Combustion of Alkanes (AQA AS Chemistry) : Revision Note
Combustion
Alkanes are combusted (burnt) on a large scale for their use as fuels
Complete combustion
When alkanes are burnt in excess (plenty of) oxygen, complete combustion will take place and all carbon and hydrogen will be oxidised to carbon dioxide and water respectively
For example, the complete combustion of octane to carbon dioxide and water

The complete combustion of alkanes
Incomplete combustion
When alkanes are burnt in only a limited supply of oxygen, incomplete combustion will take place and not all the carbon is fully oxidised
Some carbon is only partially oxidised to form carbon monoxide
For example, the incomplete combustion of octane to form carbon monoxide

The incomplete combustion of alkanes
Incomplete combustion often takes place inside a car engine due to a limited amount of oxygen present
With a reduced supply of oxygen, carbon will be produced in the form of soot:

Combustion & The Environment
Car exhaust fumes include toxic gases such as carbon monoxide (CO), oxides of nitrogen (NO/NO2) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
When released into the atmosphere, these pollutants have serious environmental consequences damaging nature and health
Carbon monoxide
CO is a toxic and odourless gas which can cause dizziness, loss of consciousness and eventually death
The CO binds well to haemoglobin which therefore cannot bind oxygen and carbon dioxide
Oxygen is transported to organs
Carbon dioxide is removed as waste material from organs
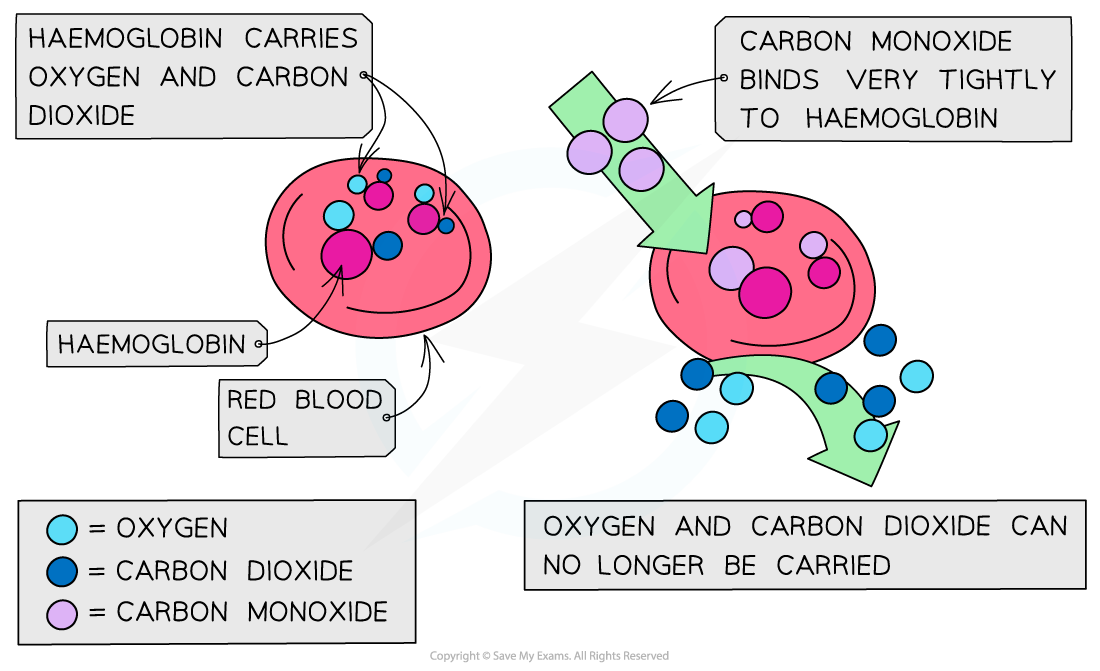
The high affinity of CO to haemoglobin prevents it from binding to O2 and CO2
Oxides of nitrogen
Normally, nitrogen is too unreactive to react with oxygen in air
However, in a car engine, high temperatures and pressures are reached causing the oxidation of nitrogen to take place:
N2(g) + O2(g) → 2NO(g)
N2(g) + 2O2(g) → 2NO2(g)
The oxides of nitrogen are then released in the exhaust fumes into the atmosphere
Car exhaust fumes also contain unburnt hydrocarbons from fuels and their oxides (VOCs)
In air, the nitrogen oxides can react with these VOCs to form peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) which is the main pollutant found in photochemical smog
PAN is also harmful to the lungs, eyes and plant-life
Nitrogen oxides can also dissolve and react in water with oxygen to form nitric acid which is a cause of acid rain
Acid rain can cause corrosion of buildings, endangers plant and aquatic life (as lakes and rivers become too acidic) as well as directly damaging human health
Catalytic removal
To reduce the amount of pollutants released in car exhaust fumes, many cars are now fitted with catalytic converters
Precious metals (such as platinum) are coated on a honeycomb to provide a large surface area
The reactions that take place in the catalytic converter include:
Oxidation of CO to CO2:
2CO + O2 → 2CO2
or
2CO + 2NO → 2CO2 + N2
Reduction of NO to N2:
2CO + 2NO → 2CO2 + N2
Oxidation of unburnt hydrocarbons:
CnH2n+2 + (3n+1)[O] → nCO2 + (n+1)H2O
Reducing sulfur dioxide emissions
The main way to reduce sulfur dioxide emissions is to treat the waste gases from coal fired power stations
The waste gases are passed into a scrubbing chamber which sprays a wet slurry of calcium oxide and calcium carbonate into the gases
This process is also known as sulfur scrubbing or flue gas desulfurisation
Calcium oxide can be used:
Calcium oxide and water reacts with sulfur dioxide to initially produce calcium sulfiite, which is then further oxidised to calcium sulfate or gypsum:
CaO (s) + 2H2O (l) + SO2 (g) + ½O2 (g) → CaSO4.2H2O (s)
Calcium carbonate can also be used
CaCO3 + ½O2 (g) + SO2 (g) → CaSO4 (s) + CO2 (g)
Sulfur dioxide scrubber

The scrubber sprays a lime slurry over the waste gases to remove 90 - 95% of the sulfur dioxide
Pollutants, their Effect & Removal Table

Examiner Tips and Tricks
Though CO2 is not a toxic gas, it is still a pollutant causing global warming and climate change.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
