The Human Gas Exchange System (Cambridge (CIE) AS Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 9700
The human gas exchange system
Gas exchange takes place in the human thorax
This is a collection of organs and tissues in the chest cavity
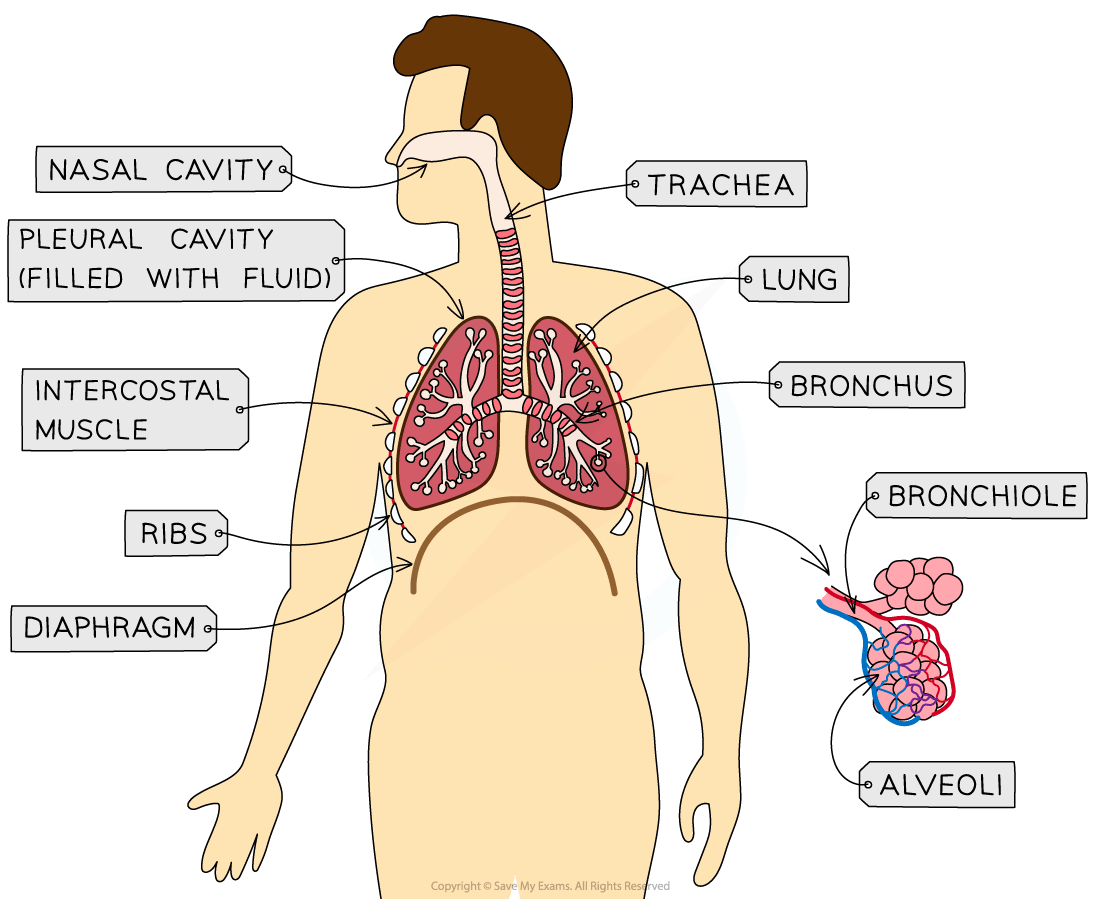
Structure in thorax | Description |
|---|---|
Lungs | Humans have two lungs, both of which are a central part of the breathing system and where gas exchange takes place |
Trachea | This airway leads from the mouth and nose to the bronchi The trachea is lined with mucus-secreting goblet cells and cilia The cilia sweep microorganisms and dust away from the lungs |
Bronchi | “Bronchi” is the plural of “bronchus” The left and right bronchi are at the bottom of the trachea and are similar in structure, but narrower The bronchi lead to bronchioles |
Bronchioles | These are narrow tubes (less than 1mm) which carry air from the bronchi to the alveoli |
Alveoli | The main site of gas exchange within the lungs These are tiny sacs with many structural adaptations to enable efficient gas exchange, such as their thin walls and large surface area to volume ratio |
Capillary network | An extensive network of capillaries surrounds the alveoli They are an exchange surface between the lungs and the blood During gas exchange, oxygen diffuses from the alveoli and into the capillaries, while carbon dioxide diffuses the other way and is exhaled |
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember to pay attention to command words in exams, as they will be asking different things. For example, a question asking you to “Describe” the structure of the alveoli is different from a question asking you to “Explain” the structure of the alveoli. “Describe” questions are asking you to give an account of something or to write events or processes in a logical order. “Explain” questions are asking you to write why something happens or to link its structure to its function—as a result of this, “because” will be an important part of your answer.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?