Derivation of P = Fv (Cambridge (CIE) AS Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
Derivation of P = Fv
The power delivered to a moving object is described by the equation:
Where:
P = power in watts (W)
F = force in newtons (N)
v = velocity in metres per second (m s-1)
This equation is only relevant where a constant force moves a body at constant velocity
Power is delivered to the object by a force in order to produce an acceleration
The force must be applied in the same direction as the velocity
Derivation
Power is the rate of doing work
Work is done when a force moves an object over a distance
At a constant velocity, the distance moved by the object can be described as:
Substituting this into the work done equation gives:
And substituting this into the power equation gives:
Worked Example
A lorry moves up a road that is inclined at 14.5° to the horizontal.
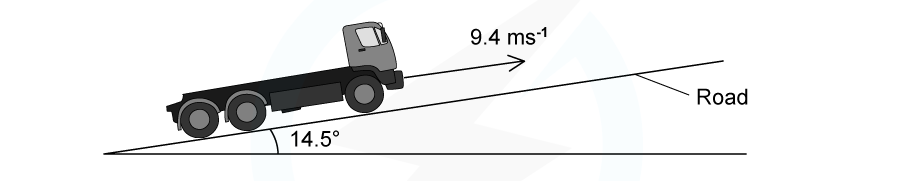
The lorry has mass 3500 kg and is travelling at a constant speed of 9.4 m s-1. The force due to air resistance is negligible.
Calculate the useful power from the engine to move the lorry up the road.
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities
Mass, m = 3500 kg
Speed, v = 9.4 m s-1
Angle of incline = 14.5°
Step 2: State the equation for power in motion
Step 3: Calculate the component of the applied force which overcomes the weight
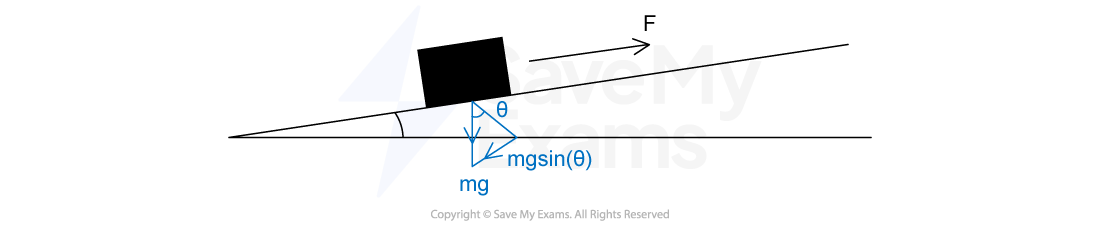
Step 4: Substitute the known values into the power equation to calculate
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The force represented in exam questions will often be a drag force. Whilst this is in the opposite direction to its velocity, remember the force needed to calculate the power is equal to (or above) this drag force to overcome it therefore you equate it to that value.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?