Transverse & Longitudinal Waves (Cambridge (CIE) AS Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
Properties of transverse & longitudinal waves
In mechanical waves, particles oscillate about fixed points
There are two types of mechanical wave:
transverse
longitudinal
The type of wave can be determined by the direction of the oscillations in relation to the direction the wave is travelling
Transverse waves
Transverse waves are defined as follows:
A wave in which the particles oscillate perpendicular to the direction of motion and energy transfer

A transverse wave travelling from left to right
Transverse waves show areas of peaks and troughs
Examples of transverse waves include:
Electromagnetic waves e.g. radio, visible light, UV
Vibrations on a guitar string
Transverse waves do not need particles to propagate, and so they can travel through a vacuum
Transverse waves can be polarised
Longitudinal waves
Longitudinal waves are defined as follows:
A wave in which the particles oscillate parallel to the direction of motion and energy transfer

A longitudinal wave travelling from left to right
As a longitudinal wave propagates, areas of low and high pressure can be observed:
A rarefaction is an area of low pressure, with the particles being further apart from each other
A compression is an area of high pressure, with the particles being closer to each other
Sound waves are an example of longitudinal waves
Longitudinal waves need particles to propagate, and so they cannot travel through a vacuum
Longitudinal waves cannot be polarised
The diagram below shows the equivalent of a wavelength on a longitudinal wave
Comparing wavelengths of longitudinal and transverse waves

Wavelength shown on a longitudinal wave
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The definitions of transverse and longitudinal waves are often asked as exam questions, make sure to remember these by heart!
The properties of waves you learned about in General Wave Properties, such as amplitude and wavelength, all apply to transverse and longitudinal waves
Graphical representations of transverse & longitudinal waves
Transverse and longitudinal waves can be represented graphically in the same way
The main difference is the meaning of 'displacement' on the y-axis
Alternatively, displacement could be exchanged for velocity or acceleration
For a transverse wave:
Displacement is perpendicular to the direction of propagation (energy transfer)
For a longitudinal wave:
Displacement is parallel to the direction of propagation (energy transfer)
Graphical representation of a progressive wave
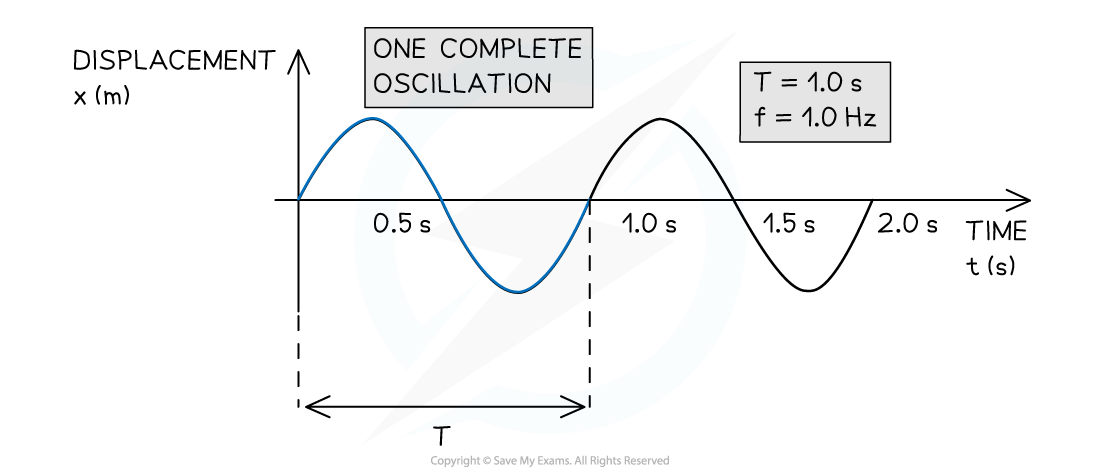
The wave has a period of 1.0 s, a frequency of 1.0 Hz and could be either transverse or longitudinal.
Worked Example
The graph shows how the displacement of a particle in a wave varies with time.

Which statement is correct?
A. The wave has an amplitude of 2 cm and could be either transverse or longitudinal.
B. The wave has an amplitude of 2 cm and a period of 6 s.
C. The wave has an amplitude of 4 cm and a period of 4 s.
D. The wave has an amplitude of 4 cm and must be transverse.
Answer: A
Step 1: Determine amplitude from the graph:
Each peak and trough is 2 cm away from the equilibrium position on the graph
So, the amplitude is 2 cm
Step 2: Determine the time period:
4 seconds pass before the wave repeats its pattern again, so the period is 4 s
The amplitude of 2 cm and period of 4 s rules out options B, C and D
Step 3: Discuss whether the wave is transverse or longitudinal:
The x-axis of this graph is time, so all that can be inferred is that the particle is displaced periodically
This occurs if a transverse wave or a longitudinal wave is causing its oscillations, as it is not mentioned how it is oscillating relative to the direction of wave travel
Therefore the wave could be either transverse or longitudinal
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Both transverse and longitudinal waves can look like transverse waves when plotted on a graph - make sure you read the question and look for whether the wave travels parallel (longitudinal) or perpendicular (transverse) to the direction of travel to confirm which type of wave it is.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?