Electrical Energy & Power (AQA AS Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 7407
Energy & Power
In mechanics, power P is defined as the rate of doing work
The potential difference is the work done per unit charge
Current is the rate of flow of charge
Therefore, the electrical power is defined as the rate of change of work done:

The work done is the energy transferred so the power is the energy transferred per second in an electrical component
The power dissipated (produced) by an electrical device can also be written as

Using Ohm's Law V = IR to rearrange for either V or I and substituting into the power equation, means power can be written in terms of resistance R

This means for a given resistor if the current or voltage doubles the power will be four times as great.
Which equation to use will depend on whether the value of current or voltage has been given in the question
Rearranging the energy and power equation, the energy can be written as:
E = VIt
Where:
E = energy transferred (J)
V = voltage (V)
I = current (A)
t = time (s)
Worked Example
Two lamps are connected in series to a 150 V power supply.
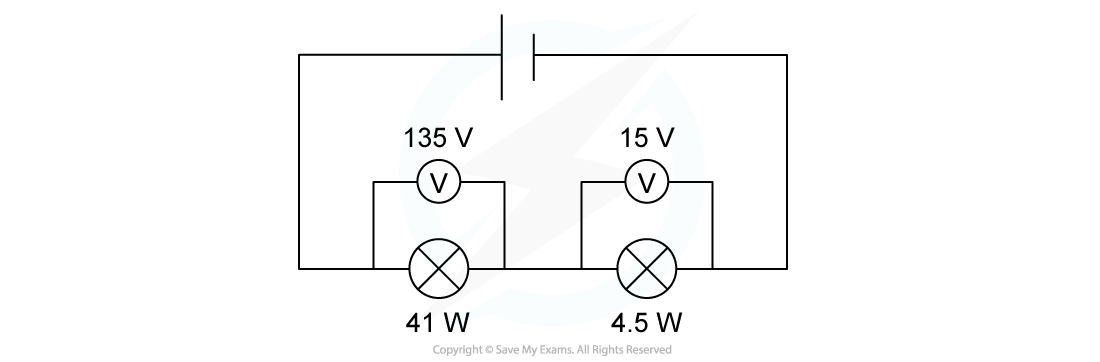
Which statement most accurately describes what happens?
A. Both lamps light normally
B. The 15 V lamp blows
C. Only the 41 W lamp lights
D. Both lamps light at less than their normal brightness
Answer: A

Examiner Tips and Tricks
You can use the mneumonic “Twinkle Twinkle Little Star, Power equals I squared R” to remember whether to multiply or divide by resistance in the power equations. When doing calculations involving electrical power, remember the unit is Watts W, therefore, you should always make sure that the time is in seconds

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?