Deriving Kinematic Equations (Cambridge (CIE) AS Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
Deriving kinematic equations of motion
The kinematic equations of motion are a set of four equations which can describe any object moving with constant acceleration
They relate the five variables:
s = displacement
u = initial velocity
v = final velocity
a = acceleration
t = time interval
It’s important to know where these equations come from and how they are derived:
Deriving v = u + at

A graph showing how the velocity of an object varies with time
Deriving s =  (u + v)t
(u + v)t

The average velocity is halfway between u and v
Deriving s = ut +  at2
at2

The two terms ut and ½at2 make up the area under the graph
Deriving v2 = u2 + 2as

This final equation can be derived from two of the others
Summary of the equations of motion
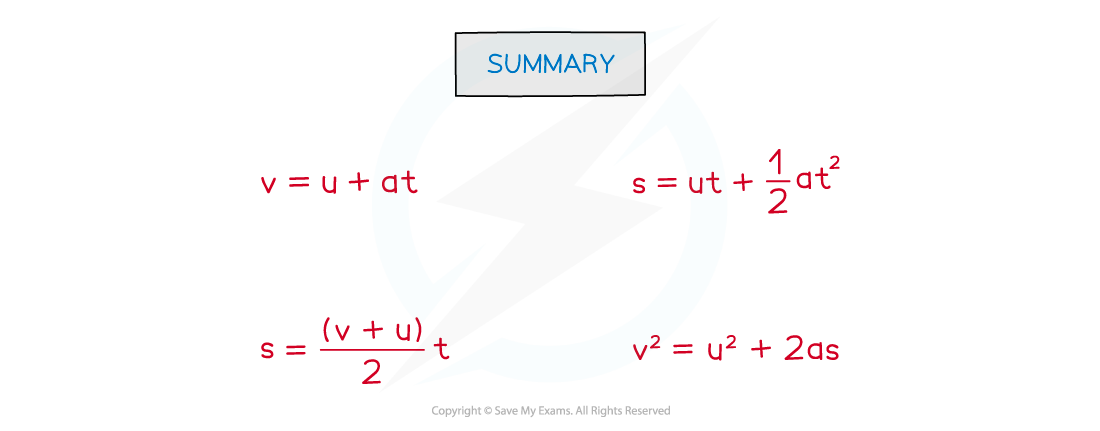
Summary of the four equations of uniformly accelerated motion
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Only and
are given on your data sheet for your exam - make sure you remember all the equations of motions and their derivations.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?