The Four Levels of Protein Structure (Cambridge (CIE) AS Biology) : Revision Note
Proteins: Structures
There are four levels of structure in proteins, three are related to a single polypeptide chain and the fourth level relates to a protein that has two or more polypeptide chains
Polypeptide or protein molecules can have anywhere from 3 amino acids (Glutathione) to more than 34,000 amino acids (Titan) bonded together in chains
Primary Structure
The sequence of amino acids bonded by covalent peptide bonds is the primary structure of a protein
DNA of a cell determines the primary structure of a protein by instructing the cell to add certain amino acids in specific quantities in a certain sequence. This affects the shape and therefore the function of the protein
The primary structure is specific for each protein (one alteration in the sequence of amino acids can affect the function of the whole protein)
Primary Structure Diagram
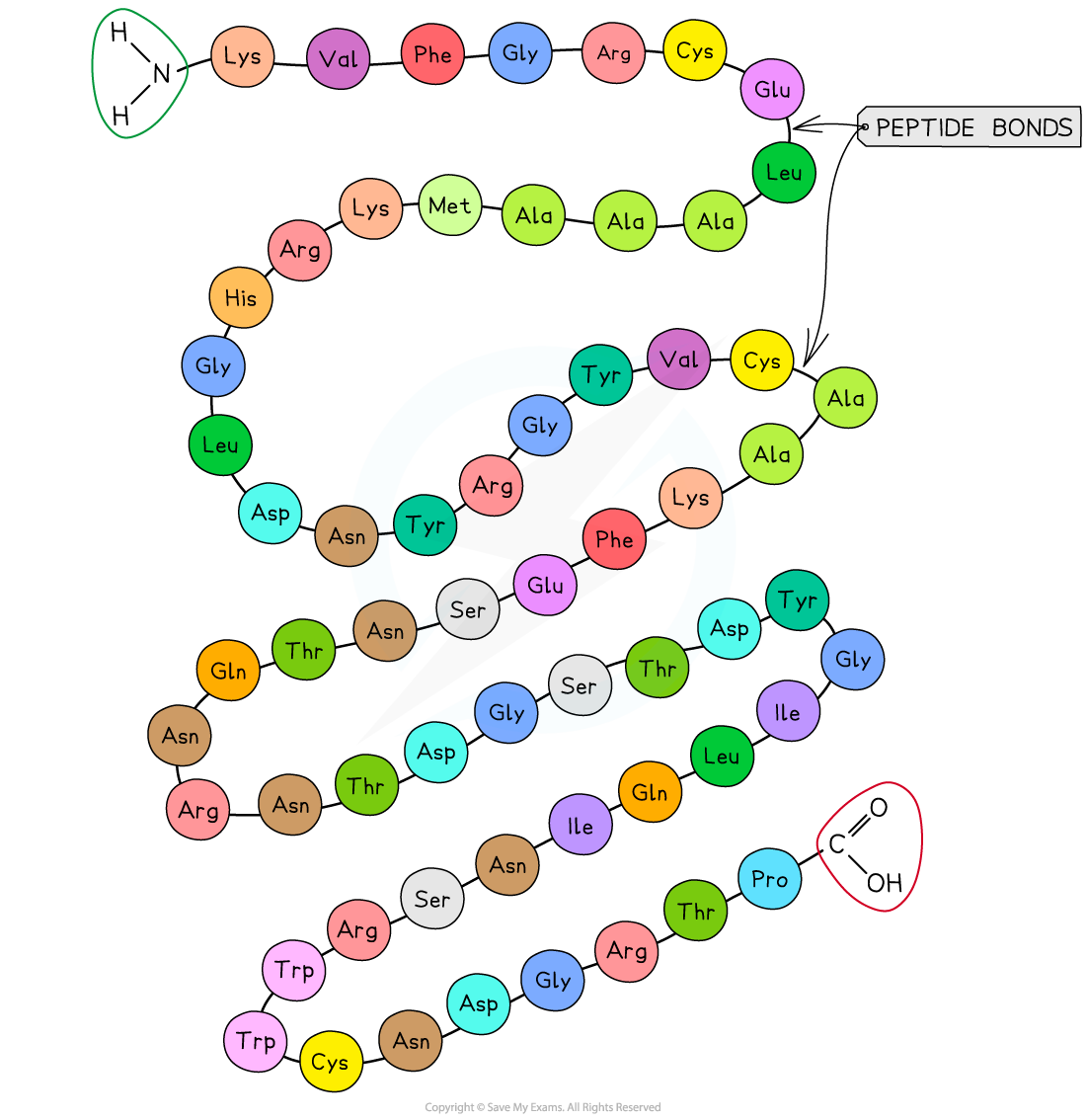
The primary structure of a protein. The three-letter abbreviations indicate the specific amino acid (there are 20 commonly found in cells of living organisms)
Secondary
The secondary structure of a protein occurs when the weak negatively charged nitrogen and oxygen atoms interact with the weak positively charged hydrogen atoms to form hydrogen bonds
There are two shapes that can form within proteins due to the hydrogen bonds:
α-helix
β-pleated sheet
The α-helix shape occurs when the hydrogen bonds form between every fourth peptide bond (between the oxygen of the carboxyl group and the hydrogen of the amine group)
The β-pleated sheet shape forms when the protein folds so that two parts of the polypeptide chain are parallel to each other enabling hydrogen bonds to form between parallel peptide bonds
Most fibrous proteins have secondary structures (e.g. collagen and keratin)
The secondary structure only relates to hydrogen bonds forming between the amino group and the carboxyl group (the ‘protein backbone’)
The hydrogen bonds can be broken by high temperatures and pH changes
Secondary Structure Diagram
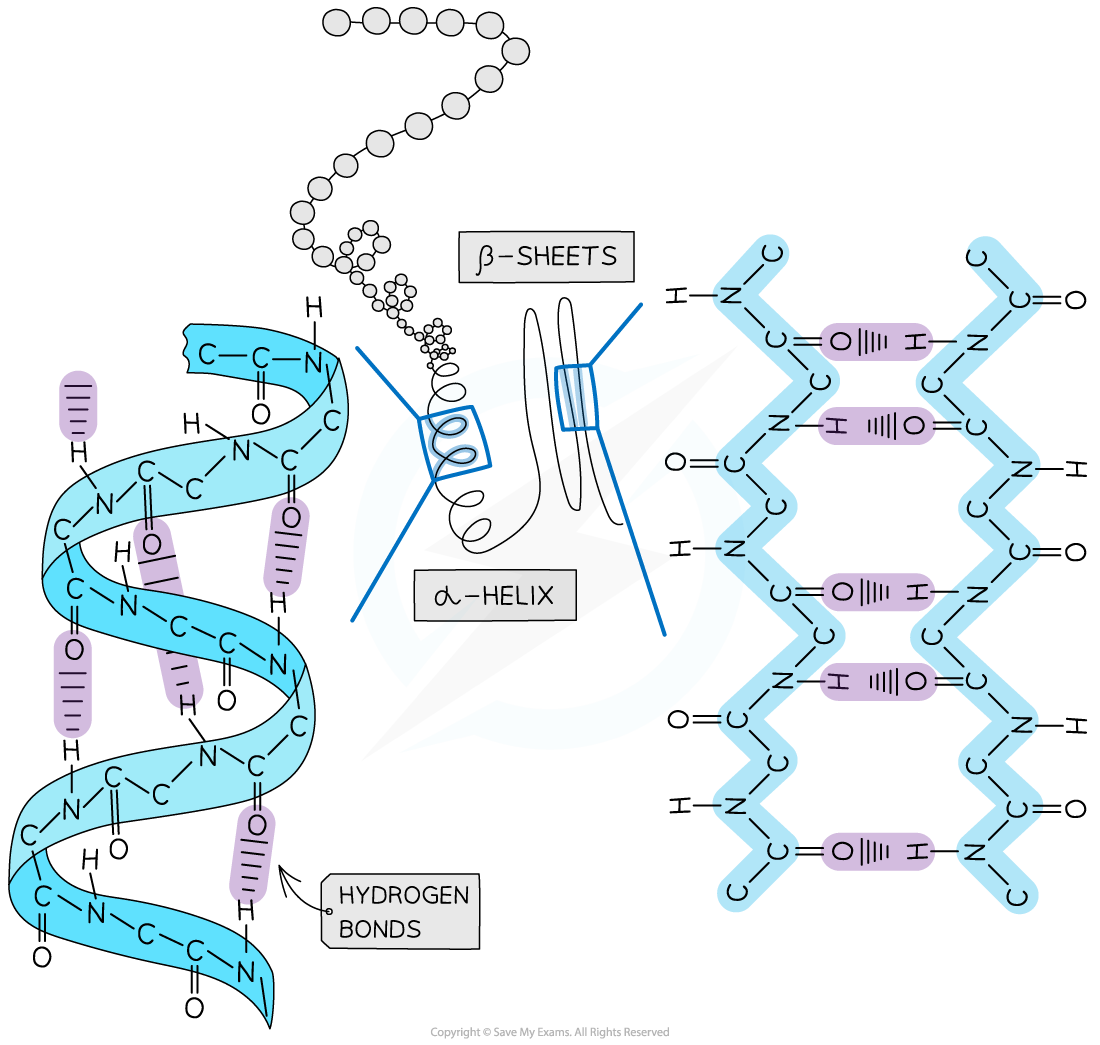
The secondary structure of a protein with the α-helix and β-pleated sheet shapes highlighted. The magnified regions illustrate how the hydrogen bonds form between the peptide bonds
Tertiary Structure
Further conformational change of the secondary structure leads to additional bonds forming between the R groups (side chains)
The additional bonds are:
Hydrogen (these are between R groups)
Disulfide(only occurs between cysteine amino acids, sometimes referred to as a disulfide bridge)
Ionic (occurs between charged R groups)
Weak hydrophobic interactions (between non-polar R groups)
This structure is common in globular proteins such as antibodies
Tertiary Structure Diagram
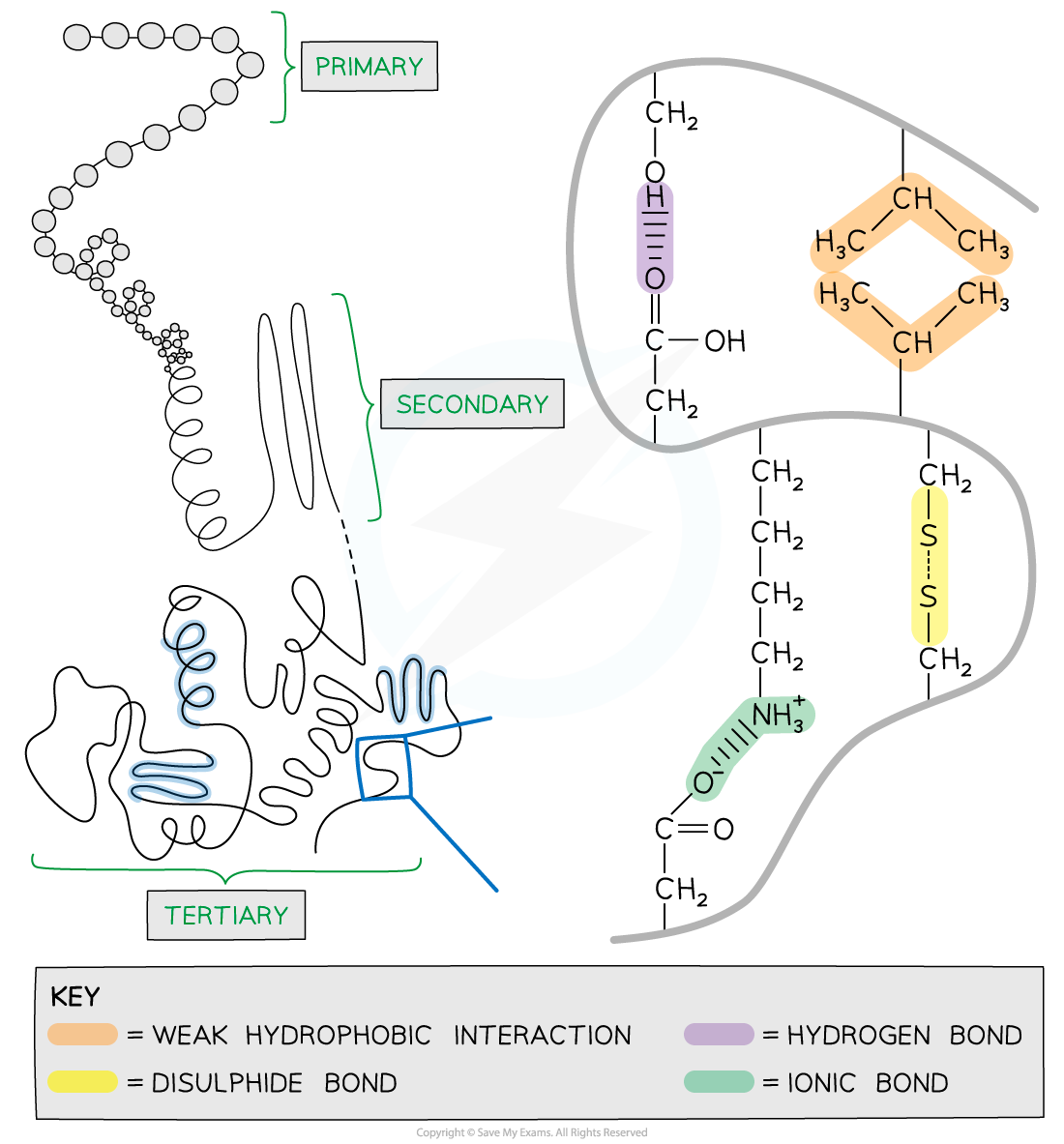
The tertiary structure of a protein with hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, disulphide bonds and hydrophobic interactions formed between the R groups of the amino acids
Quaternary Structure
Occurs in proteins that have more than one polypeptide chain working together as a functional macromolecule, for example, haemoglobin
Each polypeptide chain in the quaternary structure is referred to as a subunit of the protein
Quaternary Structure Diagram
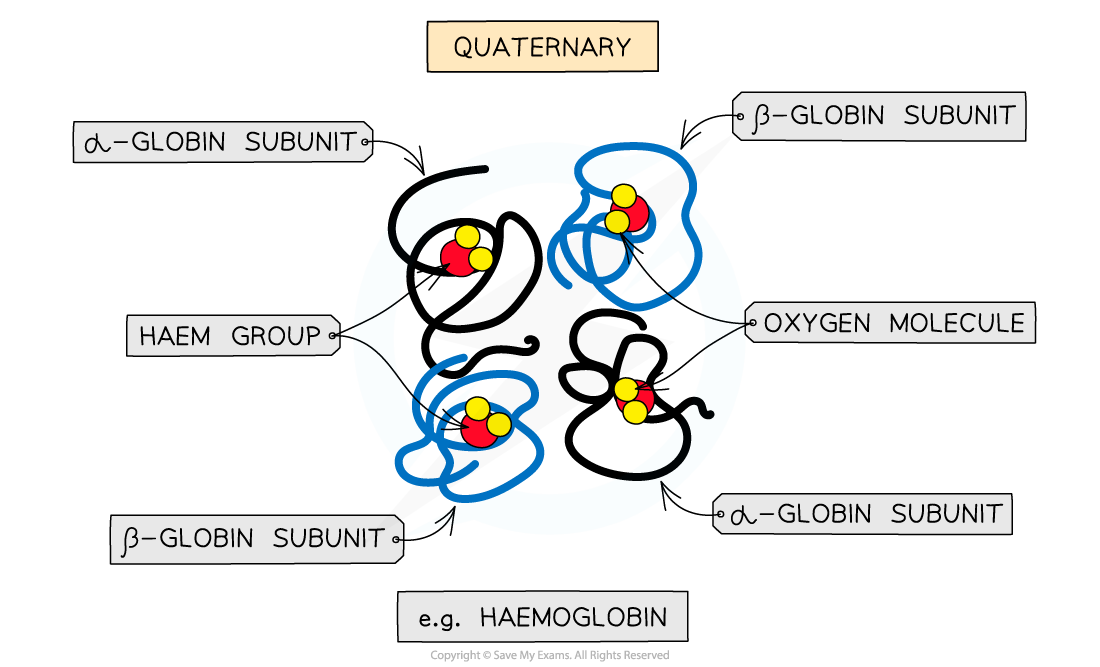
The quaternary structure of a protein. This is an example of haemoglobin which contains four subunits (polypeptide chains) working together to carry oxygen
Summary of bonds in proteins table
Bonds | Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|
Primary | Secondary | Tertiary | |
Peptide | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Hydrogen | X | ✓ (only between the amine and carboxyl groups) | ✓ (only between the R, amine and carboxyl groups) |
Disulfide | X | X | ✓ |
Ionic | X | X | ✓ |
Hydrophobic interactions | X | X | ✓ |
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Familiarise yourself with the difference between the four structural levels found in proteins, noting which bonds are found at which level. Remember that the hydrogen bonds in tertiary structures are between the R groups whereas in secondary structures the hydrogen bonds form between the amino and carboxyl groups.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
