Gas Exchange Processes (Cambridge (CIE) AS Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 9700
Gas exchange processes
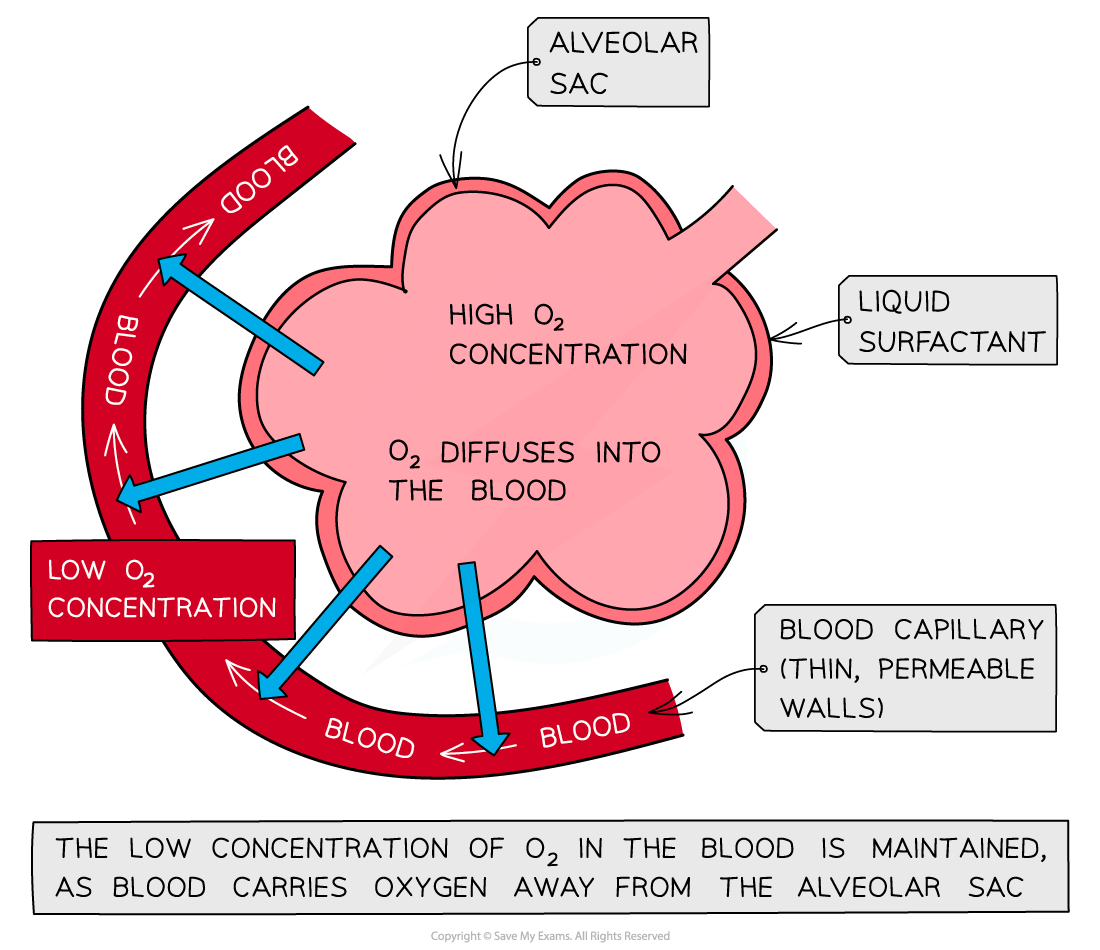
The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs between the alveoli and the capillaries in the lungs
Oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged in a process of simple diffusion
This is a passive movement from high to low concentration
The air in the alveoli contains a high concentration of oxygen
The oxygen diffuses from the alveoli and into the blood capillaries, before being carried away to the rest of the body for aerobic respiration
The blood in the capillaries has a relatively low concentration of oxygen and a high concentration of carbon dioxide
The carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood and into the alveoli and is then exhaled
Feature of alveoli | Importance |
|---|---|
Large surface area | The average human adult has around 480-500 million alveoli in their lungs This equals a surface area of 40-75m2 This enormous surface area increases the space available for oxygen and carbon dioxide to diffuse |
Thin walls | The walls of the alveoli are only one cell thick This means that gases have a very short diffusion distance and so gas exchange is as quick and efficient as possible |
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember that blood arriving to the lungs in capillaries is deoxygenated, while blood leaving the capillaries is oxygenated and returns to the left side of the heart.
You don't need to know how many alveoli there are for your exam, or their total surface area—these are only included here to show you just how large a surface area they have in total!

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?