Triglycerides (Cambridge (CIE) AS Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 9700
Triglycerides: basics
Lipids
Lipids are macromolecules which contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms. However, unlike carbohydrates lipids contain a lower proportion of oxygen
They are non-polar and hydrophobic meaning they are insoluble in water
Different types include:
Fats and Oils (composed mainly of triglycerides)
Phospholipids
Steroids and waxes (considered lipids as they are hydrophobic thus insoluble in water)
Triglycerides
These are non-polar, hydrophobic molecules
The monomers are glycerol and fatty acids
Glycerol is an alcohol (an organic molecule that contains a hydroxyl group bonded to a carbon atom)
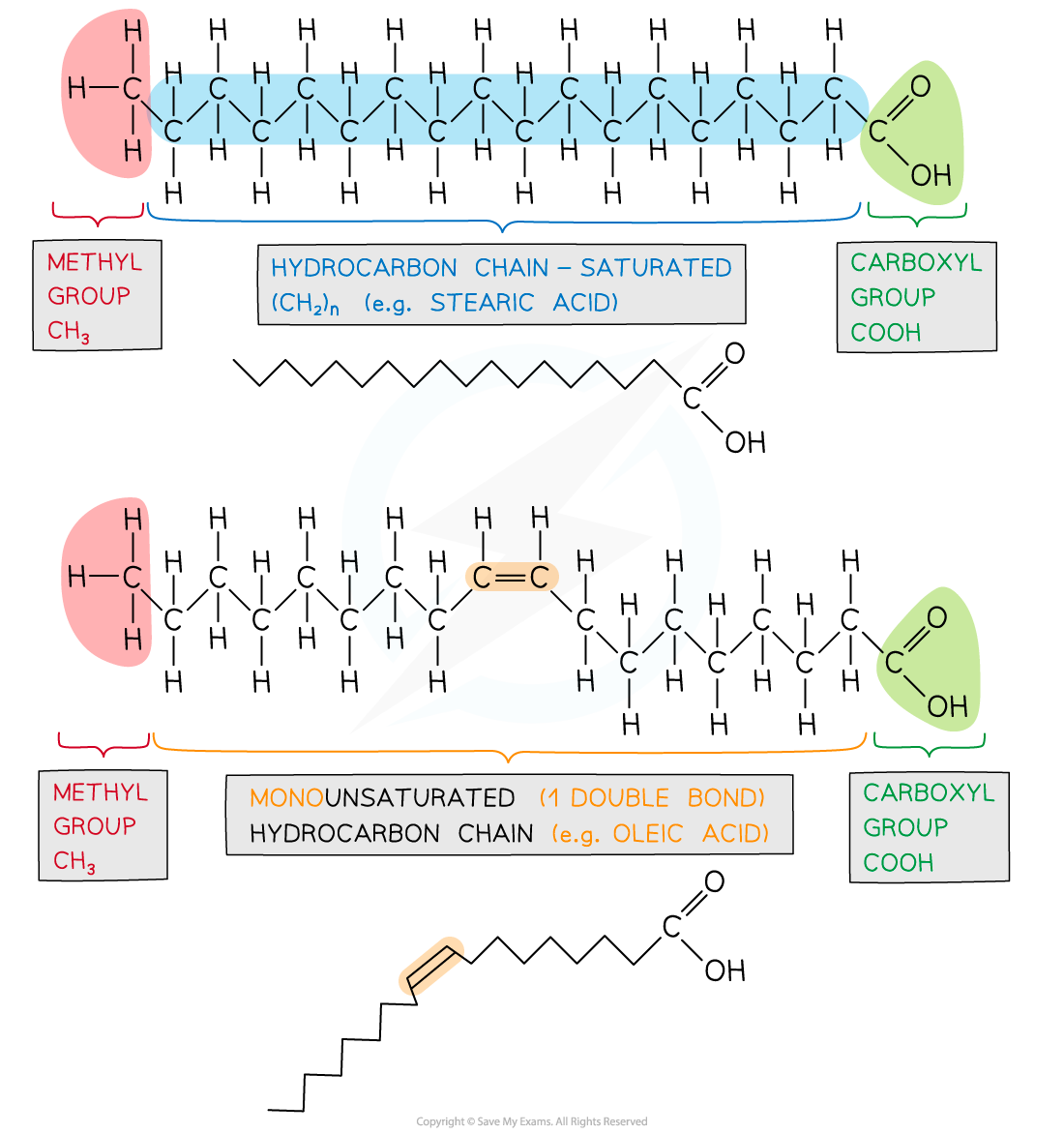
Fatty acids contain a methyl group at one end of a hydrocarbon chain (chains of hydrogens bonded to carbon atoms, typically 4 to 24 carbons long) and at the other is a carboxyl group
Fatty acids can vary in two ways:
Length of the hydrocarbon chain
The fatty acid may be saturated (mainly in animal fat) or unsaturated (mainly vegetable oils, although there are exceptions e.g. coconut and palm oil)
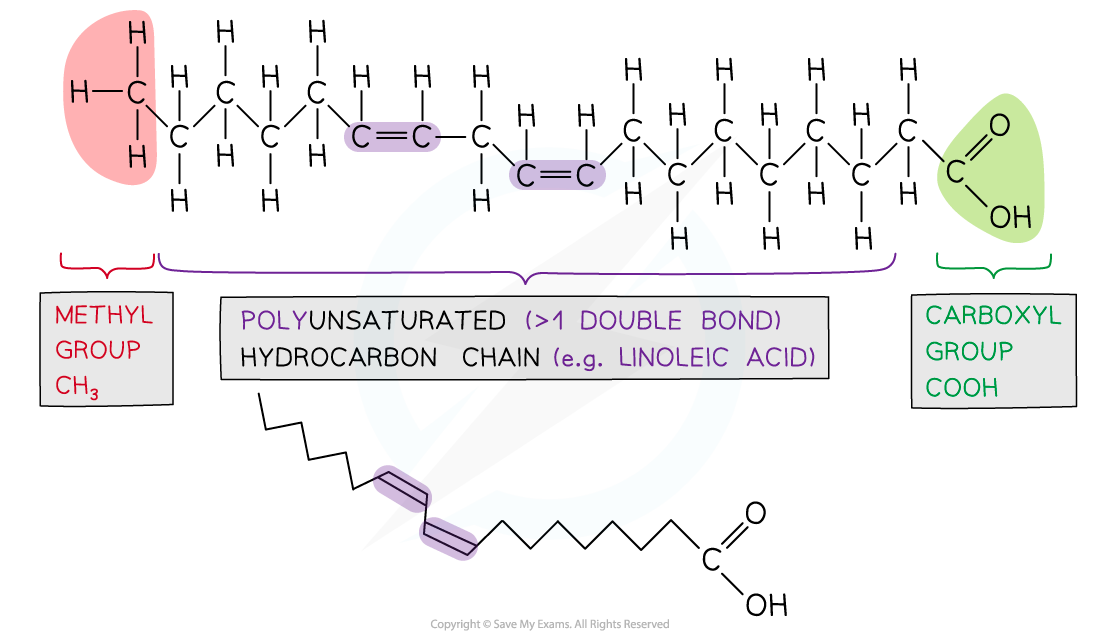
Unsaturated fatty acids can be mono or poly-unsaturated
If H atoms are on the same side of the double bond they are cis-fatty acids and are metabolised by enzymes
If H atoms are on opposite sides of the double bond they are trans-fatty acids and cannot form enzyme-substrate complexes, therefore, are not metabolised. They are linked with coronary heart disease
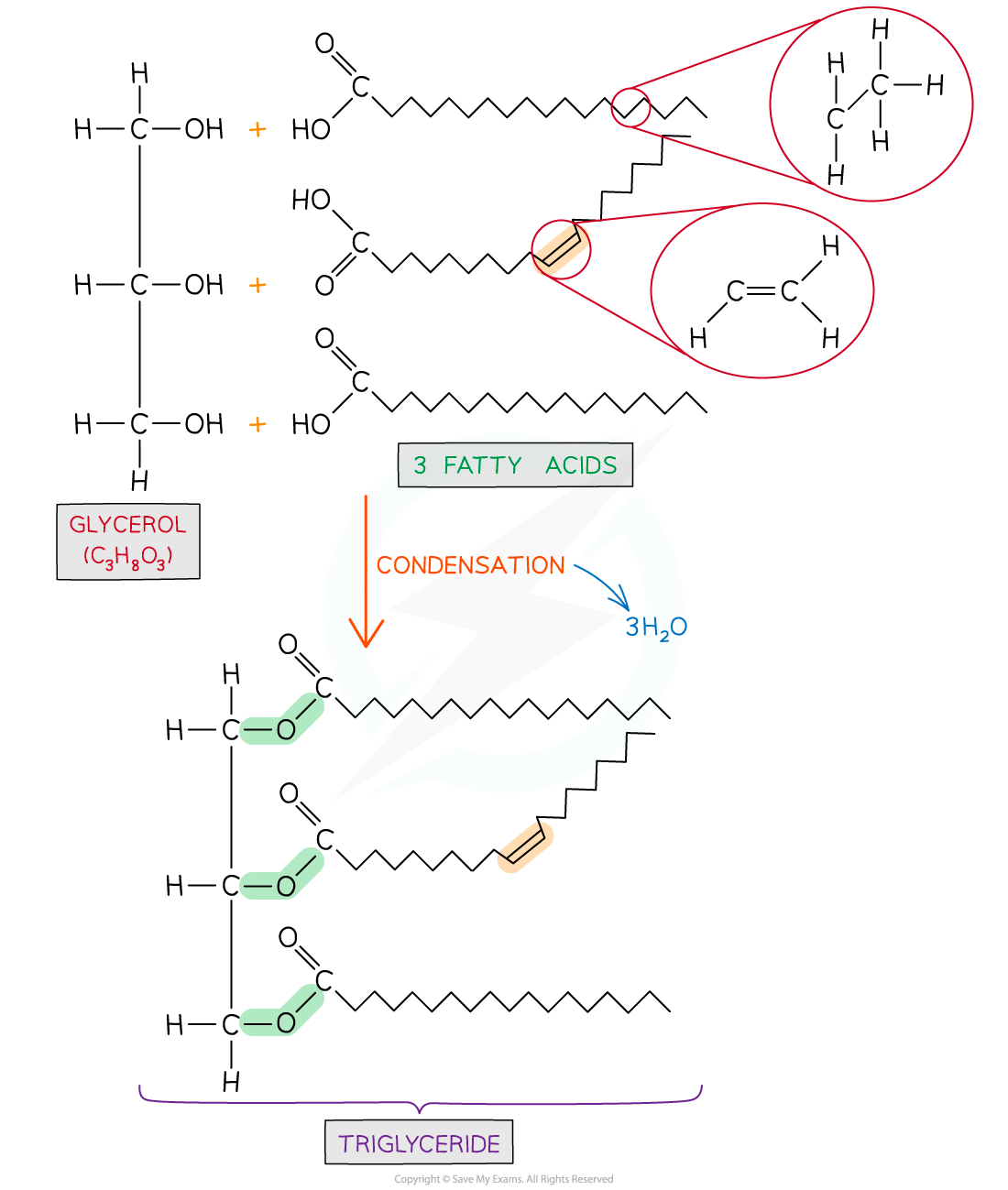
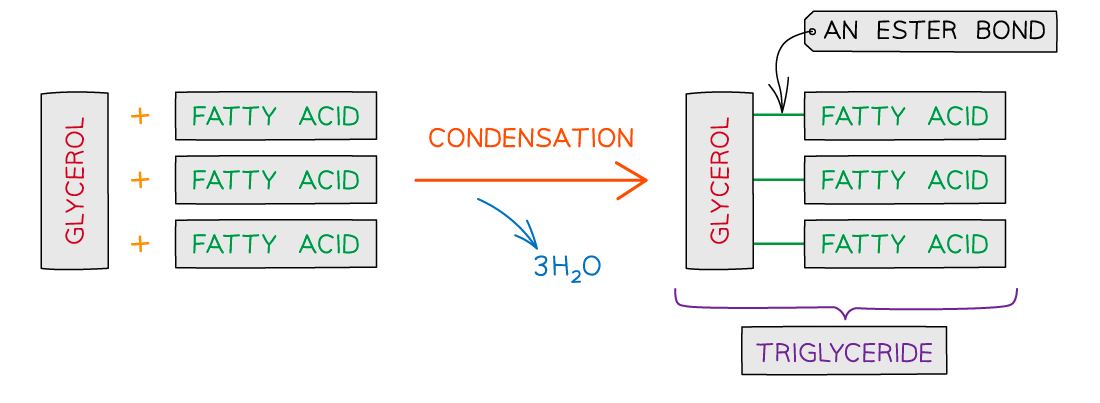
Triglycerides are formed by esterification
An ester bond forms when the hydroxyl group of the glycerol bonds with the carboxyl group of the fatty acid
For each ester bond formed a water molecule is released
Therefore, for one triglyceride to form three water molecules are released
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Ensure that you are familiar with the structure of a triglyceride and that you can recognise whether the fatty acids are saturated or unsaturated.
Triglycerides: structure & function
Energy storage
The long hydrocarbon chains contain many carbon-hydrogen bonds with little oxygen
So when triglycerides are oxidised during cellular respiration this causes these bonds to break releasing energy used to produce ATP
Triglycerides therefore store more energy per gram than carbohydrates and proteins (37kJ compared to 17kJ)
As triglycerides are hydrophobic they do not cause osmotic water uptake in cells so more can be stored
Plants store triglycerides, in the form of oils, in their seeds and fruits. If extracted from seeds and fruits these are generally liquid at room temperature due to the presence of double bonds which add kinks to the fatty acid chains altering their properties
Mammals store triglycerides as oil droplets in adipose tissue to help them survive when food is scarce (e.g. hibernating bears)
The oxidation of the carbon-hydrogen bonds releases large numbers of water molecules (metabolic water) during cellular respiration
Desert animals retain this water if there is no liquid water to drink
Bird and reptile embryos in their shells also use this water
Insulation
Triglycerides are part of the composition of the myelin sheath that surrounds nerve fibres
This provides insulation which increases the speed of transmission of nerve impulses
Triglycerides compose part of the adipose tissue layer below the skin which acts as insulation against heat loss (e.g. blubber of whales and sea lions)
Buoyancy
The low density of fat tissue increases the ability of animals to float more easily
Protection
The adipose tissue in mammals contains stored triglycerides and this tissue helps protect organs from the risk of damage
Examiner Tips and Tricks
It is common to be asked why triglycerides are energy reserves (they store more energy per gram due to their hydrocarbon chains).

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
