Equation of a Straight Line (Cambridge (CIE) AS Maths) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
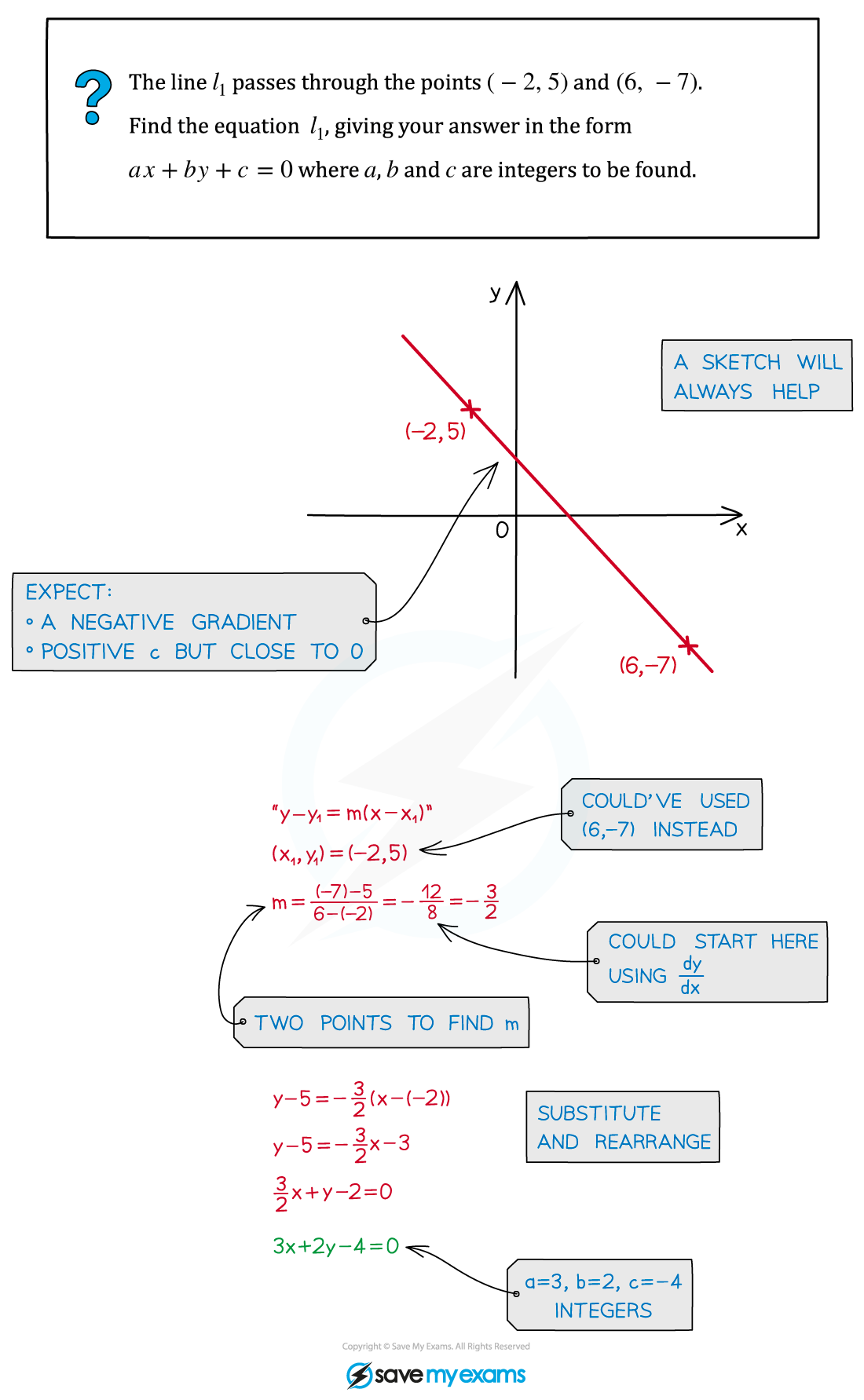
Equation of a Straight Line
What is the equation of a straight line?
y = mx + c is the equation for any straight line
m is gradient given by “difference in y” ÷ “difference in x” or dy/dx
c is the y-axis intercept
Alternative form is ax + by + c = 0 where a, b and c are integers

How do I find the equation of a straight line?
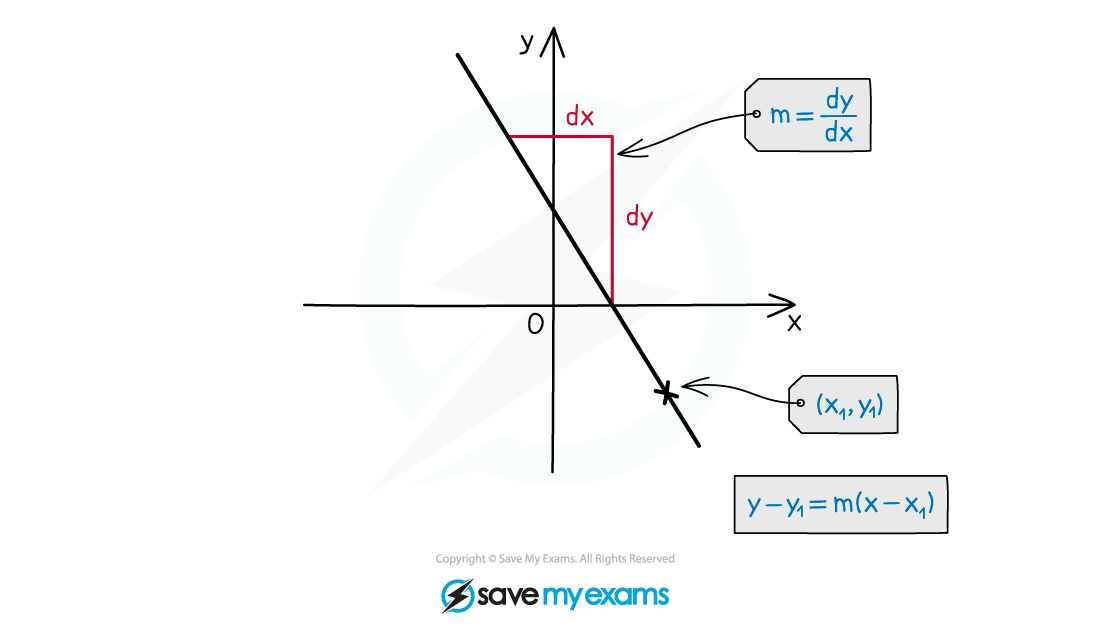
Two features of a straight line are needed
gradient, m
a point the line passes through, (x1, y1)
The equation can then be found using y – y1 = m(x - x1)
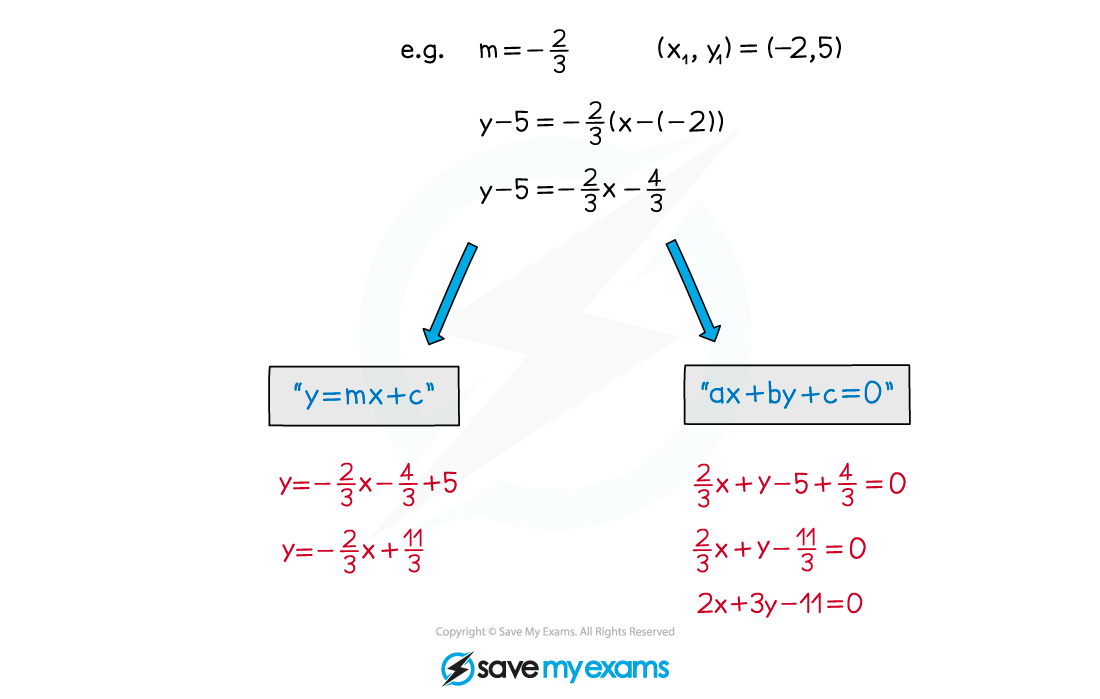
This can be arranged into either y = mx + c or ax +by + c = 0
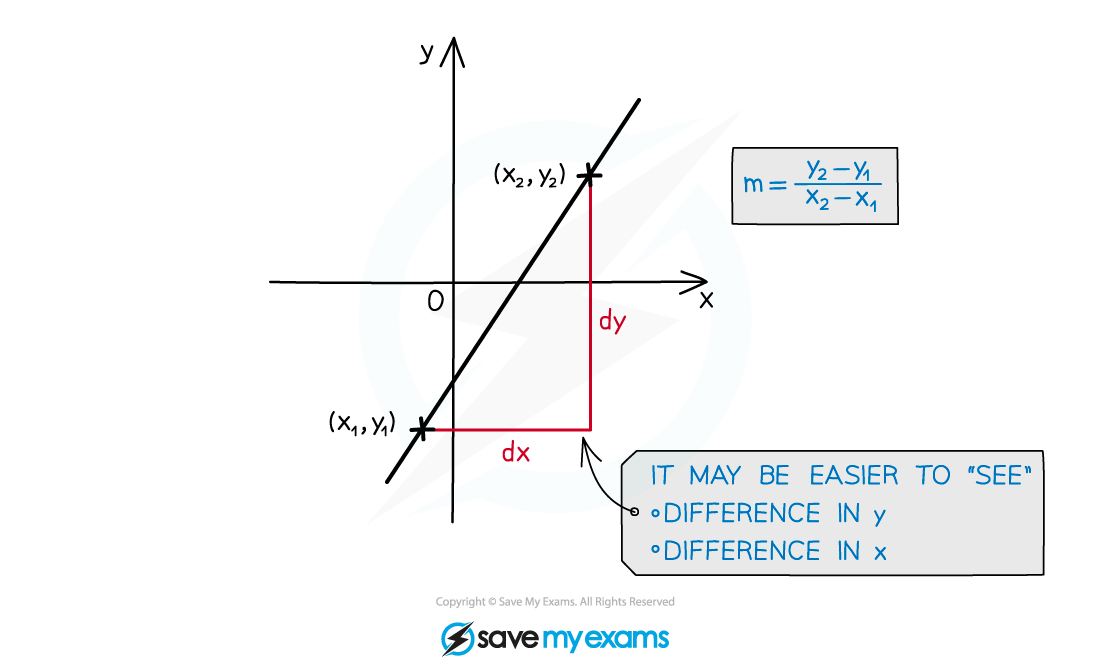
How do I find the gradient of a straight line?
There are lots of ways to find the gradient of a line
Using two points on a line to find the change in y divided by change in x
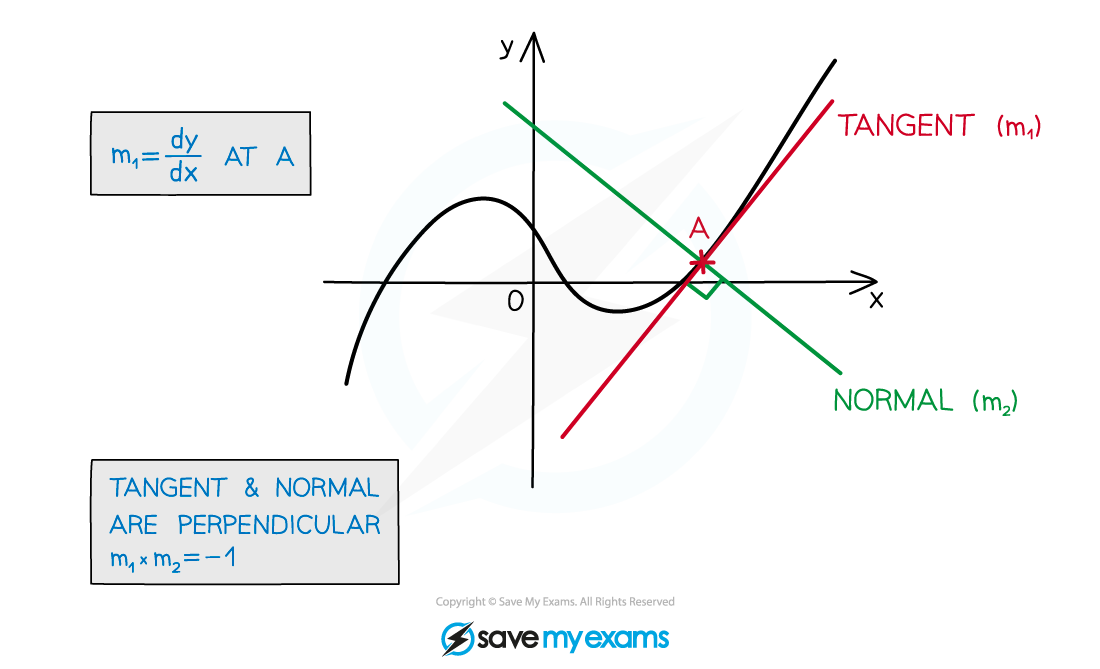
Using the fact that lines are parallel or perpendicular to another line (see Parallel and Perpendicular Gradients)

Using Tangents and Normals - Differentiation (see Gradients, Tangents & Normals)
Other ways
Collinear lines are the same straight line so gradients are equal
Angle facts and circle theorems
eg. a radius and tangent are perpendicular
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Working with straight lines can involve lots of algebra, but sketching a diagram will always help.
Use a sketch to check if answers seem about right.
Worked Example

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?
