Energy Resources (Cambridge (CIE) AS Environmental Management): Revision Note
Exam code: 8291
Renewable Energy Sources
What Are Renewable Energy Sources?
Renewable energy comes from energy sources that will not run out and includes:
Biofuels (biomass including wood, bioethanol and biogas)
Geothermal energy
Hydroelectric dams
Tidal energy
Wave energy
Solar energy
Wind energy
Once in place, these renewable energy sources do not produce any greenhouse gas emissions (with the exception of biomass):
However, it is important to note that greenhouse gases may be emitted in the production, construction and transport of the equipment required for the above renewable energy sources
Renewable Energy Sources Examples
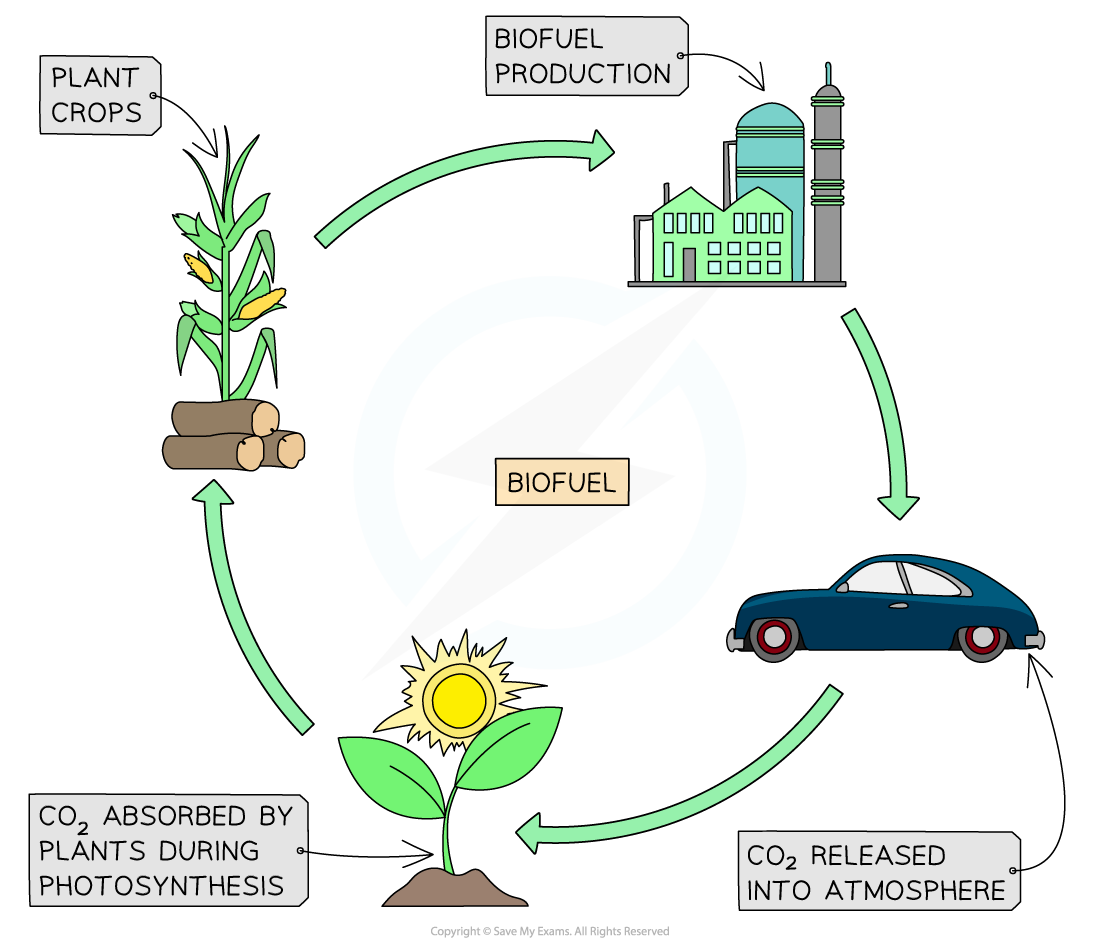
Biofuels
Biofuels (also known as biomass fuels) are renewable fuels derived from organic materials, such as plants and animal waste, that can be used as an alternative to fossil fuels:
However, they have only half the energy density of fossil fuels
The three main biofuels are:
Biodiesel - made by refining renewable fats and oils (e.g. vegetable oils, animal fats or recycled cooking oil)
Bioethanol - made by fermentation (of crops rich in sugars or starches, such as corn or sugarcane)
Biogas - released when organic waste products decompose
Advantages
Biofuel is a renewable resource - uses waste or bioproducts that can be regrown
Some vehicles can be powered by biofuel rather than using fossil fuels
Biofuel is considered to be carbon neutral
No sulfur dioxide is produced
Disadvantages
Crops of biofuel producing plants must be grown, which takes time
Growing the crops takes a lot of land, and takes resources needed for food production
Burning biofuels releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere (however, it is considered carbon neutral because plants take in carbon dioxide when they photosynthesise)
Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy is caused by the heat that is generated from within the Earth:
The Earth's interior is extremely hot, partly due to radioactive elements deep in the Earth that release energy as they decay
This geothermal energy heats up rocks in the Earth's crust, sometimes to an extremely high temperature:
Water can be poured into shafts below the Earth's surface
The water is heated and returned via another shaft as steam or hot water
Steam can be used to turn a turbine and generate electricity, and the hot water can also be used to heat homes
Advantages
Renewable resource
Reliable source of energy
Geothermal power stations are usually small compared to nuclear or fossil fuel power stations
Disadvantages
Few suitable locations on Earth, so only viable for small scale electricity production in many countries
Can result in the release of greenhouse gases from underground
Expensive to build and maintain

Hydroelectric Dams
When water is stored above ground level it has gravitational potential energy
This energy can be transferred to kinetic energy if the water is allowed to flow down the slope
Flowing water turns the turbine to generate electricity
Advantages
Can respond to demand quickly so is reliable and available
Can generate large-scale amounts of electricity in a short period of time
Often in sparsely populated areas
Disadvantages
Expensive to build and maintain
Creating reservoirs sometimes results in the need to flood valleys, which destroys habitats, towns and villages
The pumping systems (used if water needs to be pumped up to the reservoir) often rely on fossil fuels, releasing large amounts of greenhouse gases
Dam traps sediment which can affect ecosystems downstream
Visual pollution
Can prevent fish movement and migration upstream

Wave & Tidal Energy
The rise and fall of waves or the tide can be used to turn a turbine and generate electricity
Advantages
No pollution
Reliable and can produce a large amount of electricity at short notice
Renewable energy resource
Small systems are being developed to provide electricity for small islands
Disadvantages
Expensive to build and maintain
Damages fragile habitats
Very few suitable locations
The technology is not advanced enough for large-scale electricity production


Solar Energy
The energy from the Sun that falls on the Earth is transferred by radiation:
Mostly visible light and infrared radiation
The amount of energy transferred from the Sun to the Earth each hour is roughly equal to the energy use of the world for one year
Therefore, scientists are working hard to find methods of harnessing this energy:
Solar energy has a low energy density, which means large collecting devices are required
Collecting solar energy is expensive (due to the equipment required) and inefficient
Solar PV panels
Solar photovoltaic (PV) panels transfer energy from sunlight electrically producing a current and therefore generating electrical power:
Solar cells, sometimes called photovoltaic cells, are made of semiconducting materials
A number of photovoltaic cells or panels connected together can supply electricity to homes, small-scale businesses, communication devices and satellites
Energy generated can be stored in batteries for later use
Advantages
Solar energy is a renewable resource
In many places on Earth sunlight is a reliable energy resource (this means that the sun shines most of the time)
Solar farms produce no greenhouse gases or pollution
Solar energy can be generated in remote places where they don't have electricity (e.g. to power solar street signs in rural areas)
Can be small- or large-scale
Can be incorporated into building design
Technology is improving and reducing the cost
Disadvantages
Solar farms need to be large-scale to produce large amounts of electricity, which is expensive to set up
Uses large areas of land
People often don't like the appearance of large solar farms; this is known as visual pollution
In many places on Earth sunlight is not a reliable energy resource (there are not enough sunshine-hours to justify the set-up costs)

Wind Energy
Wind energy is a renewable form of energy that harnesses the power of the wind to generate electricity
It involves the use of wind turbines, which have large blades that spin when the wind blows
The rotating blades transfer kinetic energy to a generator, which converts it into electrical energy
Advantages
Wind is an abundant resource that will never run out, making wind energy a sustainable and renewable source of power
Wind energy produces no greenhouse gas emissions or air pollutants during operation, helping to reduce the negative impact on climate change and air quality
Wind energy reduces dependence on fossil fuels and foreign energy sources, promoting energy independence and security
The wind energy industry creates jobs in manufacturing, installation, operation and maintenance of wind turbines
Can be small- or large-scale
Can be on land or offshore
Cheap to run
Disadvantages
Wind is not constant, and the availability of wind energy fluctuates
Electricity generation from wind turbines depends on wind speed and consistency
Wind turbines can be visually intrusive, especially when installed in large numbers
Some people may find the noise generated by wind turbines to be disruptive
Wind farms require large areas of land, which can have an impact on agricultural or natural landscapes
Birds and bats may occasionally collide with wind turbines, causing some impact on local wildlife populations

Non-renewable Energy Sources
Non-renewable energy comes from energy sources that will eventually run out, including:
Fossil fuels
Nuclear energy (using uranium as a fuel)
What Are Fossil Fuels?
Fossil fuels include:
Coal
Natural gas (mostly methane) which is used in domestic boilers and cookers
Crude oil, which is refined into petrol, diesel and other fuels
Fossil fuels are formed from the remains of plants and animals:
Chemical energy stored in fossil fuels originally came from sunlight
Energy from the sun was transferred to chemical energy stores within plants through photosynthesis (plants use energy from sunlight to make food)
Animals ate the plants and the energy was then transferred to their chemical store

Advantages
The current systems of transport and electricity generation used by human societies rely heavily on fossil fuels, which are generally readily available on a daily basis
In the past fossil fuels have been reliable for large-scale energy production (although this is changing as supplies deplete and prices rise)
Efficient - fossil fuels typically have a high energy density (they produce a large amount of energy per kilogram)
Disadvantages
It takes millions of years for fossil fuels to form:
This is why they are considered to be a non-renewable energy resource
The increasing demand for a decreasing supply causes prices to increase:
Fossil fuels are predicted to completely run out within the next 200 years
Burning fossil fuels pollutes the atmosphere with harmful gases such as:
Carbon dioxide, which contributes to the greenhouse effect
Sulphur dioxide, which produces acid rain
Both carbon and sulphur can be captured upon burning, preventing them from being released into the atmosphere, but this is expensive to do
Oil spills can occur during transport of fossil fuels, which damage the environment and wildlife over very large areas
Prices fluctuate rapidly
Supplies can be affected by conflict and political disagreements (e.g. the war in Ukraine)

Uses of Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels are mainly used for:
Transport
Generating electricity
Heating
Transport
The majority of vehicles in the world are powered by petroleum products such as petrol, diesel and kerosene:
These resources all originate from crude oil, which is a fossil fuel
A growing number of vehicles are now being powered by electricity:
The advantage of this is that while the vehicle is being driven, it produces zero carbon emissions
The disadvantage is that when the vehicle is being charged, it is connected to the National Grid, which currently uses a combination of renewable and non-renewable energy sources
Electricity generation
Fossil fuels, such as coal and oil, are used to produce energy on-demand when energy is needed:
This is done by burning the materials when the energy is required
When coal is burned, it produces thermal energy
This is used to boil water creating steam
Steam is forced around the system and this turns a turbine
The turbine turns coils in a magnetic field in the generator:
This generates electricity
The electricity is transferred through a step-up transformer and is carried out of the system by electrical lines
The steam within the turbine will cool and condense and then be pumped back into the boiler to repeat the process

Energy Demand
The demand for energy across the globe is rising
Population growth and development are the two main causes of the increase in energy demand:
The higher demand for food leads to more intensive farming, which requires more energy for machines, light and heat
Increasing industry requires energy for heating, lighting and machinery
There is more transport, all of which requires energy in the form of petrol, diesel or electricity
Urbanisation increases with the development increasing domestic appliances, heating and lighting
Increased wealth means people buy more appliances and technology, which require energy

Nuclear Energy
Energy stored in the nucleus of atoms can be released when the nucleus is broken in two:
This is known as nuclear fission
Nuclear power stations use fission reactions to create steam to turn turbines to generate electricity
Nuclear power is a low carbon, low-emission, non-renewable resource but is controversial due to the radioactive waste it produces and the potential scale of any accident
Advantages
No pollution released into atmosphere
Nuclear reactors are perfectly safe as long as they are functioning properly (rigorous safety checks must be routinely carried out and rigorous safety procedures followed)
Nuclear power stations can generate electricity reliably on a large scale to be available as needed
Small amounts of uranium are needed, and large reserves are available
Reduces reliance on fossil fuels
Increases energy security
Disadvantages
Uranium ore found in the ground is used for fission reactions and since there is a finite supply, nuclear power is a non-renewable resource
Nuclear fuels produce radioactive waste, which needs to be stored for thousands of years
Safe ways of storing radioactive waste are very expensive
If an accident occurs at a nuclear reactor, radioactive waste can leak out and spread over large areas
Cost of decommissioning (shutting down) nuclear power plants is very high

Nuclear energy is often used in countries who do not have their own supplies of fossil fuels, such as France
In 2019 approximately 4% of the global primary energy supply was from nuclear power
There are 439 active nuclear reactors across the world. Most of these are in just five countries:
USA (92)
France (56)
China (54)
Russia (37)
Japan (33)


Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
