Elastic Potential Energy (College Board AP® Physics 1: Algebra-Based): Study Guide
Elastic potential energy
The potential energy of common physical systems can be described using the physical properties of that system
Elastic potential energy is defined as:
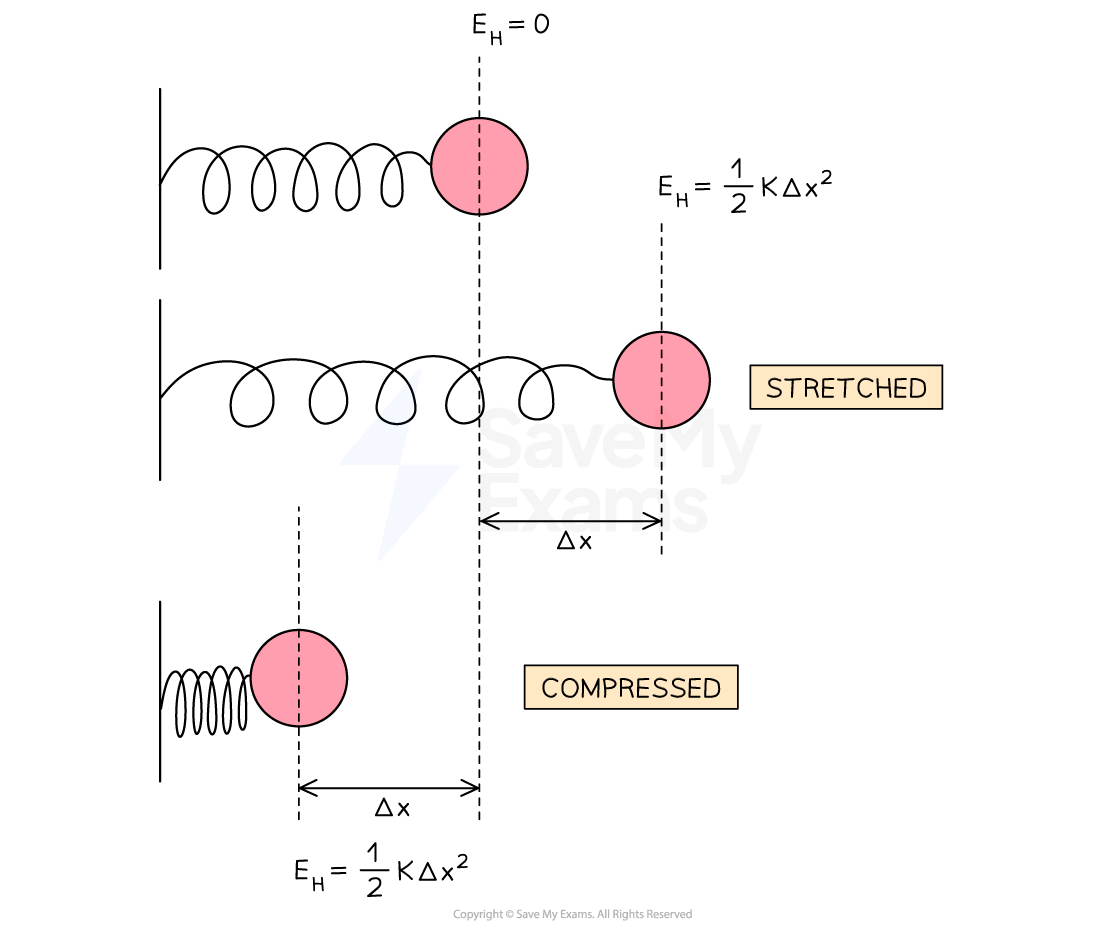
The energy stored within a material (e.g. a spring) when it is stretched or compressed
Therefore, for a material obeying Hooke’s Law, the elastic potential energy of an ideal spring can be calculated using:
Where:
= elastic potential energy, measured in
= spring constant, measured in
= distance the spring has been stretched or compressed from it's equilibrium length, measured in
Elastic potential energy is a scalar quantity with magnitude only
It is very dangerous if a wire under large stress suddenly breaks because the elastic potential energy of the strained wire is converted into kinetic energy
This equation shows
The greater the extension of a wire
the greater the speed
it will have when it breaks
Worked Example
Cars are built with shock absorbers to make a ride more comfortable. Shock absorbers are strong springs that absorb energy when the car goes over a bump.
A shock absorber spring has a spring constant of is fixed next to a wheel and compressed a distance of
. Which of the following is the correct value for the elastic potential energy of the spring?
A:
B:
C:
D:
The correct answer is B
Step 1: List the known values
Spring constant,
Compression,
Step 2: Substitute the values into the elastic potential energy equation

You've read 0 of your 5 free study guides this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?