Graphical Representation of SHM (College Board AP® Physics 1: Algebra-Based): Study Guide
Graphical representation of SHM
Displacement, velocity and acceleration all vary throughout each cycle in SHM
This can be shown graphically
The graphs of each quantity look different, depending on the start position of the system in SHM:
The system may start at the amplitude position (i.e. maximum displacement)
The system may start at the equilibrium position
Quantities in SHM starting from maximum displacement
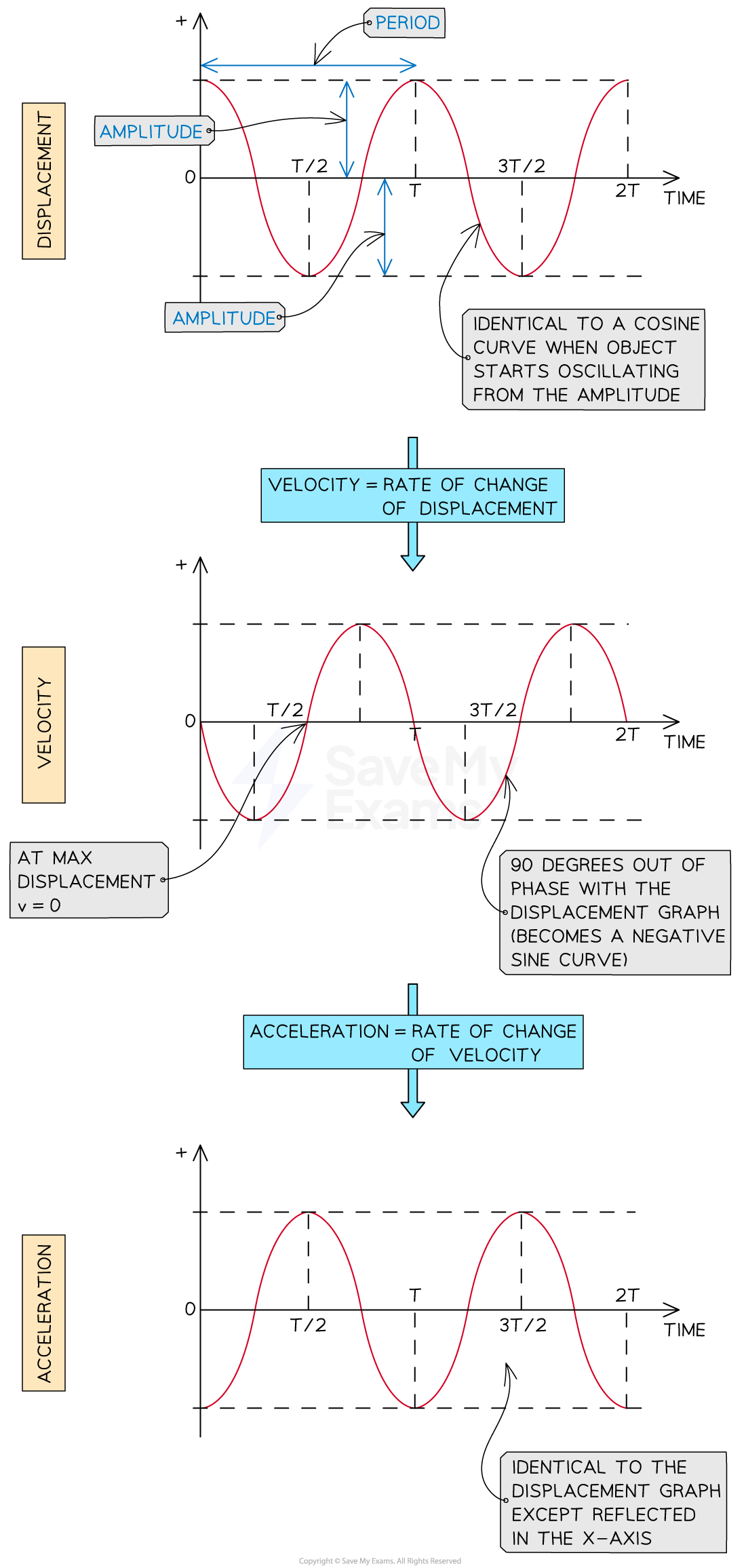
In the above graphs starting from the positive amplitude position:
Displacement begins with a maximum value and then oscillates
Velocity begins at zero and then oscillates
Acceleration begins with a minimum value and then oscillates
All oscillate with the same frequency
Quantities in SHM starting from equilibrium
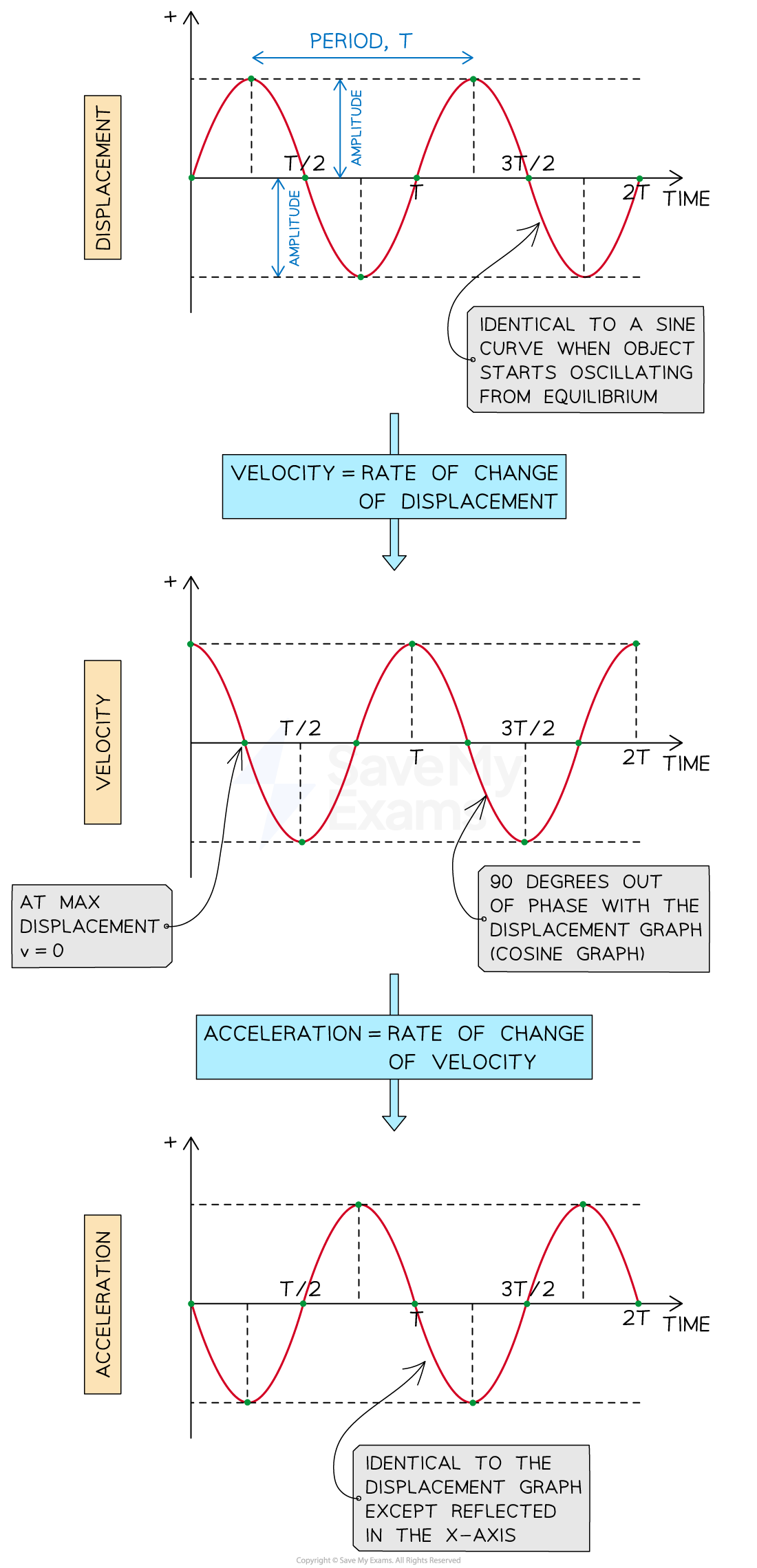
In the above graphs starting from the equilibrium:
Displacement begins at zero and then oscillates
Velocity begins at a maximum value and then oscillates
Acceleration begins at zero and then oscillates
All oscillate with the same frequency
Translating between graphs
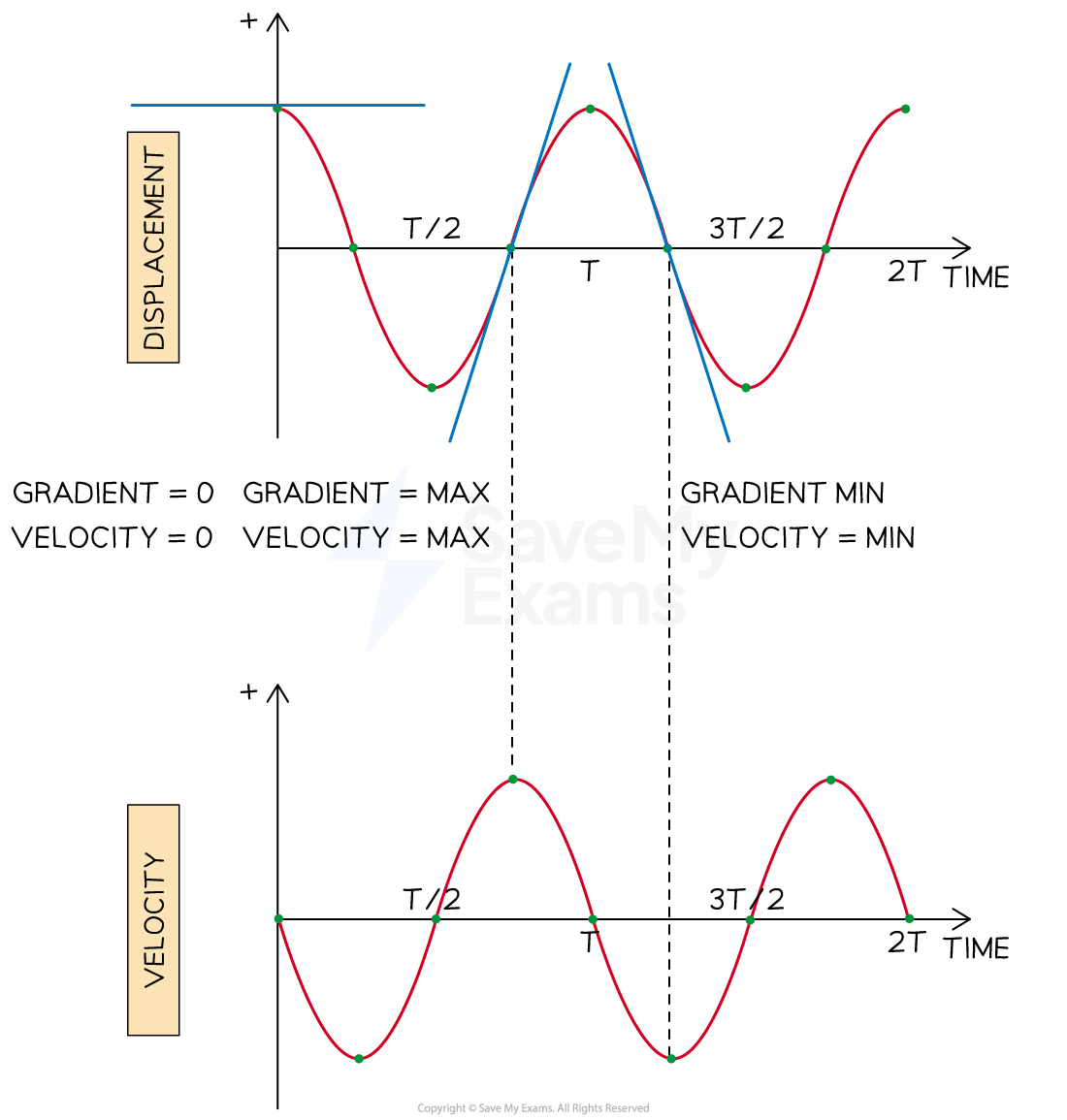
Recall that velocity is the rate of change of displacement
On a position-time graph, the rate of change of displacement is represented by the gradient
The velocity-time graph for an object in SHM can also be produced by plotting the gradient of a displacement-time graph against time
Just plotting the zeroes, maxima and minima gives enough information to plot the graph
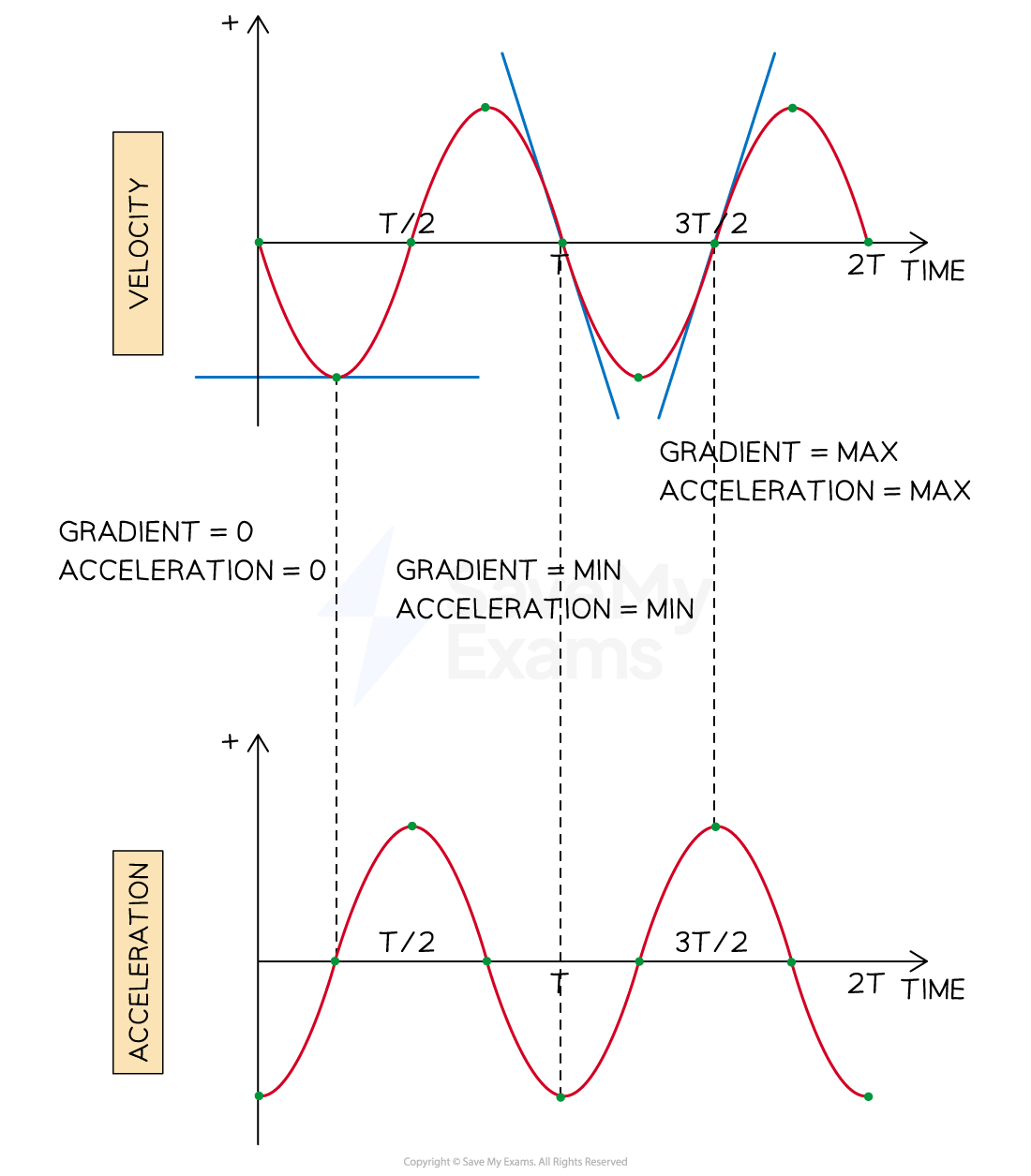
The same can be done to a velocity-time graph to produce an acceleration graph
Gradient of a position graph
Gradient of a velocity graph
Worked Example
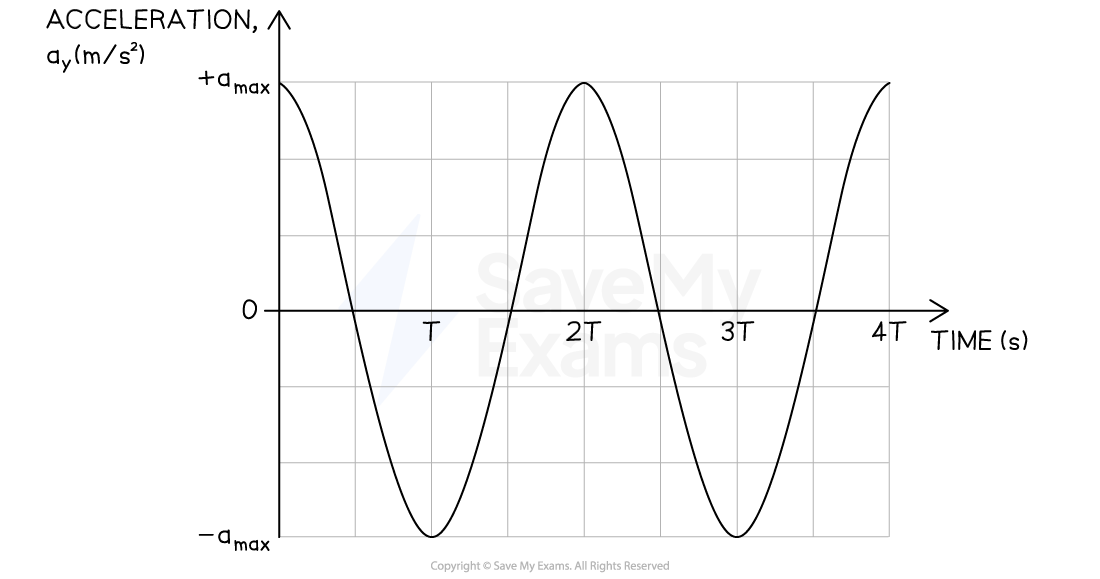
A system features a vertical spring of spring constant . An object of mass
is suspended from the spring and oscillates in simple harmonic motion with amplitude
.
Describe the starting position of the object if upwards is defined as the positive direction in the system. Justify your answer.
Answer:
Step 1: Analyze the scenario
From the acceleration graph, the system begins with acceleration at a maximum
Step 2: Apply the specific conditions
The system is in SHM
Recall that the condition for SHM is that acceleration is proportional to displacement but in the opposite direction
Upwards is the positive direction, so displacement below equilibrium will be negative and displacement above will be positive
Step 3: Describe the starting position
The object will be a distance
below the equilibrium position
Step 4: Justify the answer
If initial acceleration is at its greatest magnitude and positive, initial displacement will be at its greatest magnitude but negative
Displacement will be at a minimum
Negative displacement is below equilibrium position

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?