Magnification Calculations (Cambridge (CIE) AS Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 9700
Magnification calculations
Magnification is the number of times that a real-life specimen has been enlarged to give a larger view/image
E.g. a magnification of x100 means that a specimen has been enlarged 100 times to give the image shown
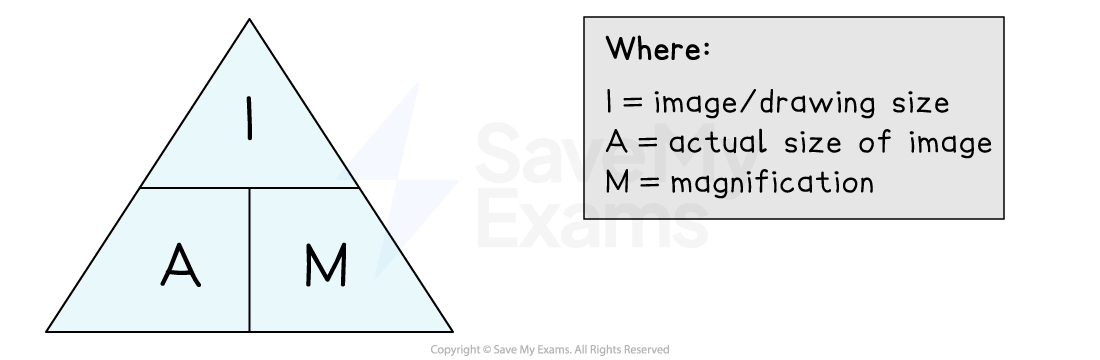
The magnification (M) of an object can be calculated if both the size of the image (I), and the actual size of the specimen (A), is known
When carrying out calculations relating to magnification, the following steps should be followed:
Rearrange the equation
A = I ÷ M
M = I ÷ A
I = A x M
Read and measure the relevant values from the question stem and/or any images provided
Convert any units
Substitute numbers into the rearranged equation
Consider whether this value makes sense in the context provided
Converting units during magnification calculations
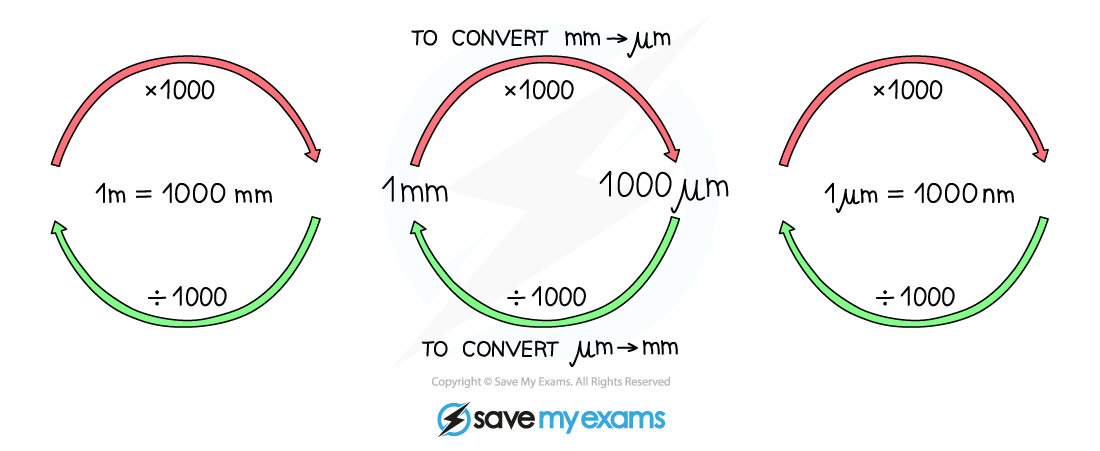
Cellular structures are usually measured in either micrometres (μm) or nanometres (nm), while any measurements carried out in an exam with a ruler are likely to be in millimetres (mm)
There are 1000 µm in a mm
There are 1000 nm in a µm
When doing calculations all measurements must be expressed using the same units
It is best to use the smallest unit of measurement shown in the question
Note that magnification does not have units
To convert units, multiply or divide depending on whether the units are increasing or decreasing
Multiply when converting from a larger unit to a smaller unit
Divide when converting a smaller unit to a larger unit
Worked Example
A starch grain inside a plant cell was viewed under a microscope at a magnification of x850. The image of the starch grain captured using the microscope is shown below.
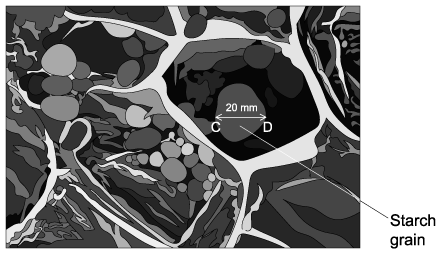
Calculate the actual diameter of the starch grain between points C-D in the image.
Give your answer in μm.
Answer:
Step 1: Rearrange the equation
We have been asked to calculate actual size, A, so the new equation should be:
Actual size = image size ÷ magnification
Step 2: Read and measure relevant values
We need to know the image size and the magnification
The image size has been given in the image as 20 mm
The magnification has been included in the question stem and is x850
Step 3: Convert any units
The actual diameter of a structure inside a cell would normally be measured in μm
The image size has been given in mm, so we need to convert this to μm
1 mm = 1000 μm, so we multiply mm by 1000 to give the value in μm
20 x 1000 = 20 000 μm
Step 4: Substitute number into the equation
Actual size = 20 000 ÷ 850
Actual size = 23.53 μm
Step 5: Consider whether the value makes sense
Plant cells measure between 10-100 μm, and the starch grain takes up a large proportion of the cell in the image
A diameter of around 23 μm could therefore be correct for this starch grain
If we had forgotten to convert the units and come up with a value of 0.024 μm, then this step would show us that this is probably too small and that we must have therefore made a mistake somewhere
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Magnification calculations will usually involve measuring images on a page, so you must have a ruler with you in an exam!
Be aware that the unit conversions given above only work if the initial measurement is taken in mm, not in cm. Any measurements taken in cm will need to be converted into mm before multiplying by 1000 to give μm.
Some exam questions may expect you to use a scale bar to calculate the magnification of an image. Remember that you can use a scale bar to find both actual size (written on the scale bar) and image size (the measured length of the bar), so these values can be used to calculate magnification using the equation M = I ÷ A

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
