Impacts of Climate Change (Cambridge (CIE) AS Environmental Management): Revision Note
Exam code: 8291
Environmental Impacts of Climate Change
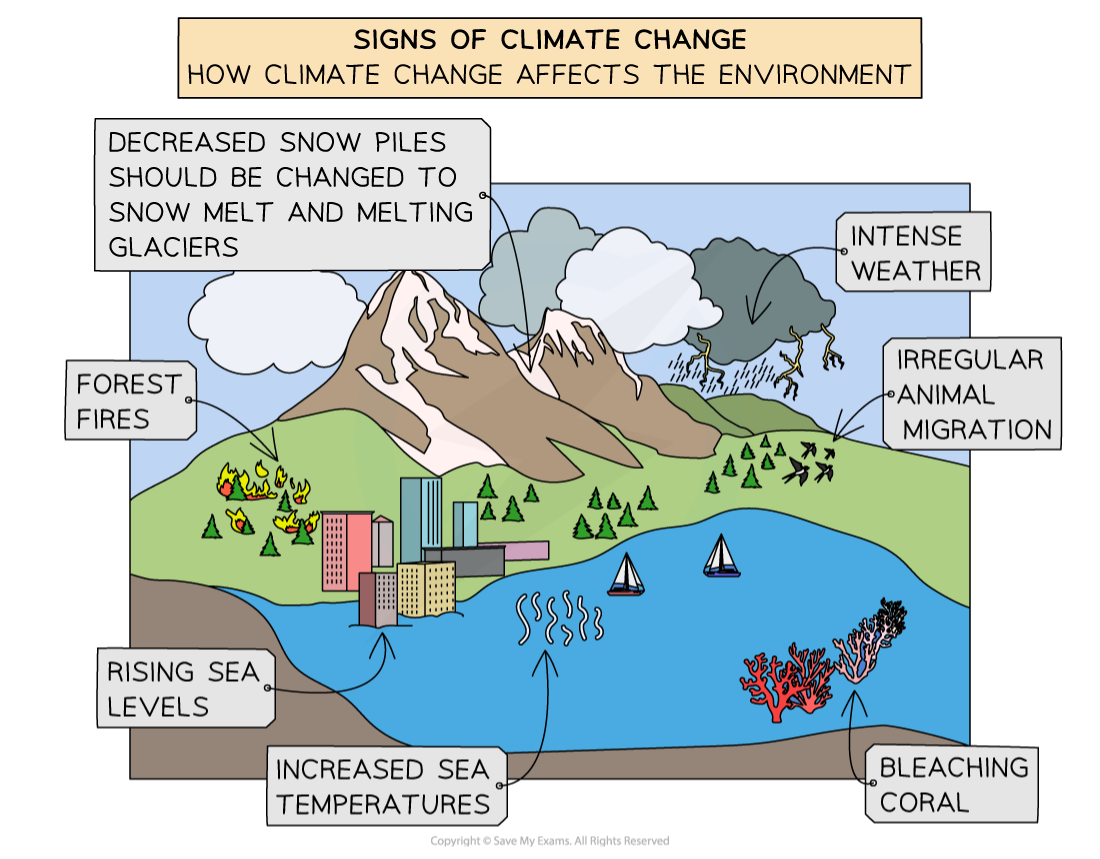
Impacts of Climate Change on the Environment
Change | Impacts | Examples |
|---|---|---|
Temperature and precipitation | Alteration of ecosystems and habitats due to shifting temperature regimes | Coral bleaching events leading to widespread loss of coral reefs |
Changes in precipitation patterns leading to droughts or increased flooding | Increased frequency and intensity of wildfires in forested regions due to severe droughts combined with heatwaves | |
Disruption of agricultural cycles affecting crop yields and food security | Decline in crop productivity due to heat stress and water shortages | |
Sea level | Coastal erosion and loss of land due to rising sea levels | Submergence of low-lying island nations such as Tuvalu and the Maldives |
Increased risk of flooding in low-lying coastal areas and estuaries | Inundation of coastal cities like Miami and New York during storm surges | |
Ocean and wind circulation | Disruption of ocean currents affecting marine ecosystems and weather patterns | Slowing of the Gulf Stream leading to altered weather patterns in Europe |
Changes in wind patterns impacting agriculture, transportation and weather | Shifts in monsoon patterns affecting agricultural productivity in Asia | |
Melting of sea ice, ice sheets, glaciers and permafrost | Accelerated melting contributing to sea level rise and coastal inundation | Melting of Greenland's ice sheet |
Release of stored greenhouse gases (e.g. methane) from thawing permafrost | Thawing permafrost in the Arctic releasing methane, accelerating global warming | |
Loss of habitat for polar species dependent on ice-covered environments | Decline in polar-bear populations due to loss of sea ice hunting grounds | |
Species distribution and biodiversity | Range shifts and habitat loss for plants and animals due to changing climates | Poleward migration of species such as butterflies and birds |
Increased extinction risk for species unable to adapt or migrate | Decline in populations of coral-dependent fish species due to bleaching events | |
Disruption of ecological interactions and food webs affecting biodiversity | Disruption of pollinator populations, such as bees and butterflies, affecting plant reproduction and ecosystem stability |
Sea-level Rise
Warmer temperatures cause the water in seas and oceans to expand, increasing the sea level
Melting ice is adding to the increasing volume of water:
Average sea levels have risen 23 cm since 1880
Sea levels are forecast to increase a further 30 cm by 2050
Low-lying coastal areas and islands are at higher risk of flooding:
The Maldives may be uninhabitable by 2050
Beach erosion will increase leading to greater coastal erosion
Coastal ecosystems including coral reefs and mangrove swamps will be affected
Saltwater ingress is contaminating freshwater supplies and affecting coastal agriculture

Polar Habitat Change
Many species rely on the ice that forms at the poles for their habitat:
Sea ice forms when the ocean freezes
Sea ice that is attached to land is known as landfast ice
Global warming means that there is less sea ice, and the ice that does form breaks apart and detaches from the land earlier in the year than previously, causing problems for breeding animals:
Emperor penguins, Aptenodytes forsteri
These birds breed on Antarctic sea ice, laying and incubating their eggs and raising their young
The early melting of sea ice is not giving them enough time to raise their young
Walruses, Odobenus rosmerus
These mammals rely on Arctic sea ice, where mothers can alternate periods of feeding their young and hunting for food in the ocean nearby
The early loss of ice means that nursing mothers need to care for their young further from the water's edge, leaving young without protection for longer periods when the mothers hunt for food

Range Shifts of Temperate Species
Species exist within tolerance limits, meaning that they can only survive in habitats where the environmental conditions fall within their range of tolerance:
E.g. a marine species may only be able to survive in seawater that falls within certain temperature limits
Climate change is causing changes to many local environmental factors; when this causes the conditions of a habitat to change beyond what a species can tolerate, the species must either migrate to a new habitat or face extinction
This migration may involve a shift in range distribution towards the poles, or to a higher altitude, to an area where temperatures are cooler:
A range shift towards the poles is described as a poleward shift
A range shift to a higher altitude is an upslope shift
Upslope Range Shifts in Montane Bird Species
Montane, i.e. mountain-dwelling, species will live at an altitude that suits their needs:
Altitude affects temperature and oxygen availability, so will influence plant growth and rates of aerobic respiration
Evidence gathered in the mountains of Papua New Guinea over a 50 year period shows that many bird species have migrated to higher altitudes over this time period:
This is not the case for all species; a few have stayed in the same place or moved downslope
E.g. data gathered from Mt Karimui show that bird species have moved upslope in this region by an average of more than 100 m

Examiner Tips and Tricks
Note that you will not be expected to know the Latin names of species in an exam, but it is useful to know some examples of species that are being negatively impacted by climate change
Human Impacts of Climate Change
Impacts of Climate Change on Human Populations
Impact | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
Increased frequency and severity of extreme weather events | More frequent and intense hurricanes, cyclones and typhoons leading to widespread flooding and destruction of infrastructure | Hurricane Katrina (2005) devastated New Orleans, causing extensive flooding and displacement of residents |
Severe droughts resulting in water shortages, crop failures and wildfires, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions | The California drought (2011-2017) led to water rationing, crop losses and increased wildfire activity across the state | |
Damage to property and loss of life during extreme weather events | Destruction of homes, buildings and critical infrastructure during storms, floods and heatwaves, resulting in economic losses | Superstorm Sandy (2012) caused widespread damage along the U.S. East Coast, resulting in billions of dollars in property damage |
Loss of life due to heat-related illnesses, drowning and injuries caused by extreme weather events | Heatwaves in Europe (2003) resulted in thousands of deaths, particularly among vulnerable populations such as the elderly | |
Forced migration | Displacement of communities due to rising sea levels, flooding, drought and conflicts over dwindling resources | Climate refugees from Bangladesh are relocating to urban areas due to coastal erosion and flooding caused by sea level rise |
Migration from rural to urban areas as agricultural livelihoods become unsustainable due to changes in climate and water availability | Farmers in regions of Sub-Saharan Africa are migrating to cities in search of alternative livelihoods due to drought and crop failures | |
Impacts on crop yields and increased pest outbreaks | Decreased crop productivity and yield losses due to changes in temperature, precipitation patterns and water availability | Decline in wheat yields in Australia due to heat stress and reduced rainfall |
Expansion of pest populations and diseases affecting crops, leading to reduced agricultural output and food security | Outbreak of coffee leaf rust in Central America resulting in significant losses for coffee farmers | |
Impacts on food, energy and water security | Disruption of food production and distribution systems, leading to food shortages, price volatility and insecurity | Food shortages and price spikes following extreme weather events, such as hurricanes or droughts |
Reduced availability and quality of freshwater resources due to changes in precipitation patterns and increased evaporation | Water rationing in Cape Town, South Africa, during a prolonged drought leading to severe water shortages (2017-2018) | |
Increased demand for energy resources for cooling during heatwaves and for water pumping during droughts, straining energy systems | Power outages in California during heatwaves due to high demand for air conditioning |

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?