Biological Molecules: Key Terms (AQA AS Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 7401
Did this video help you?
Biological molecules: key terms
There is a great variety of life within and between organisms, but the biochemical basis of life is similar for all living things
The key molecules that are required to build structures that enable organisms to function are:
carbohydrates
proteins
lipids
nucleic Acids
water
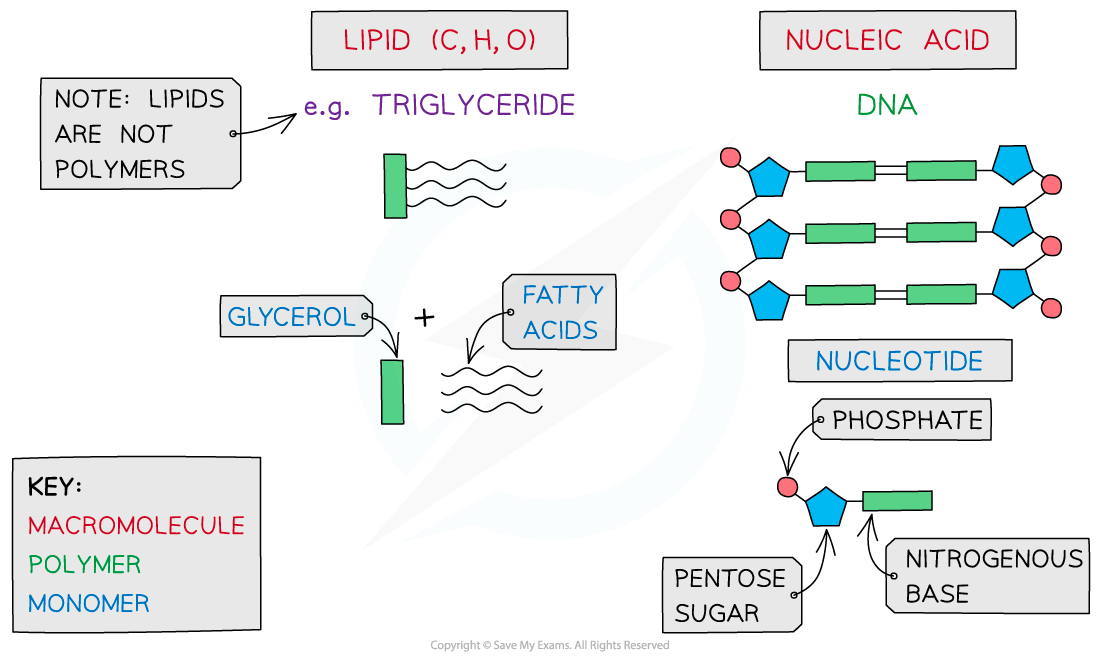
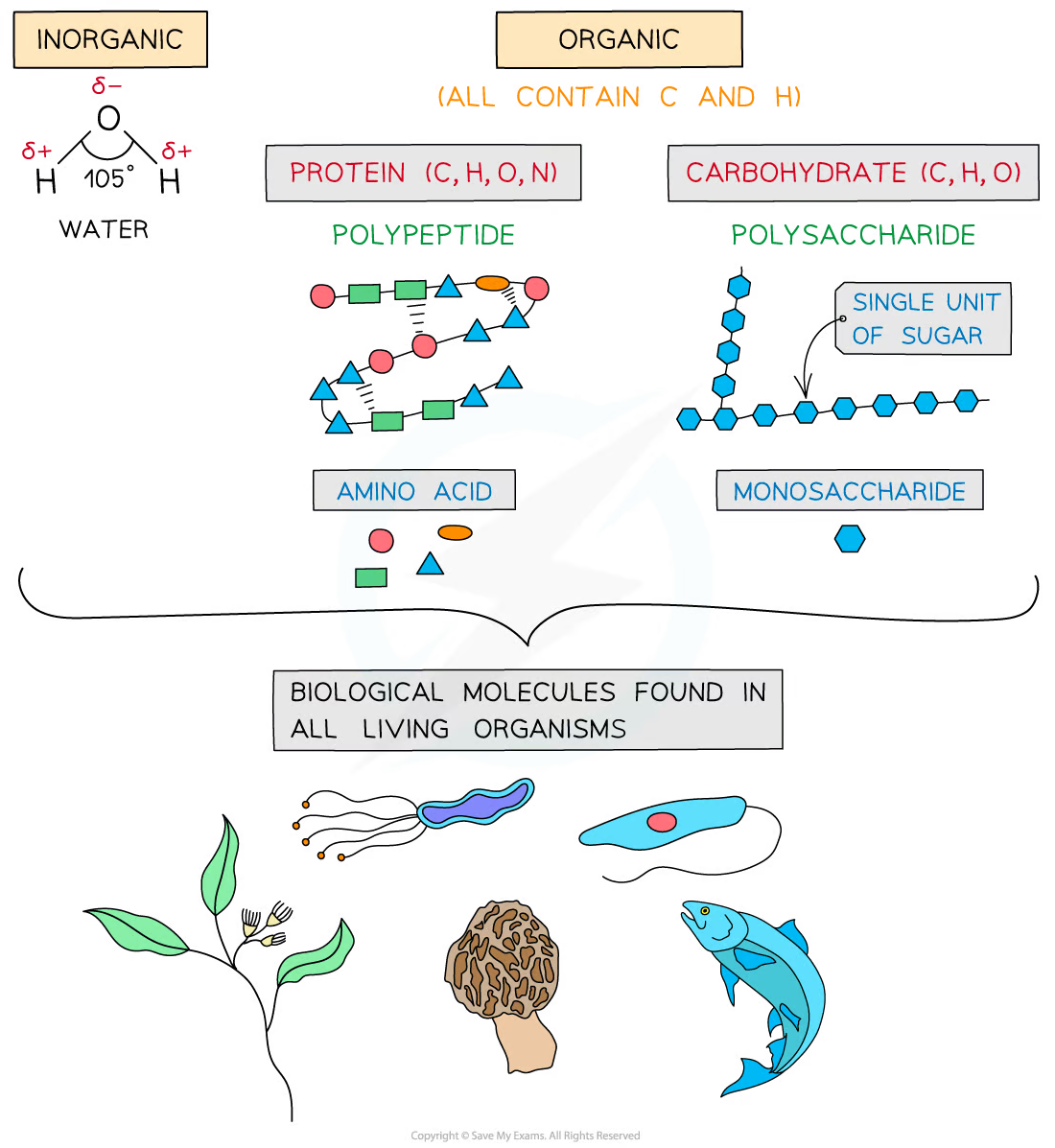
Monomers are the smaller units from which larger molecules are made
Polymers are molecules made from a large number of monomers joined together in a chain during a process called polymerisation
Organic compounds include carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids as they all contain the elements carbon (C) and hydrogen (H)
Macromolecules are very large molecules
They contain 1000 or more atoms, therefore having a high molecular mass
Polymers can be macromolecules, however, not all macromolecules are polymers, as the subunits of polymers have to be the same repeating units
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When discussing monomers and polymers, give the definition but also name specific examples, e.g. a nucleic acid is a polymer made of nucleotide monomers.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?