The Young Modulus (AQA AS Physics) : Revision Note
The Young Modulus
The Young modulus is the measure of the ability of a material to withstand changes in length with an added load
This gives information about the stiffness of a material
This is useful for engineers to make sure the materials they are using can withstand sufficient forces
The Young Modulus is defined as the ratio of tensile stress and tensile strain
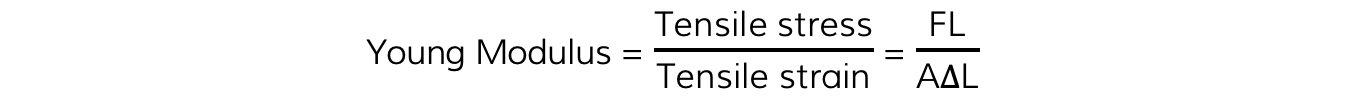
Where:
F = force (N)
L = original length (m)
A = cross-sectional area (m2)
ΔL = extension (m)
Since strain is dimensionless, the units of the Young Modulus is pascals (Pa)
The Young Modulus of a material is typically a very large number, in the order of GPa
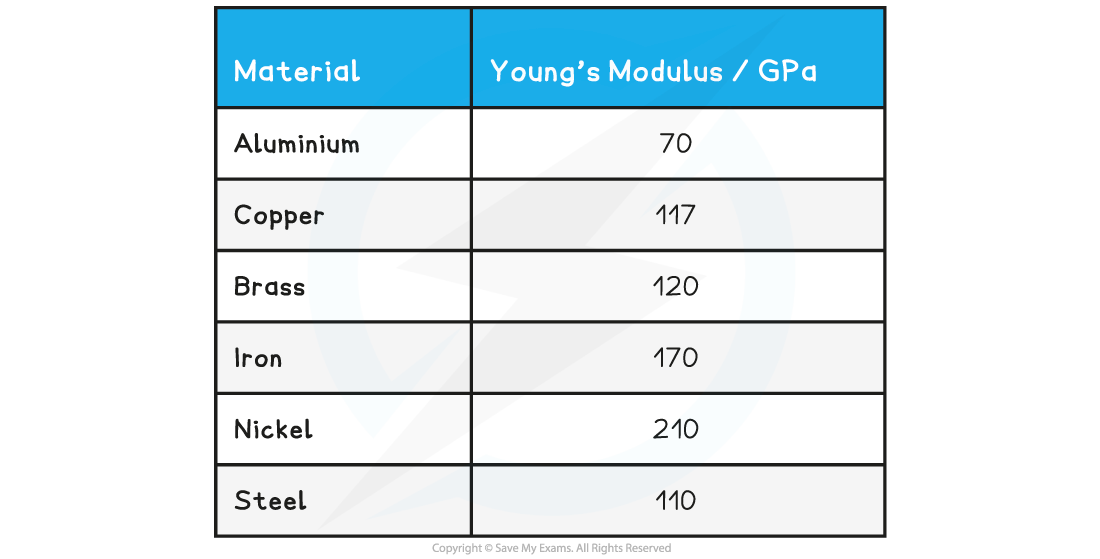
Table of the Young's Modulus for Materials
Worked Example
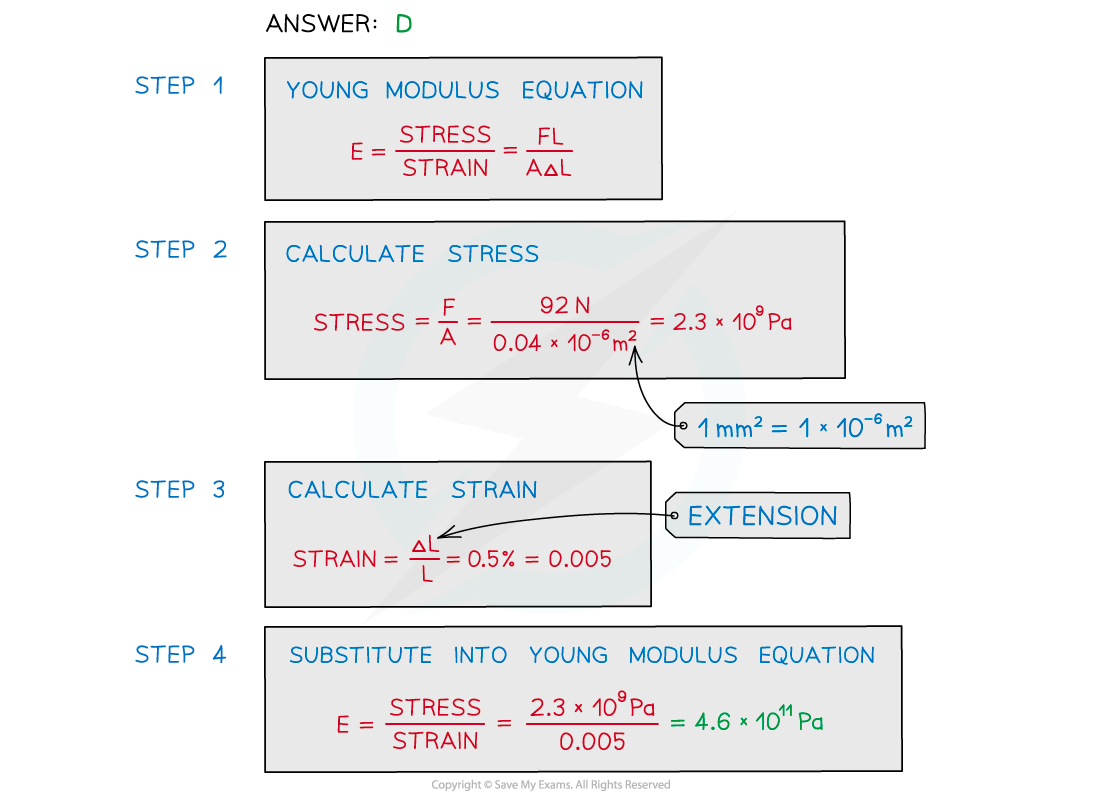
A metal wire that is supported vertically from a fixed point has a load of 92 N applied to the lower end.
The wire has a cross-sectional area of 0.04 mm2 and obeys Hooke’s law.
The length of the wire increases by 0.50%.What is the Young modulus of the metal wire?
A. 4.6 × 107Pa B. 4.6 × 1012 Pa C. 4.6 × 109 Pa D. 4.6 × 1011 Pa
Examiner Tips and Tricks
To remember whether stress or strain comes first in the Young modulus equation, try thinking of the phrase ‘When you’re stressed, you show the strain’ i.e. Stress ÷ Strain.
The Young Modulus from Stress-Strain Graphs
The Young Modulus is equal to the gradient of a stress-strain graph when it is linear (a straight line)
This is the region in which Hooke's Law is obeyed
The area under the graph in this region is equal to the energy stored per unit volume of the material

A stress-strain graph is a straight line with its gradient equal to the Young modulus
Worked Example
The graph below shows the stress-strain graph for a copper wire.
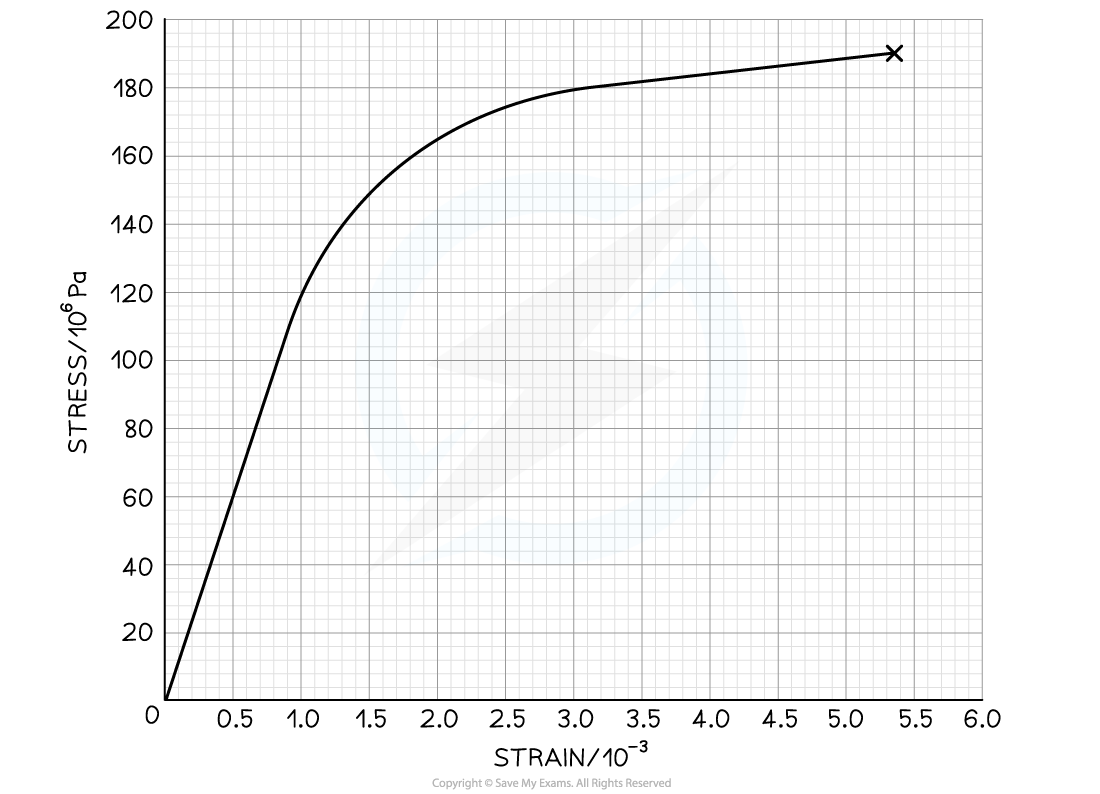
Use the graph to calculate the Young Modulus of copper.
Answer:
Step 1: Determine the stress and strain where the linear region ends
The Young Modulus is the gradient of the linear region of a stress-strain graph
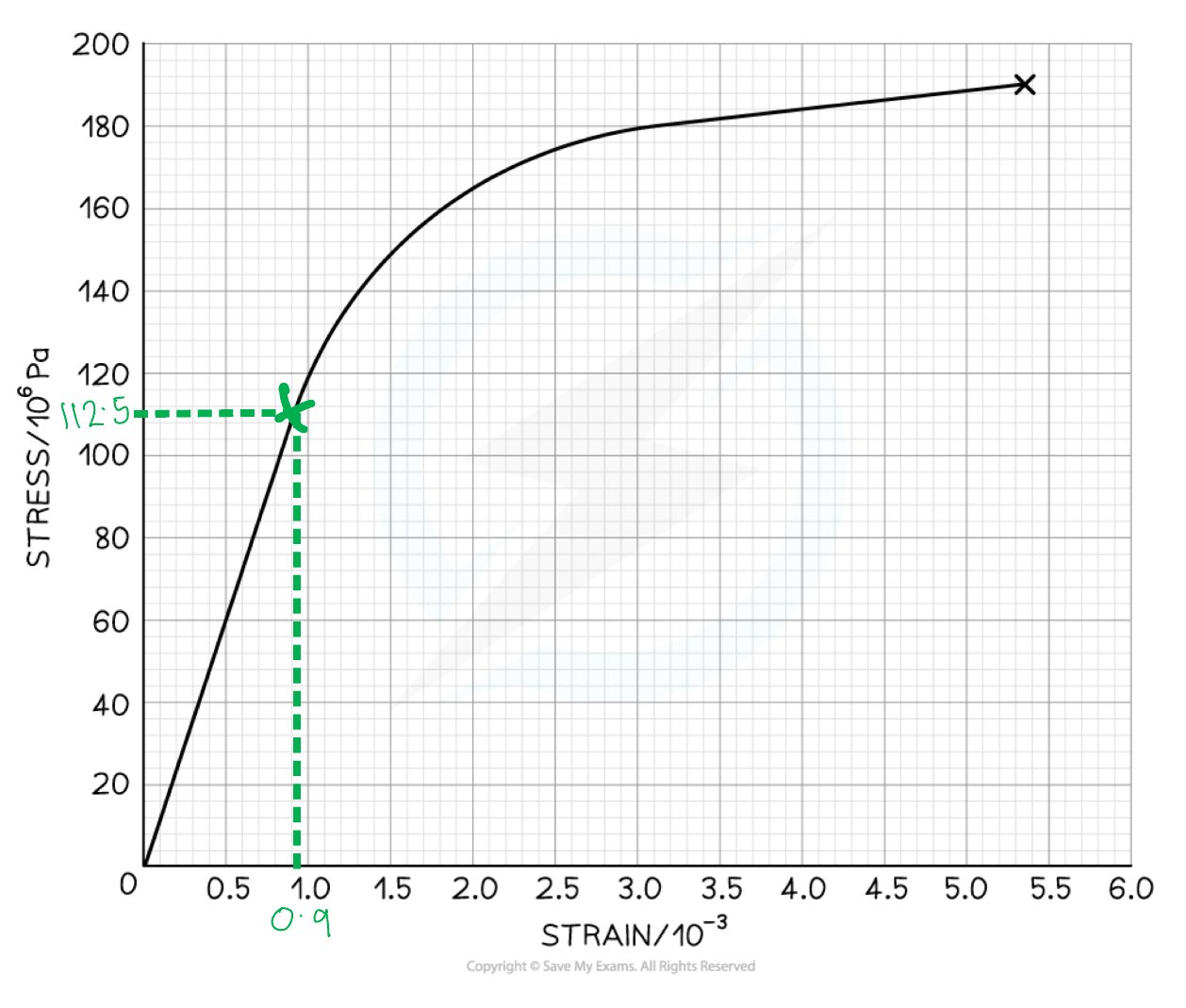
Step 2: Calculate the gradient of the graph in this region

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
