Biological Molecules: Key Terms (Cambridge (CIE) AS Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 9700
The two forms of glucose
The most well-known carbohydrate monomer is glucose
Glucose has the molecular formula C6H12O6
Glucose is the most common monosaccharide and is of central importance to most forms of life
There are different types of monosaccharide formed from molecules with varying numbers of carbon atom, for example:
Trioses (3C) e.g. glyceraldehyde
Pentoses (5C) e.g. ribose
Hexoses (6C) e.g. glucose
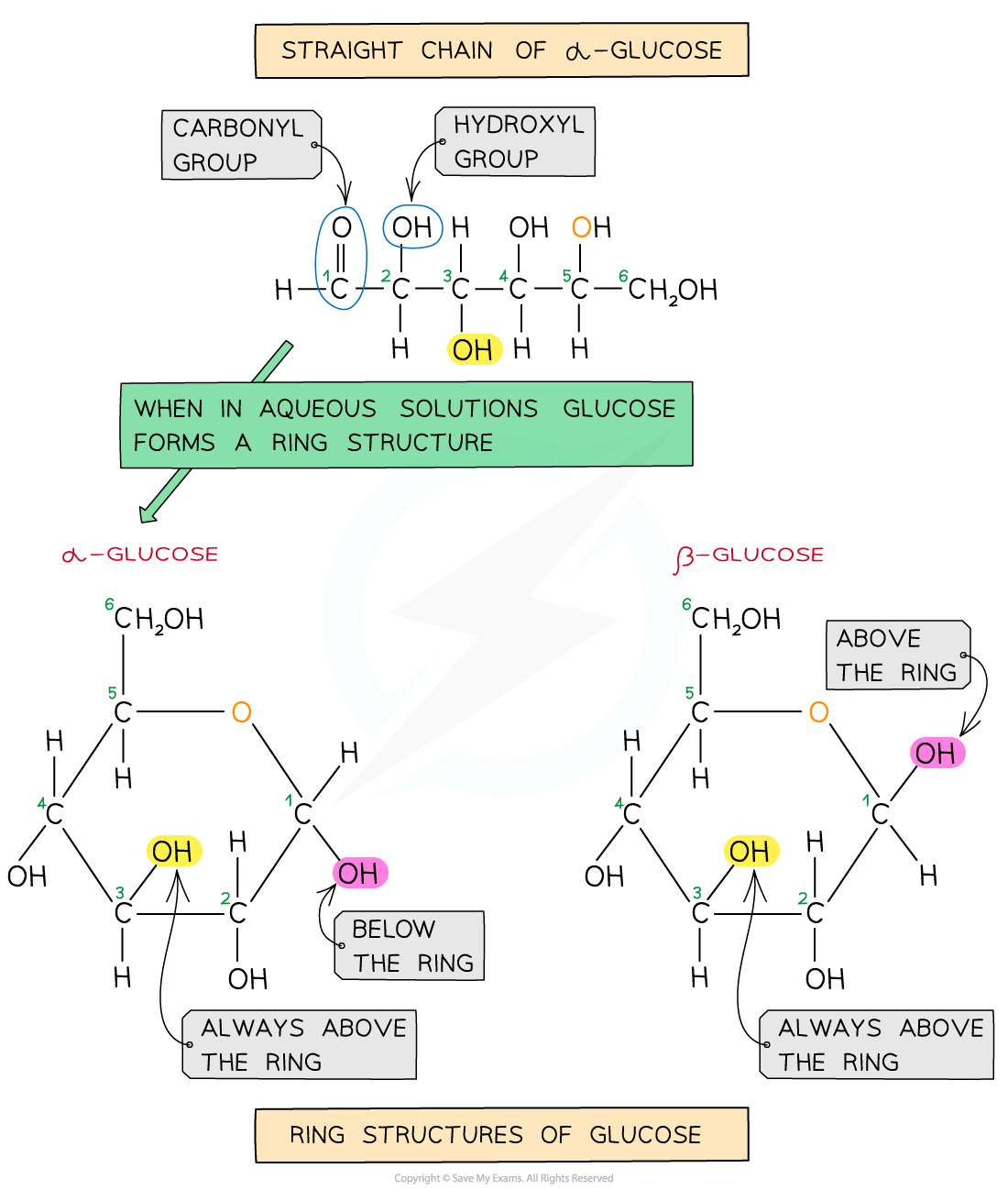
Glucose exists in two structurally different forms – alpha (α) glucose and beta (β) glucose and is therefore known as an isomer
This structural variety results in different functions between carbohydrates
Different polysaccharides are formed from the two isomers of glucose
Polysaccharide | Alpha Glucose | Beta Glucose |
|---|---|---|
Starch | ✓ | X |
Glycogen | ✓ | X |
Cellulose | X | ✓ |
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You must be able to recognise and draw the isomer rings of α and β glucose.
Biological molecules: key terms
The key molecules that are required to build structures that enable organisms to function are:
Carbohydrates
Proteins
Lipids
Nucleic Acids
Water
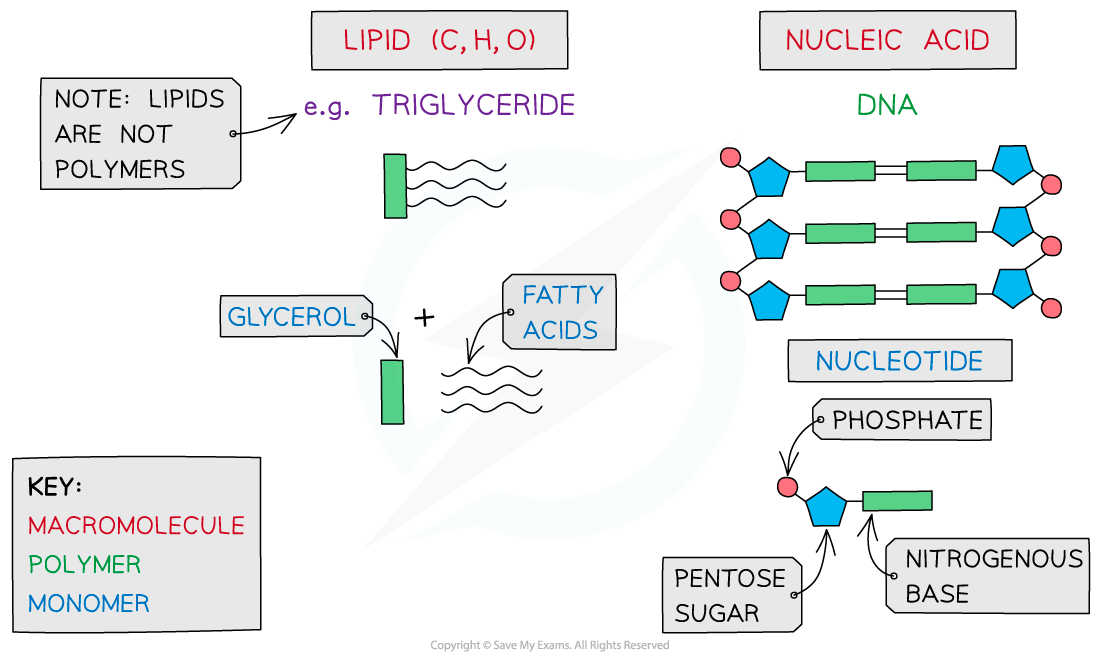
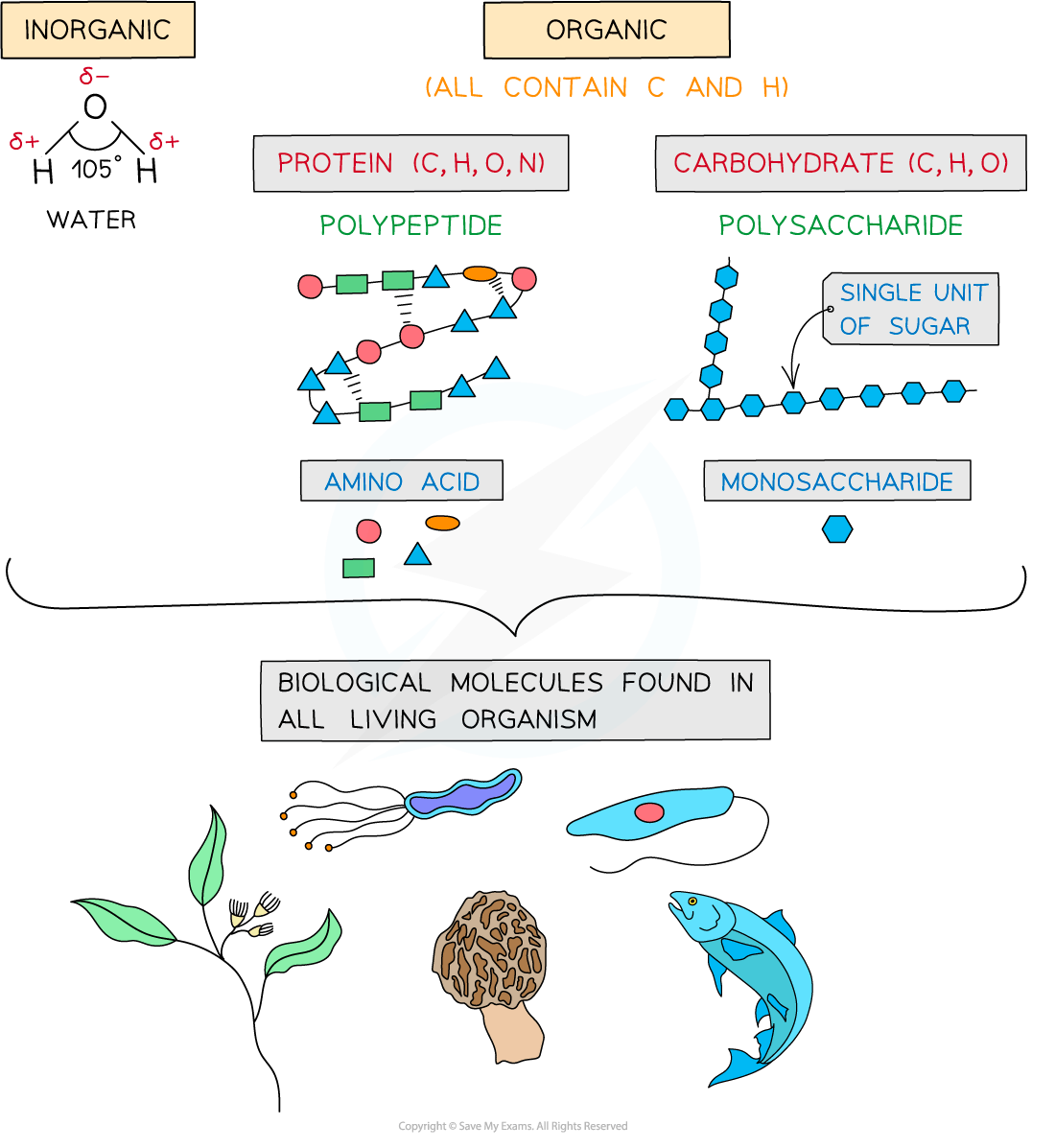
Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids contain the elements carbon (C) and hydrogen (H) making them organic compounds
Carbon atoms are key to the organic compounds because:
Each carbon atom can form four covalent bonds – this makes the compounds very stable (as covalent bonds are so strong they require a large input of energy to break them)
Carbon atoms can form covalent bonds with oxygen, nitrogen and sulfur
Carbon atoms can bond to form straight chains, branched chains or rings
Carbon compounds can form small single subunits called monomers, that bond with many repeating subunits to form large molecules called polymers, by a process called polymerisation
Macromolecules are very large molecules
That contain 1000 or more atoms therefore having a high molecular mass
Polymers can be macromolecules, however not all macromolecules are polymers as the subunits of polymers have to be the same repeating units
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are one of the main carbon-based compounds in living organisms
All molecules in this group contain C, H and O
As H and O atoms are always present in the ratio of 2:1 (e.g. water H2O, which is where ‘hydrate’ comes from) they can be represented by the formula Cx (H2O)y
The three types of carbohydrates are monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides
Types of carbohydrate table
| Monosaccharide | Disaccharide | Polysaccharide |
|---|---|---|---|
Definition | A single sugar monomer, all of which are reducing sugars | A sugar formed from two monosaccharides joined by a glycosidic bond in a condensation reaction | A polymer formed by many monosaccharides joined by a glycosidic bond in a condensation reaction |
Examples | Glyceraldehyde (3C) Ribose (5C) Glucose (6C) | Maltose (α glucose + α glucose) Sucrose (α glucose + fructose) Lactose (α glucose + β galactose) | Cellulose (monomer is β glucose) Starch (monomer is α glucose) Glycogen (monomer is α glucose) |
Function | Energy in respiration Building blocks of polymers | Sugar in germinating seeds (maltose) Mammal milk sugar (lactose) Sugar stored in cane sugar (sucrose) | Energy storage (plants - starch; animals - glycogen) Structural cell wall (cellulose) |
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When discussing monomers and polymers, give the definition but also name specific examples e.g. nucleic acids – the monomer is a nucleotide.
You need to be able to define the terms monomer, polymer, macromolecule, monosaccharide, disaccharide and polysaccharide.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?