Xylem Vessels Elements (Cambridge (CIE) AS Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 9700
Xylem vessel elements: structure & function
The functions of xylem tissue in a plant are:
Vascular tissue that transports dissolved minerals and water around the plant
Structural support
Food storage
Xylem tissue is made up of four cell types that function together:
Tracheids (long, narrow tapered cells with pits)
Vessel elements (large with thickened cell walls and no end plates when mature)
Xylem parenchyma
Sclerenchyma cells (fibres and sclereids)
Most of the xylem tissue is made up of tracheids and vessel elements, which are both types of water-conducting cell
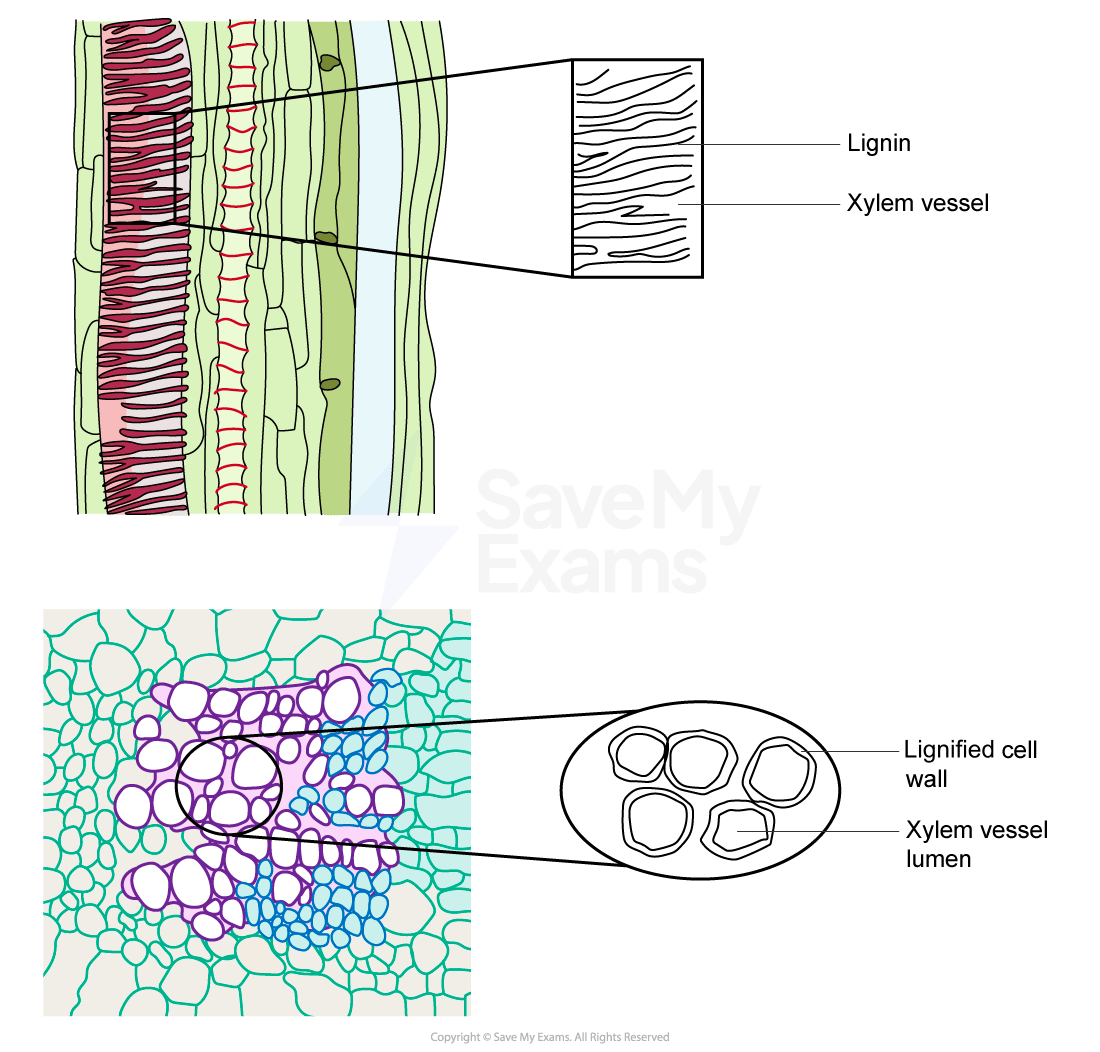
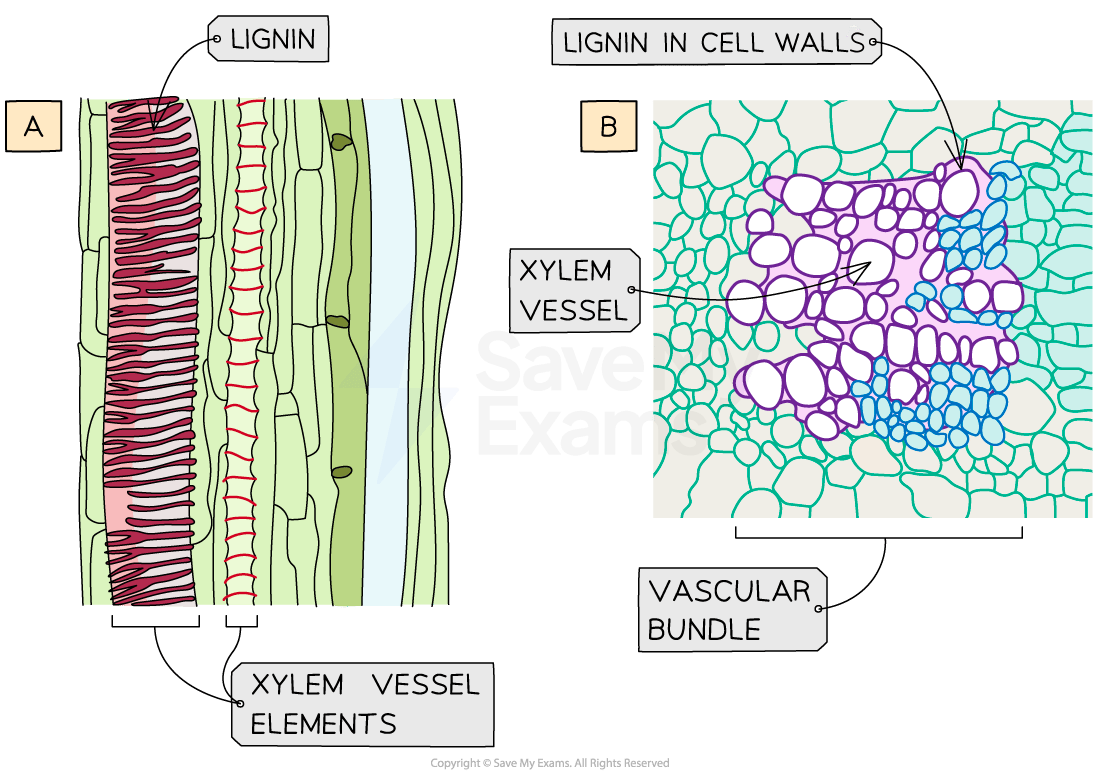
Structure | Function |
|---|---|
Lignified cell walls | Adds strength to withstand hydrostatic pressure so vessels do not collapse. Impermeable to water |
No end plates | Allows for mass flow of water and dissolved solutes as cohesive (between water molecules) and adhesive (between water molecules and xylem wall) forces are not impeded |
No protoplasm (cells are dead when mature) | Does not impede the mass flow of water and dissolved solutes |
Pits in walls (in non-lignified sections) | Lateral movement of water allows for continuous flow in case of air bubbles forming in the vessel |
Small diameter of vessels (although larger than tracheids) | Helps prevent the water column from breaking |
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You must be able to recognise the xylem vessel elements in images, so look for a thicker cell wall and a larger diameter.
You should be able to draw xylem vessel elements from micrograph images. For more detail on how to make biological drawings see our revision notes here.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?