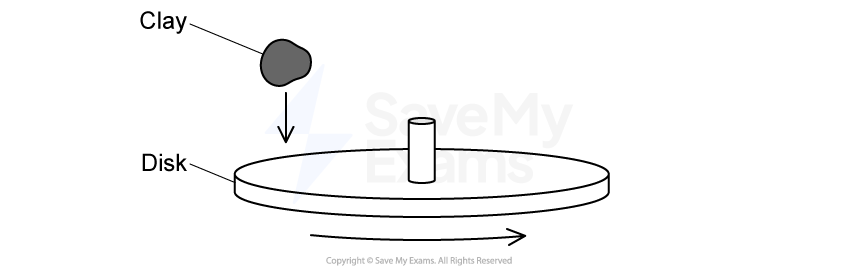
A small ball of clay is dropped from rest onto a large rotating disk, as shown in the figure. Following the collision, the clay sticks to the disk.
How does the total angular momentum and kinetic energy of the wheel-clay system change after the collision?
Angular Momentum | Kinetic Energy | |
|---|---|---|
A | Increases | Decreases |
B | Increases | Remains Constant |
C | Remains Constant | Decreases |
D | Remains Constant | Remains Constant |
Did this page help you?












