Uniform Circular Motion (College Board AP® Physics 1: Algebra-Based): Study Guide
Period and frequency of uniform circular motion
An object traveling in a circular path at a constant linear speed is traveling in uniform circular motion
The revolution of an object traveling in a circular path at a constant linear speed can be described using period and frequency
The time to complete one full circular path, one full rotation, or a full cycle of oscillatory motion is defined as period,
The rate at which an object is completing revolutions is defined as frequency,
The equation linking period and frequency is:
Where:
= period, measured in
= frequency, measured in
For an object traveling at a constant linear speed,
, in a circular path, the period is given by the equation
Where:
= period, measured in
= radius, measured in
= object's linear speed, measured in
The linear speed is tangential to the circle of motion
Linear speed always acts at right angles to the radius of the circle
Linear speed and radius in uniform circular motion
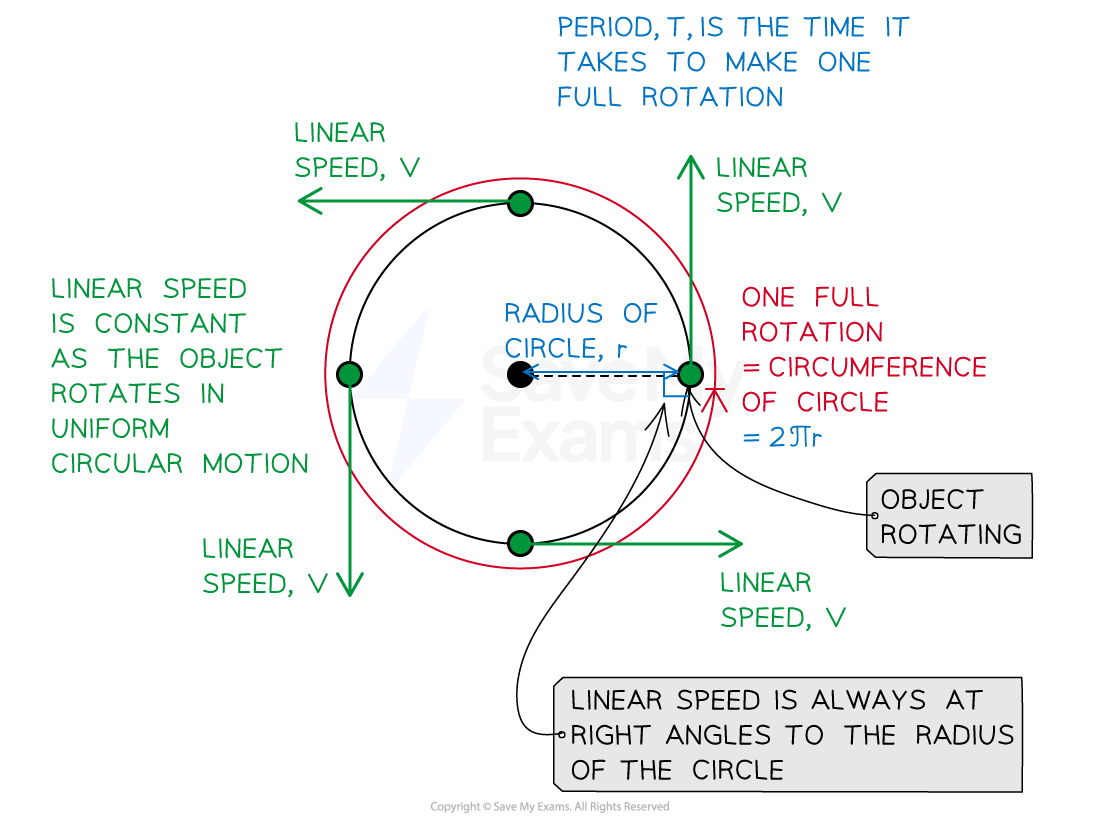
Derived equation
For an object traveling at a constant linear speed
in a circular path, the period is given by the equation
Derivation:
Step 1: Identify the fundamental principle
The equation linking period and frequency is given by
Where:
= period, measured in
= frequency, measured in
Step 2: Apply the specific conditions
The frequency of an oscillation dictates the number of oscillations in a certain time period
The equation linking period and frequency means there is one oscillation in period
In circular motion, one oscillation covers the distance of the circumference of the circle
The circumference of a circle of radius,
, is given by the equation
Average speed is calculated using the equation
So the linear speed
is given by the equation
Where
linear speed
is equivalent to average speed, measured in
the circumference of a circle is equivalent to the total distance traveled, measured in
period is equivalent to the total time taken, measured in
Rearrange to make period
the subject:
Worked Example
The London Eye is a giant Ferris wheel in the city of London that was built as part of the millennium celebrations. It rotates slowly enough so people on board can observe what is happening in the city below. The radius of the London Eye is 67.5 m and it takes 30 minutes to complete one full rotation.
Which of the following is the linear speed of the London Eye?
A
B
C
D
The correct answer is A
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities
Radius of London Eye,
Period of rotation,
Step 2: Substitute the known quantities into the equation for linear speed
The answer is therefore A
Examiner Tips and Tricks
An object in uniform circular motion travels at a constant linear speed but at a changing linear velocity, . This is because the direction of motion is constantly changing.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?