Domestic Issues (College Board AP® US History): Study Guide
Timeline & Summary
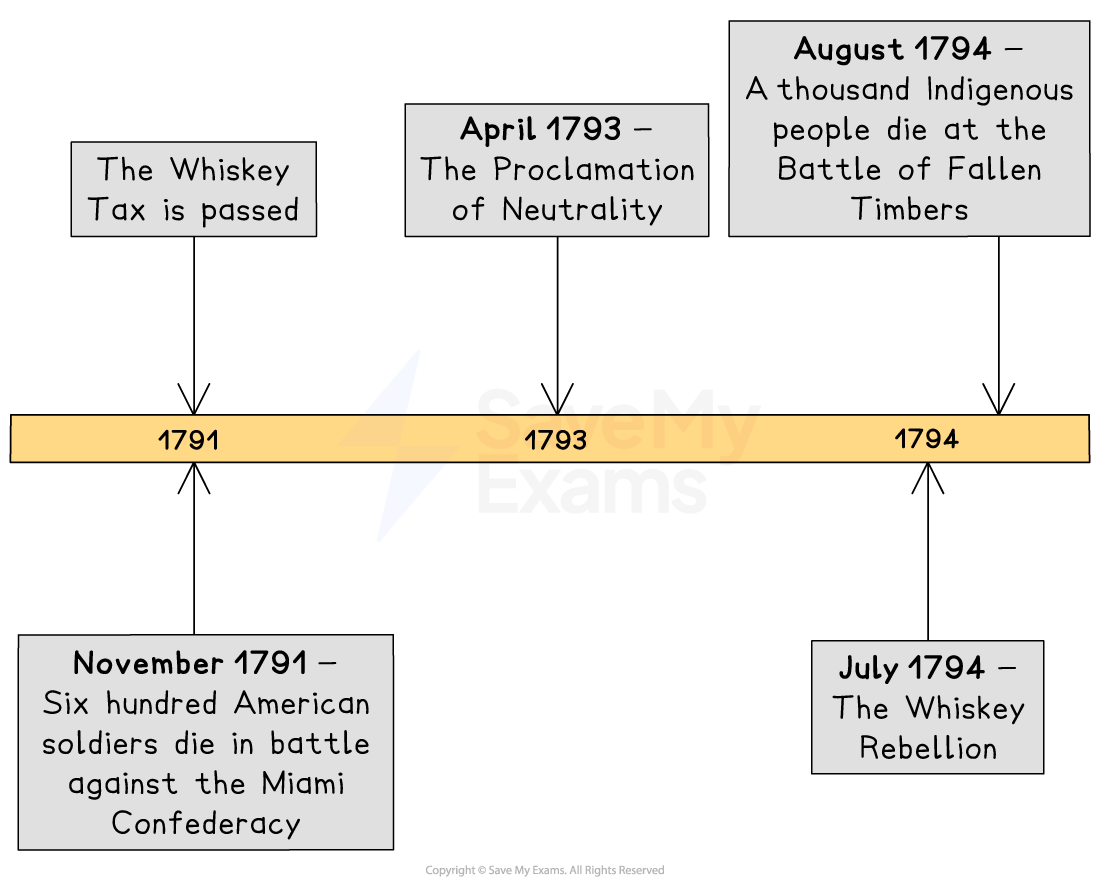
One of the earliest federal taxes was on the production and sale of whiskey. Whiskey producers in western Pennsylvania were especially angered by this tax. The resulting Whiskey Rebellion in 1794 was swiftly ended by federal troops and sent Americans a powerful message about the strength of their national government.
Indigenous peoples also learned hard lessons about the federal government’s strength. Encouraged by Great Britain and Spain, the frequent conflicts between Indigenous groups and Anglo-American settlers in the Northwest Territory eventually became all-out wars in the early 1790s. Indigenous groups in the area were ultimately defeated and forced to cede their native lands to white settlers.
Whiskey Rebellion
The US government wanted to make money by collecting taxes on several domestic products, including whiskey
In 1791, Congress passed a tax on the making and sale of whiskey
This upset farmers in western Pennsylvania, where whiskey was made
Whiskey was so common that it was often used as a form of money
It was easier to transport than grain
In July 1794, armed rioters attacked tax collectors and burned down buildings
The government viewed the Whiskey Rebellion as a challenge to the federal government’s power, like that of Shays’ Rebellion
Washington sent troops from other states to stop the uprising
This showed the nation that the US government would use force to maintain order
Northwest Territory Disputes
Americans began moving into the Northwest Territory during George Washington’s presidency
Despite the Treaty of Paris (1783), Great Britain still held land in North America near the Northwest Territory
The British started causing problems between the Indigenous people who already lived in the Northwest Territory and the Anglo-Americans who moved there
The British wanted to maintain their trade relationships with local Indigenous groups
They traded furs with several Indigenous groups and sold alcohol and firearms to the people of the Miami Confederacy
Spain had control of the Louisiana Territory, which also bordered the Northwest Territory
The Spanish also encouraged conflict between Indigenous people and Anglo-Americans by providing weapons and supplies
Spain wanted to minimize American expansion in the frontier because it could potentially encroach on Spanish land
To avoid conflict, Washington signed treaties with several Indigenous groups
The treaties were meant to preserve Indigenous land
Anglo-Americans ignored the treaties and settled wherever they wanted, including on Indigenous land
The Miami Confederacy opposed American expansion
Its leaders said the Ohio River was the boundary between the United States and Indigenous lands
This meant that groups within the Miami Confederacy would not tolerate any white Americans within the Northwest Territory
Battles broke out between white Americans and Indigenous groups
In 1791, 600 American soldiers died in battle against the Miami Confederacy
In 1794, American soldiers defeated 1,000 Indigenous warriors at the Battle of Fallen Timbers
The Treaty of Greenville (1795) gave almost all Indigenous land in what is now Ohio to Anglo-American settlers

Examiner Tips and Tricks
It is important to remember that Anglo-Americans and Indigenous peoples were not the only groups who contributed to the conflict in the Northwest Territory. The Spanish and British both hoped for disputes about the shared land. Spain wanted a buffer between its territory and the United States, and Great Britain wanted to continue its profitable trading relationship with Indigenous groups in the area. Both countries supplied Indigenous groups with firearms, ammunition, and other supplies they would need to push Anglo-Americans out of the Northwest Territory.
You can remember the effects of Britain and Spain’s involvement in this domestic problem by picturing the Northwest Territory as a campfire. Anglo-Americans and Indigenous groups had enough disagreements — the campfire’s logs — to maintain a big fire. But campfires also need little pieces of wood and brush, called kindling. Kindling catches fire and burns easily, which is why it is often used to get fires started. Great Britain and Spain acted as the kindling in this situation. Their involvement in the Northwest Territory made the conflict between Anglo-Americans and Indigenous peoples burn hotter and faster.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?