Interphase (AQA AS Biology) : Revision Note
The cell cycle
Mitosis is part of a precisely controlled process known as the cell cycle
The cell cycle is the regulated sequence of events that occurs between one cell division and the next
The cell cycle has three phases:
interphase
nuclear division (mitosis)
cell division (cytokinesis)
The transition from one phase to another is triggered by chemical signals called cyclins
The length of the cell cycle is variable depending on environmental conditions, the cell type and the organism
E.g. onion root tip cells divide approximately once every 20 hours and human intestine epithelial cells divide approximately once every 10 hours
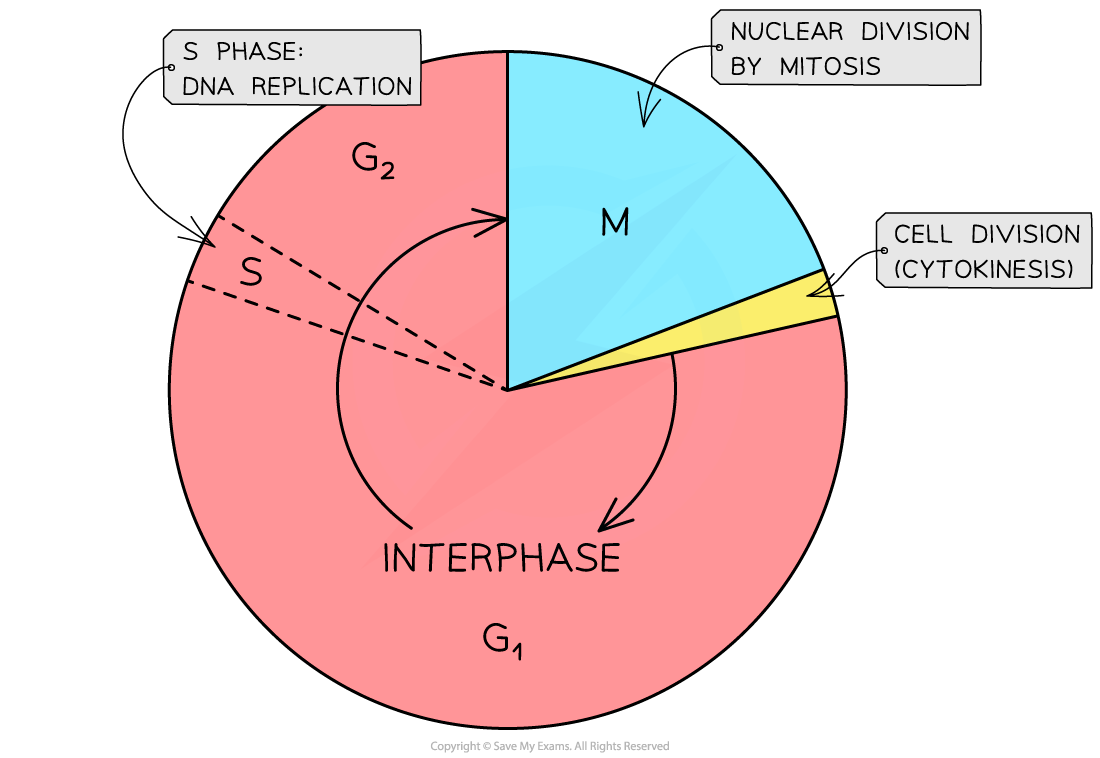
Interphase
During interphase the cell increases in size and carries out normal cellular functions, e.g. synthesising proteins and replicating DNA ready for mitosis
Interphase consists of three phases:
G1:
G stands for gap
Cells make enzymes and other proteins required for growth
At some point during G1 a signal is received, telling the cell to divide again; at this point the cell will progress into S phase
S phase:
S stands for synthesis (of DNA)
The DNA in the nucleus replicates, after which each chromosome consists of two identical sister chromatids
S phase is relatively short
G2 phase
The cell continues to grow and the new DNA is checked so that any errors can be repaired
Other preparations for cell division are made, e.g. the production of tubulin protein, which is used to make microtubules for the mitotic spindle
Stage of interphase | Main event(s) |
|---|---|
G1 | Cell grows and receives a signal to divide |
S | Synthesis of new DNA |
G2 | Further cell growth |
Nuclear division (e.g. mitosis)
Nuclear division follows interphase
In normal body cells this will be mitosis, while in the production of gametes this will be meiosis
Cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm follows nuclear division
Once the nucleus has divided into two genetically identical nuclei, the whole cell divides and one nucleus moves into each cell to create two genetically identical daughter cells
In animal cells cytokinesis involves constriction of the cytoplasm between the two nuclei
In plant cells a new cell wall is formed

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?


