Newton’s First Law in Rotational Form (College Board AP® Physics 1: Algebra-Based): Study Guide
Newton’s first law in rotational form
The rotational analog of Newton’s first law states:
If the net torque exerted on a system is zero, the angular velocity of that system will remain constant
A constant angular velocity could also be an angular velocity of zero, i.e. when the system is not rotating
If the net torque acting on a system is zero, it is said to be in rotational equilibrium
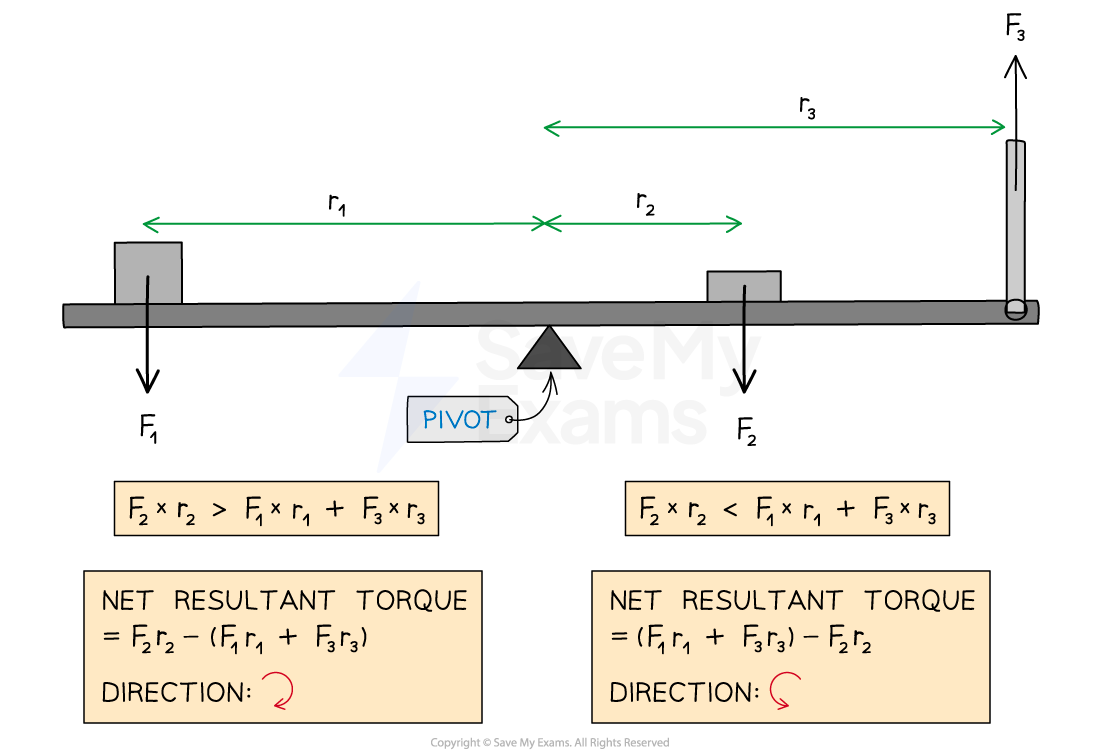
Unbalanced torque
According to Newton’s second law, if the torques exerted on a rigid system are not balanced, the system’s angular velocity must be changing
Therefore, a net torque produces an angular acceleration
The direction of this angular acceleration depends on the direction of the net torque
Beam with an unbalanced torque
Worked Example
Three forces act on a wheel which is free to rotate about its center O, as shown in the diagram.
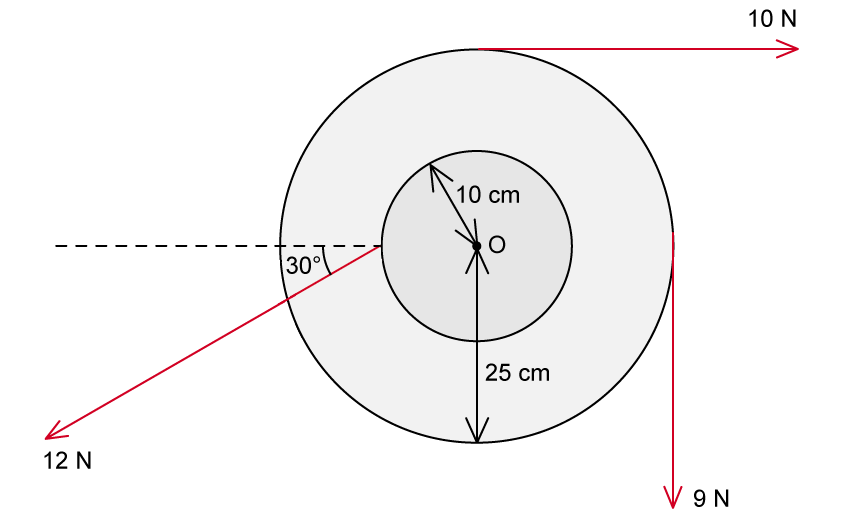
Calculate the net torque about O and state whether the angular acceleration that is produced is clockwise or counterclockwise.
Answer:
Step 1: Analyze the scenario
The magnitude of the torque about the axis of rotation O is given by
The 9 N force and the 10N force are both perpendicular to the radius and produce a torque in the clockwise direction
The perpendicular component of the 12 N force produces a torque in the counterclockwise direction
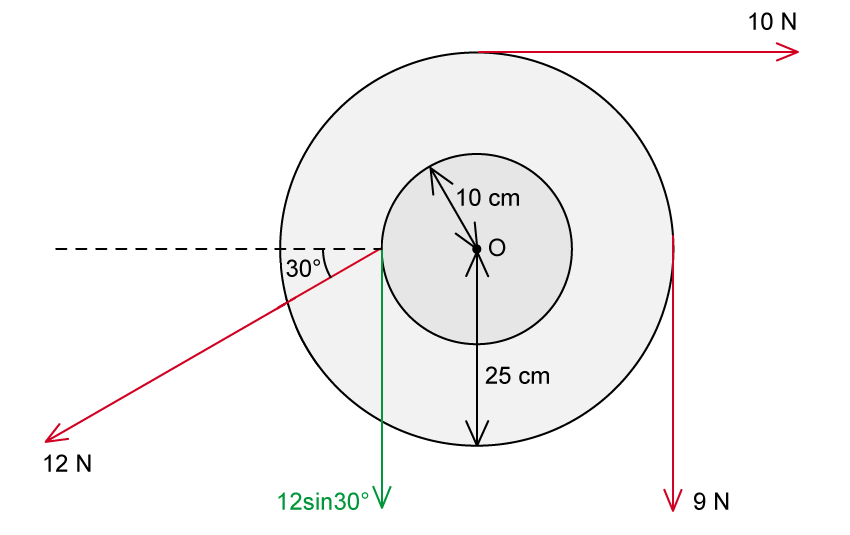
Step 2: Calculate the total clockwise torque
The torque due to the 10 N force is
The torque due to the 9 N force is
Therefore, the total clockwise torque = 2.5 + 2.25 = 4.75 N m
Step 3: Calculate the total counterclockwise torque
The torque due to the 12 N force is:
Therefore, the total counterclockwise torque = 0.6 N m
Step 4: Determine the net torque and direction of angular acceleration
Net torque = total clockwise torque − total counterclockwise torque
Net torque = , clockwise
The net torque and angular acceleration both act in the clockwise direction
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In the AP Physics 1 exam, you will not be expected to analyze rotation in multiple planes. When analyzing the torques exerted on a system, you only need to be able to consider whether they produce clockwise or counterclockwise motion

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?