Simpson's Index (OCR AS Biology) : Revision Note
Simpson's Index of Diversity
Once the abundance of different species in an area has been recorded the results can be used to calculate the species diversity or biodiversity for that area
Species diversity looks at the number of different species in an area (species richness) but also the evenness of abundance across the different species in that area (species evenness)
Simpson’s index of diversity (D) can be used to quantify the biodiversity of an area
Simpson's index
The formula is:

Where:
n = total no. of organisms for a single species
N = total no. of organisms for all species
To calculate Simpson’s Index:
Step 1: First calculate n / N for each species
Step 2: Square each of these values
Step 3: Add them together and subtract the total from 1
To understand what the value of D means you need to know the following:
The value of D can fall between 0 and 1
Values near 1 indicate high levels of biodiversity
Values near 0 indicate low levels of biodiversity
Worked Example
Samples of different insect species in a back garden were collected using sweep nets and identification keys. Use the data to calculate Simpson’s Index.
Answer:
The results and working out are seen in the table below. The figures have been rounded to three decimal places for columns 3 and 4
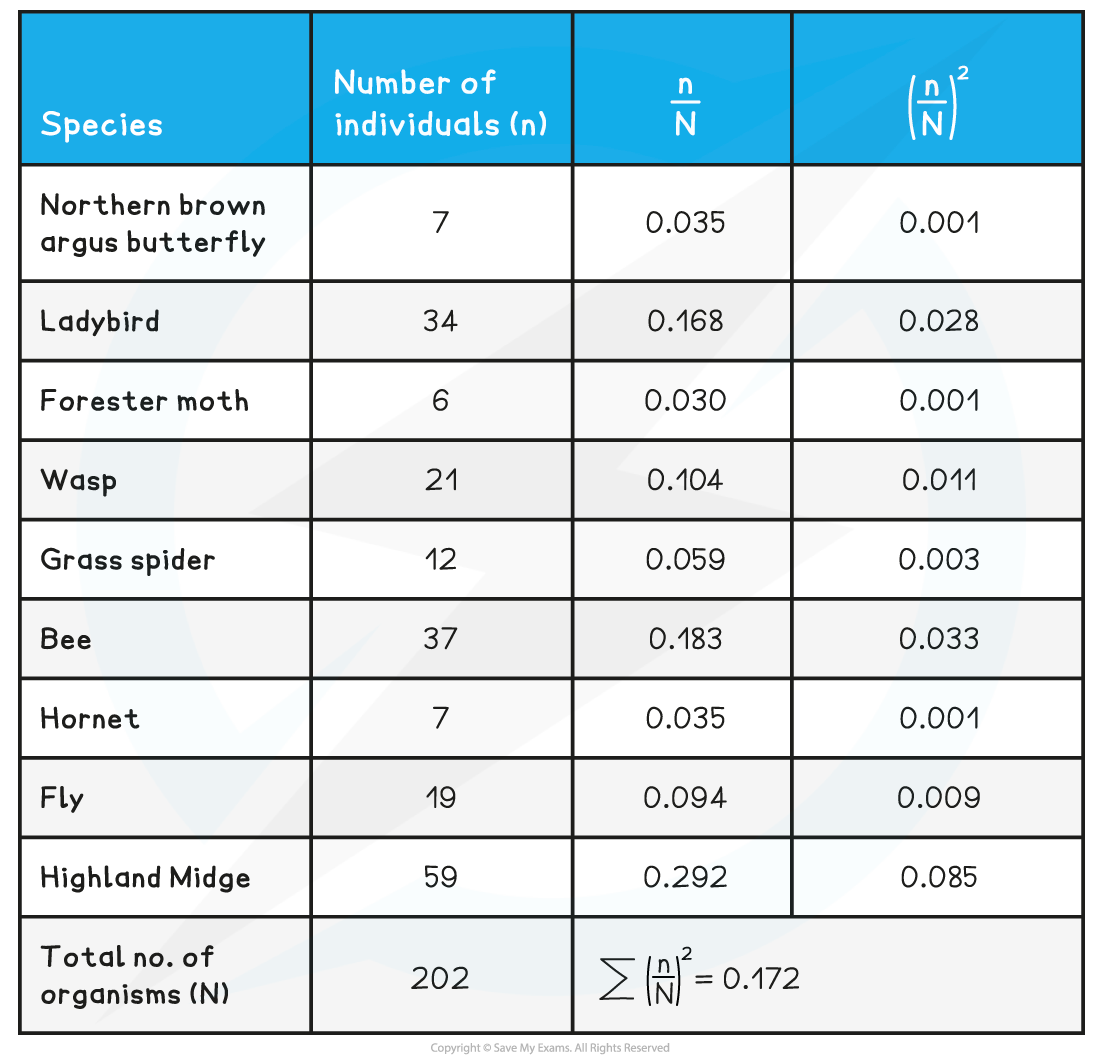
D = 1 - 0.172 = 0.828
As the value of D is much closer to 1 than 0, it can be said that this is a relatively high value for biodiversity.
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember, you will be provided with the formula for Simpson’s Index in the exam so you do not need to recall this.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?
