Two-Way Tables & Relative Frequencies (College Board AP® Statistics): Study Guide
Two-way tables
What is a two-way table?
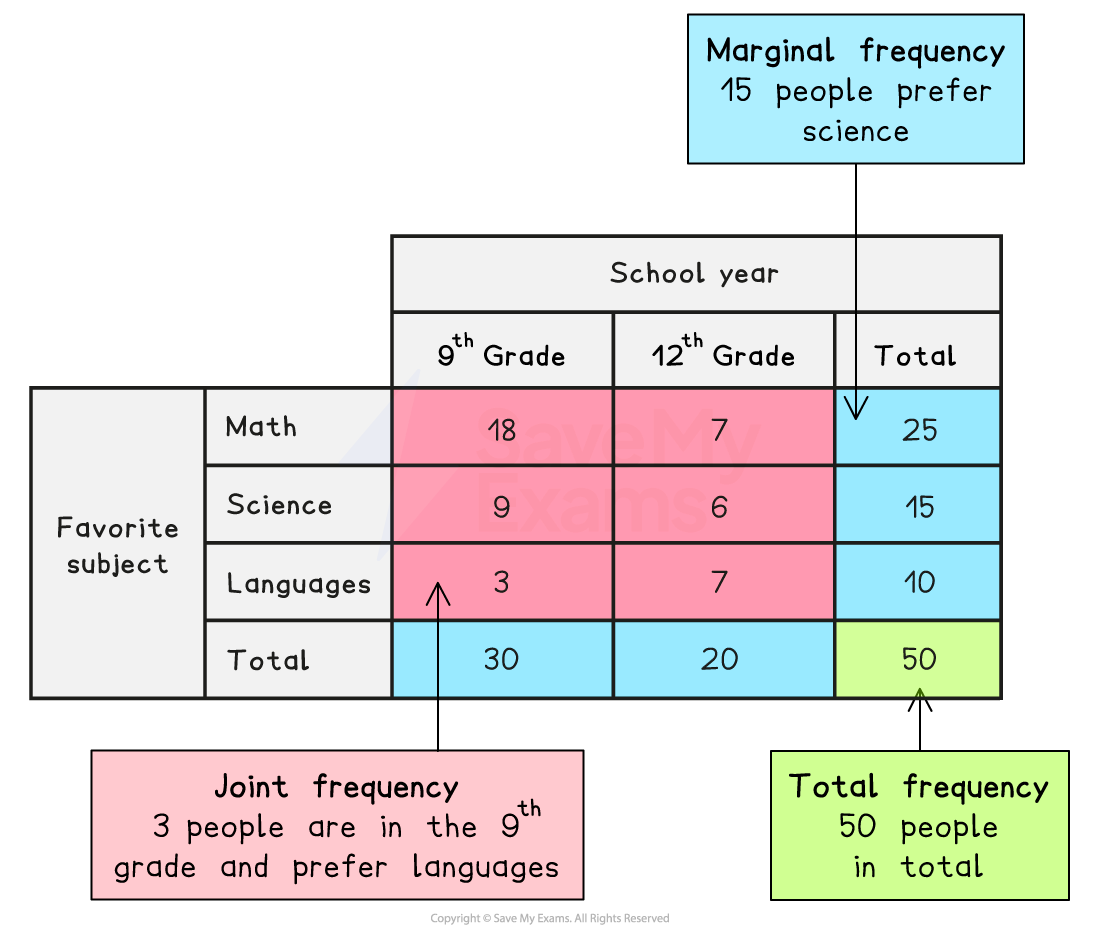
A two-way table is used when there are two categorical variables
e.g. the school year and favorite subject of a random sample of students
The rows represent one variable and the columns represent the other variable
The number in a cell of a two-way table represents the frequency of the data, which satisfies the relevant values of both variables
This is called the cell frequency or the joint frequency
The totals for each row and each column are usually included in a two-way table
These are called marginal frequencies
Joint, marginal & conditional relative frequencies
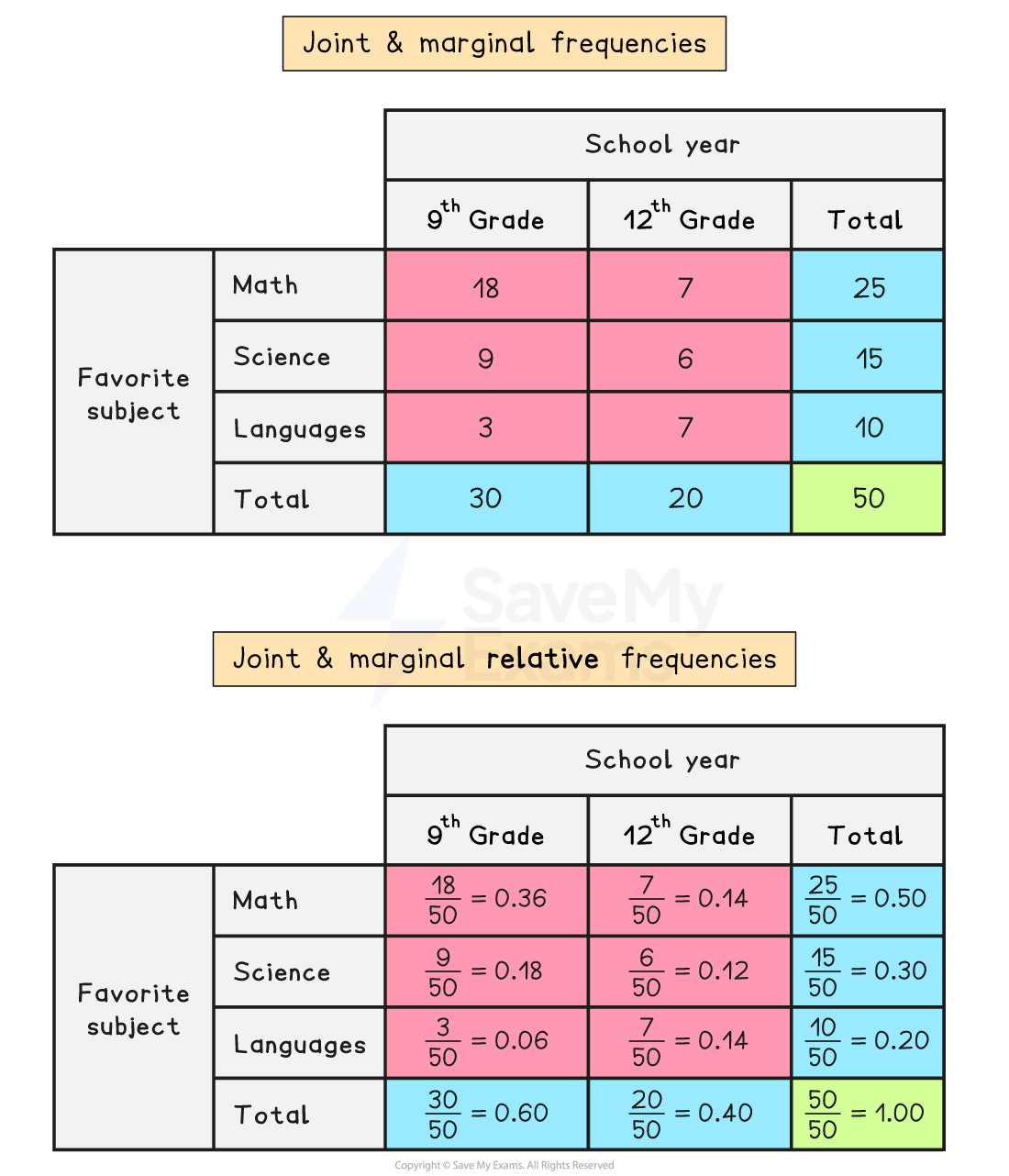
What are joint relative frequencies?
The joint relative frequencies are the proportions of the total that belong to each cell
To calculate a joint relative frequency for a cell
divide the joint (cell) frequency by the total frequency
e.g. divide the number of students in the 9th grade who say math is their favorite subject by the total number of students
If a two-way table is used to display joint relative frequencies then the total for the table is 1
What are marginal relative frequencies?
The marginal relative frequencies are the proportions of the total that belong to each row or column
To calculate a marginal relative frequency for a row or column
divide the marginal frequency by the total frequency
e.g. divide the number of students in the 9th grade by the total number of students
If a two-way table is used to display joint relative frequencies then each row or column will add up to the corresponding marginal relative frequency
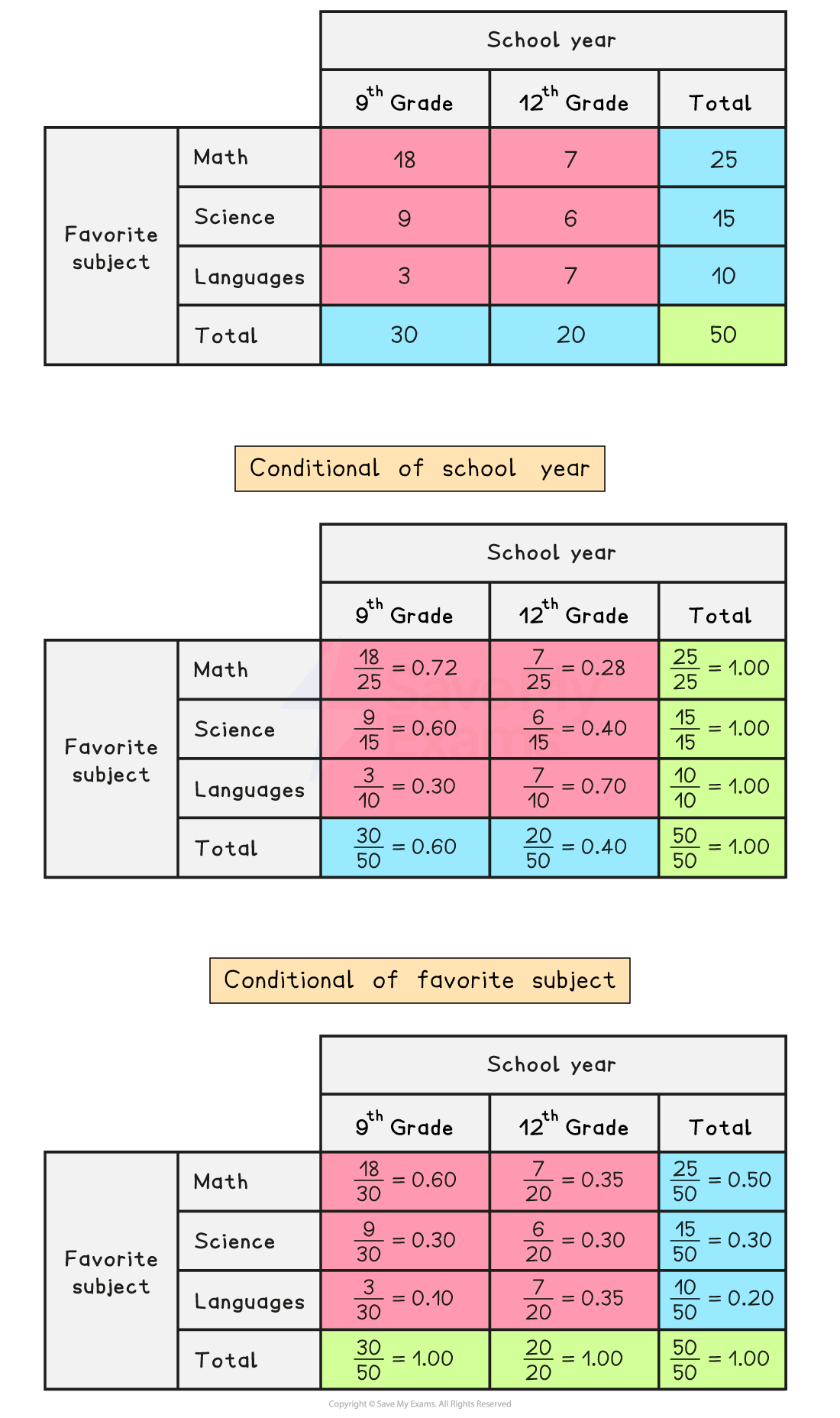
What are conditional relative frequencies?
A conditional relative frequency is the proportion of the total of a row or column that belongs to that cell
e.g. the proportion of students in the 9th grade who say math is their favorite subject is a conditional relative frequency
To calculate a conditional relative frequency
divide the joint (cell) frequency by the relevant marginal frequency
e.g. divide the number of students in the 9th grade who say math is their favorite subject by the total number of students in the 9th grade
If a two-way table is used to display conditional relative frequencies which are conditional of the row variable
then the conditional relative frequencies in each row will add up to 1
If a two-way table is used to display conditional relative frequencies which are conditional of the column variable
then the conditional relative frequencies in each column will add up to 1

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?