Hooke's Law (Cambridge (CIE) AS Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
Hooke's law
A material demonstrating elastic behaviour obeys Hooke’s Law if its extension is directly proportional to the applied force (load)
The Force-extension graph of an object obeying Hooke's law is a straight line through the origin
This linear relationship is represented by the Hooke’s law equation
Where:
F is force applied in N
k is the spring constant in N m−1
x is the extension of the spring
The spring constant
k is the spring constant of the spring and is a measure of the stiffness of a spring
A stiffer spring will have a larger value of k
k is defined as the force per unit extension up to the limit of proportionality
The SI unit for the spring constant is N m-1
Rearranging the Hooke’s law equation shows the equation for the spring constant is
Therefore, the spring constant k is the gradient of the linear part of a force-extension graph
Gradient of force-extension graph

Spring constant is the gradient of a force vs extension graph
Worked Example
A spring was stretched with increasing load.
The graph of the results is shown below.

Determine the value of the spring constant.
Answer:
Step 1: Rearrange Hooke's Law:
Spring constant, k, is:
Step 2: Relate the gradient of this graph to k :
The y axis of this graph is length L and the x axis is load F
Gradient is change in y over change in x:
The change in length is the extension x
Therefore:
Step 3: Determine the gradient of the graph:
Choose a large section of the graph line to determine the changes in the x and y axes
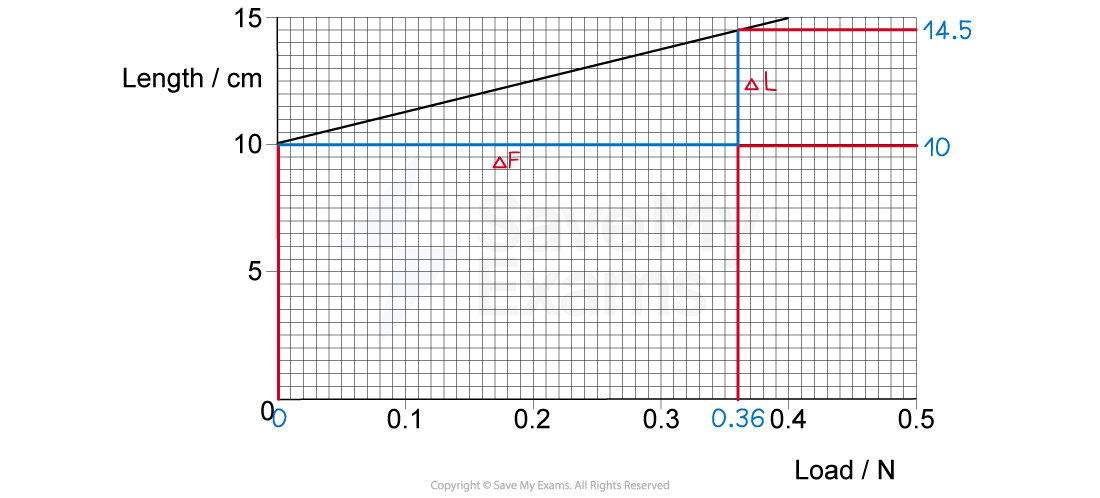
Convert the extension from cm to m
Step 4: Calculate the spring constant:
The spring constant is
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Double check the axes before finding the spring constant as the gradient of a force-extension graph. Exam questions often swap the load onto the x-axis and length on the y-axis. In this case, the spring constant is and not the spring constant.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
