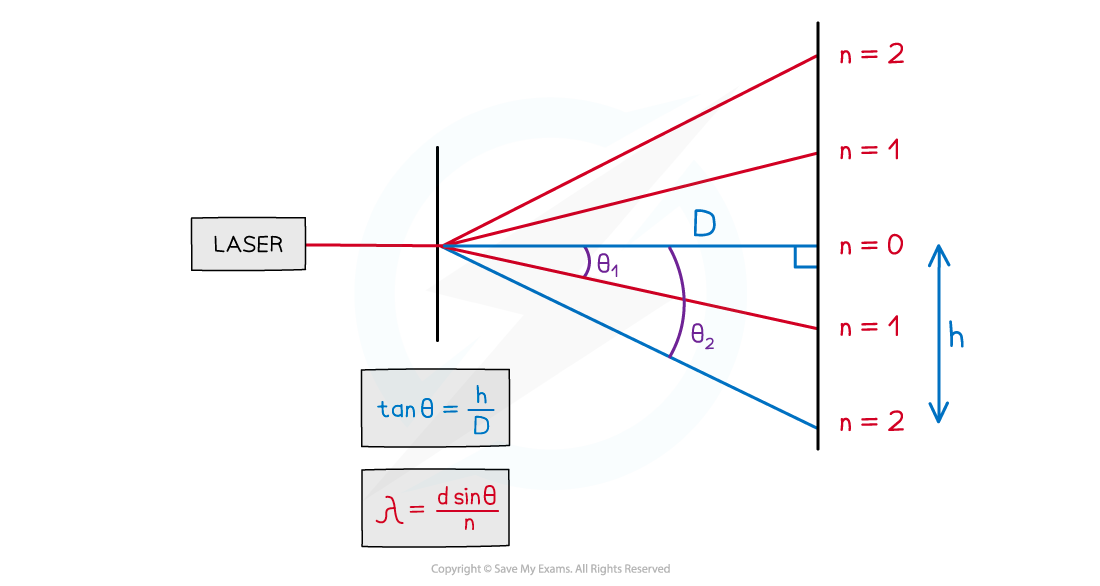
The wavelength of light is calculated by the angle to the order of maximum
Calculate the inverse of tan to find
Substitute for θ back into the diffraction grating equation to find the value of the wavelength (with the corresponding order n)
Improving the experiment and reducing uncertainties
The fringe spacing can be subjective depending on its intensity on the screen. Take multiple measurements of h (between 3-8) and find the average
Use a Vernier scale to record h, in order to reduce percentage uncertainty
Reduce the uncertainty in h by measuring across all fringes and dividing by the number of fringes
Increase the grating to screen distance D to increase the fringe separation (although this may decrease the intensity of light reaching the screen)
Conduct the experiment in a darkened room, so the fringes are clearer
Use grating with more lines per mm, so values of h are greater to lower percentage uncertainty

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

