Given that scalar quantities have magnitude (size), but not direction, and vector quantities have both direction and magnitude.
State whether the quantity discussed in each of the following statements is a scalar or a vector.
Did this page help you?
Given that scalar quantities have magnitude (size), but not direction, and vector quantities have both direction and magnitude.
State whether the quantity discussed in each of the following statements is a scalar or a vector.
Did this page help you?
Standardised (S.I.) units for length, time and mass are meters (m), seconds (s) and kilograms (kg) respectively.
Convert the following into S.I. units:
Did this page help you?
S.I. units can be combined to form derived compound units for quantities such as velocity , acceleration
and force
etc.
Convert the following into S.I. units:
Did this page help you?
A film crew record a cheetah running for , it covers a distance of
Calculate the cheetah’s average speed in ?
Did this page help you?
Label the following diagrams with the names of the forces given in each case.
A toy being pulled along on a string: tension, friction, weight, normal reaction.


Did this page help you?
A toy train is being pulled over a carpeted floor by a string.
Explain what effect the following assumptions have on the model described above.
Did this page help you?
Draw a simple diagram to represent each of the following models. Label your diagrams, where appropriate, with any of the following words: air or water resistance (drag), buoyancy, friction, normal reaction, tension, forward thrust, weight.
Did this page help you?
List three assumptions you may need to make in order to create a simple model for each of the following. It may help to think about things that might be affecting the way the object moves, the sorts of external forces that might be acting on the object and also about what factors may be ignored.
Did this page help you?
Each day a train travels in a straight line between three stations, A, B and C and as shown in the diagram below.

Starting at A it travels directly to C. It then travels back to B before returning to its starting position at station A.
Taking the positive direction as shown in the diagram, state whether the following are positive or negative:
Did this page help you?
State whether the quantity discussed in each of the following statements is a scalar or a vector.
Did this page help you?
Convert the following into S.I. units:
Did this page help you?
State the S.I. units which would be used to measure the following.
Did this page help you?
Car A is travelling at , Car B travels
in 5 minutes. Find the difference in their average speeds. Giving your answer in
, correct to three significant figures.
Did this page help you?
Label the following diagrams with the appropriate forces.
A snowboarder sliding down a ski slope.

A parachuting penguin.

Did this page help you?
Two blocks, A and B are attached by means of a light inextensible string running over a smooth pulley, as shown in the diagram below. Block A is accelerating along a smooth horizontal surface in the direction shown, block B is moving towards the ground. Both A and B are modelled as particles.

Explain what effect each of the following assumptions have on the model described above.
Did this page help you?
Draw a simple diagram to represent each of the following models. Labelling your diagrams with the appropriate forces involved.
Did this page help you?
List any assumptions you may make in order to create a simple model for each of the following.
Did this page help you?
A canal barge travels in a straight line from home to two locks, A and B, as shown in the diagram below. The barge travels at a speed of on stretches of the canal that are over
long and 4 km h-1 on stretches that are under
long.

Taking the positive direction as shown in the diagram, state the following in relation to the canal barge:
Did this page help you?
Convert the units in the following statements into S.I. units.
Did this page help you?
Roger throws a frisbee upwards, releasing it at a height of .
The motion of the frisbee is modelled by the equation
where h m is the height of the frisbee above the ground and x m is the horizontal distance travelled.
Write down the value of H needed to complete the model and explain why the model is only valid for .
Use the model to predict how far horizontally the frisbee will have travelled by the time it reaches the ground.
What is the maximum height the frisbee reaches?
Did this page help you?
By converting to S.I. units compare which of the following accelerates quickest.
A: A motorbike accelerates at .
B: A cheetah accelerates at .
C: A race car accelerates at per square min.
Did this page help you?
Define each of the following and give an example of how they could be used in a mathematical model, include any related assumptions which can be made.
A lamina and a non-uniform rod.
A bead and wire.
Did this page help you?
Label the following diagrams with the appropriate forces.
A speed boat travelling through water.

A climber abseiling down a cliff.

Did this page help you?
Fishing company, Fin-tastic Rods, are designing a new fishing pole. They set up a model as shown in the diagram below to consider the forces involved in catching a fish.

Explain what effect the following assumptions would have on the model described above and whether or not they are suitable.
Did this page help you?
Draw a simple diagram to represent each of the following models. Label your diagrams with the appropriate forces involved and detail any assumptions you make about your model.
Did this page help you?
List any assumptions you could make in order to create a simple model for each of the following.
Did this page help you?
A yo-yo moves in a straight line up and down a 1 m string. As it travels down the string it has a velocity of and a velocity of
when returning towards the hand. In order to do certain tricks, the yo-yo stops at different places along the string as shown in the diagram below. The stops of one particular trick, ‘The Mechanic’, are as follows: Hand-2-1-3-1-Hand
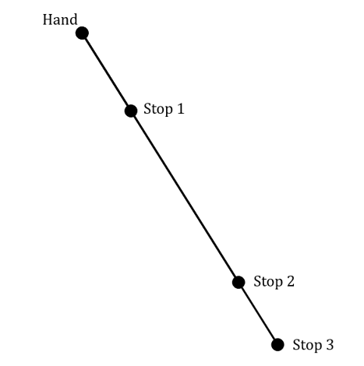
Stop 1 is of the way along the string, Stop 2 is
of the way along the string. When the yo-yo reaches Stop 3 the string is fully extended.
By indicating your chosen positive direction clearly on the diagram above, state the following in relation to the yo-yo:
Did this page help you?
A speedboat accelerates from rest to 90 in 5
. The distance travelled, d
, in time t
, can be modelled by a quadratic equation in the form
. When
the speedboat has travelled a distance of
.
Did this page help you?
Melody throws a netball into a net. The path of the ball from leaving Melody’s hand to passing through the net is modelled by the function
where h m is the height of the netball above the ground and x m is the horizontal distance travelled.
Find the height of the ball when it horizontally half way from being thrown to reaching its maximum height.
The above model is valid for , where k m is the horizontal distance of the net from the player. The standard height of a netball hoop is
.
Find the value of k. Give your answer to three significant figures.
Explain why the model is not valid for .
Did this page help you?
A stone is thrown from the edge of a lake into the water. The height of the stone above the water level h m, at time t after it is thrown is modelled by a quadratic equation in the form
.
Explain why the value of a must be negative and what the variable c must indicate.
Did this page help you?
The diagram below shows a child holding onto a kite flying in the wind. Label the diagram with the appropriate forces, explain any assumptions you make about the diagram.

Did this page help you?
Define each of the following and give an example of how they could be used in a mathematical model, include any related assumptions which can be made.
Did this page help you?
The diagram below shows a basketball player taking a shot.
Label the forces on the ball at the three different stages of the throw.
A: As the player takes the shot, with their hands still in contact with the ball.
B: When the ball is in flight at its maximum height.
C: When the ball reaches the basket, hitting the back of the metal rim.

List any assumptions you made for each, or all, stages of the throw A, B and C in order to answer part (a).
Did this page help you?
Draw a simple diagram to represent each of the following models. Label your diagrams with the appropriate forces involved and detail any assumptions you make about each model.
A boxer hitting a punch bag suspended from the ceiling.
The forces acting on a cat batting at a piece of string held by its owner.
Did this page help you?
A particle is attached to the end of a rod. One end of the rod is fixed to a wall using a hinge, the other end is held using a piece of string before it is let go.
State all the assumptions that would need to be made to model the situation above. You may draw a diagram to support your answer.
Did this page help you?