Pedigree Diagrams (Edexcel AS Biology (A) SNAB) : Revision Note
Pedigree Diagrams
Family pedigree diagrams can be used to trace the pattern of inheritance of a specific trait, e.g. a genetic disorder, through generations of a family
Pedigree diagrams can provide information such as
Whether a trait is caused by a dominant or recessive allele
Whether a trait is more likely to be inherited by males or females
The genotypes of individuals in the family
The probability that an individual in the family will inherit a trait
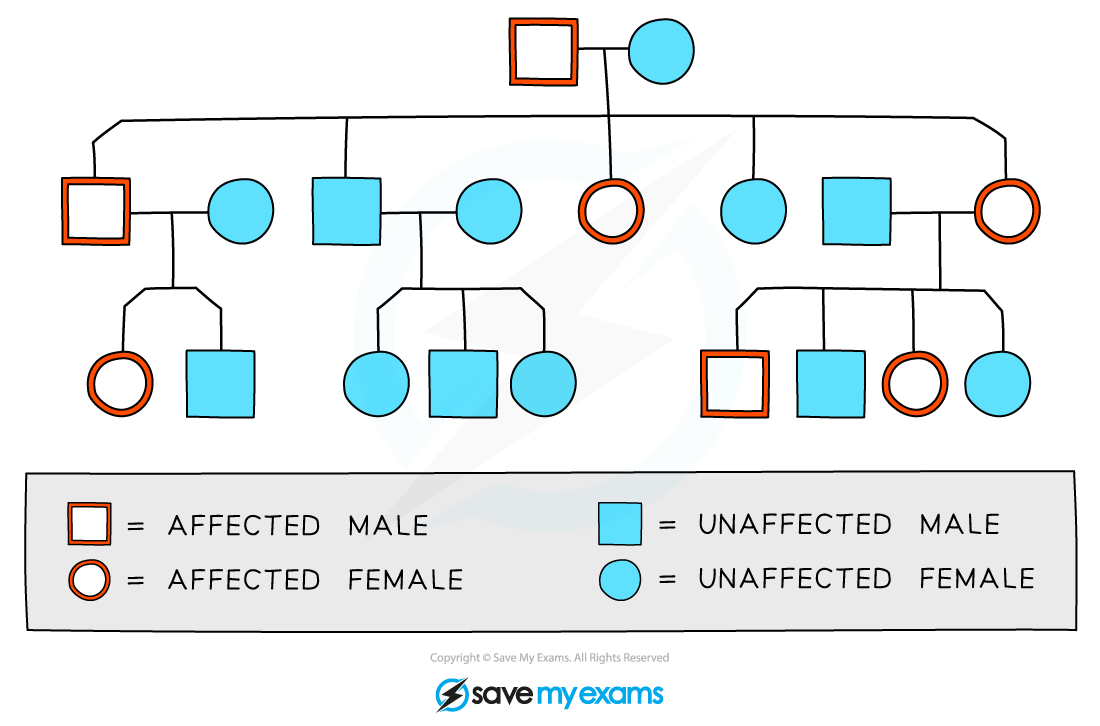
Pedigree diagrams can be used to show the pattern of inheritance of a genetic trait
Males are indicated by the square shape and females are represented by circles
Affected and unaffected individuals can be indicated using colour, shading, or cross-hatching
Horizontal lines between males and females show that they have produced children
Vertical lines show the relationship between parent and child
Roman numerals may be used to indicate generations
For each generation the eldest child is on the left and each individual is numbered
The family pedigree above shows the following
Both males and females are affected by the trait in question
Every generation has affected individuals
The eldest son in the second generation is affected
There is one family group that has no affected parents or children
The diagram above does not contain enough information to show
Whether the trait is caused by a dominant or recessive allele
The genotypes of the individuals involved
Worked Example
The pedigree diagram below traces the inheritance of albinism through several generations. Albinism affects the production of the pigment melanin leading to lighter hair, skin and eyes.

Using the pedigree chart, deduce and explain the following:
The type of allele that causes albinism
The genotype of individuals 9 and 7
The possible genotypes of 10 and 11
Answer:
Question 1
Albinism is caused by a recessive allele
Person number 9 is an affected individual despite parents 6 and 7 being unaffected; 6 and 7 must both be carriers of the recessive allele and 9 has inherited one recessive allele from each parent
Question 2
The genotype of person 9 must be homozygous recessive (aa) and the genotype of 7 must be heterozygous (Aa)
Person 9 is an affected individual with albinism; as this is determined by the recessive allele they must have two copies of the albinism allele
Person 7 must be heterozygous as he does not have albinism but has passed on the recessive allele to person 9
Question 3
The possible genotypes of 10 and 11 are heterozygous (Aa) or homozygous dominant (AA)
They are both unaffected individuals so must possess at least one dominant allele (A), however, it is possible that they each might have inherited a recessive allele (a) from one parent (both parents must have a copy of the recessive allele in order for person 9 to have albinism)
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When answering questions about pedigree charts for genetic diseases, it is always useful to remember which phenotype is caused by the homozygous recessive genotype. You can write these genotypes onto your chart and it will give you a good starting point for working out the possible genotypes of the rest of the individuals in the chart.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
