Generating energy from fossil fuels (College Board AP® Environmental Science): Study Guide
The combustion of fossil fuels
Combustion is a quick thermochemical reaction that requires
Fuel such as hydrocarbons and alcohols
Oxygen
An ignition or trigger such as a spark, flame, a buildup of heat or exposure to oxygen
Coal, when exposed to high levels of oxygen, will begin to react and heat up
Where there is poor airflow, coal will form hot spots, which can then spontaneously ignite as heat builds up
Combustion generates heat and light in the form of a flame
The release of heat means combustion is an exothermic reaction
The burning of fossil fuels releases the gases carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, oxides of nitrogen and oxides of sulfur
When the fuel is a hydrocarbon (e.g. crude oil), then water (H₂O) and carbon dioxide (CO₂) are released
Hydrocarbon compounds undergo complete and incomplete combustion
Complete combustion occurs when there is excess oxygen
Incomplete combustion occurs when there is insufficient oxygen to burn and gives rise to unburned hydrocarbons and carbon particulates
The products of these reactions are unburnt fuel (soot), carbon monoxide and water
Coal produces more CO₂ than any other fossil fuel when burned to generate electricity
The particulate matter of coal irritates respiratory tracts of humans and animals
Produces toxic ash with lead, mercury, and arsenic
Coal waste is taken and stored in ash ponds in landfills, which can leak into the ground, surface water, or the soil
Burned coal releases sulfur and nitrogen oxide, which is an irritant and contributes to smog and acid rain
The continued burning of fossil fuels is the main contributor to the rise of carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere
Steam turbine
Fossil fuels, such as gas and coal, are used to produce energy on demand when energy is needed
The fossil fuel is burned (combusted) and used to heat water to produce steam
This changes the chemical energy in the fuel into thermal energy
The steam turns a turbine
The turning of the rotor turns thermal energy into mechanical energy
The turbine turns a generator, which turns mechanical energy into electricity (electrical energy)
The current produced is transmitted via a power grid
The steam is condensed into water to be used again
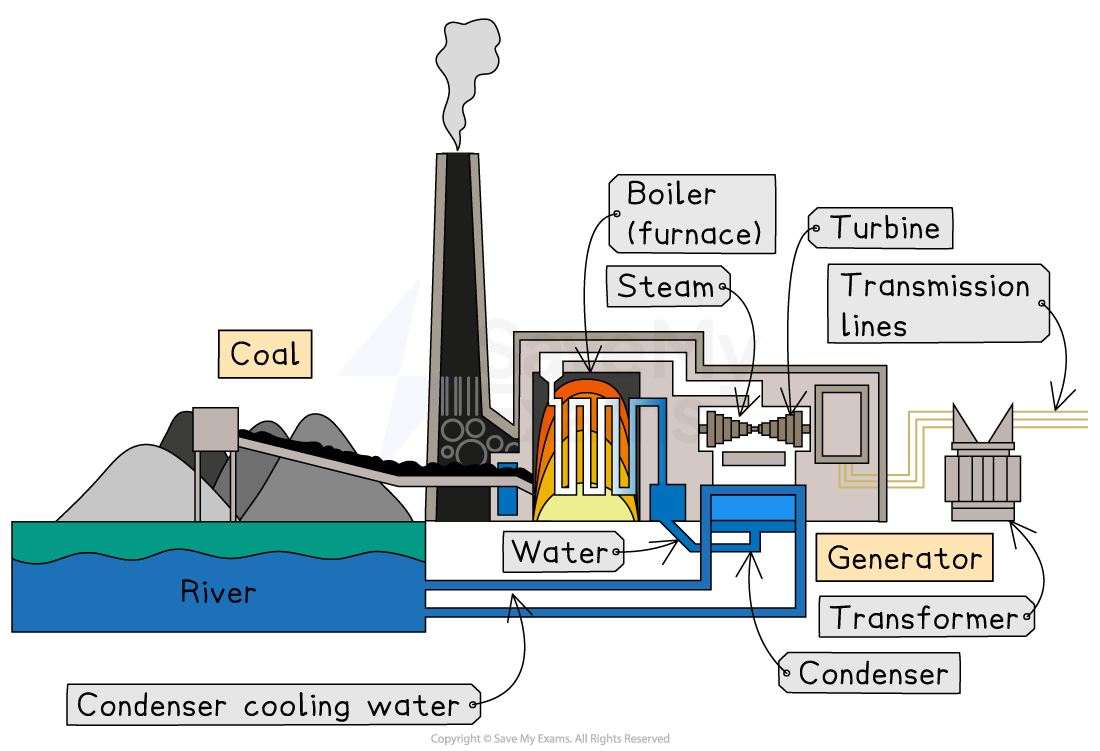
Heat turns water into steam, which turns a turbine. The turbine powers a generator, which makes electricity.
Coal is approximately 30% efficient as a fuel sources, whereas natural gas is roughly 60% efficient
This means that 60% of the available energy in gas is released as heat and is more efficient at generating electricity than coal when burned
The extraction of fossil fuels
Since fossil fuels are hidden deep underground, they can be reached in a number of ways
surface mining
underground mining
vertical drilling
horizontal drilling
hydraulic fracturing (fracking)
Mining is used to extract solid fuels, such as coal and uranium
Drilling is used to extract gaseous or liquid fuels, such as natural gas and crude oil
Vertical drilling is the most common form of drilling
Horizontal drilling uses a steerable drill bit and reduces the number of wells
Hydraulic drilling is the main method to crush the rocks and extract unconventional natural gas
Acidizing dissolves rocks that block the path of the fuel
Extracting oil
Oil extraction can be multi-staged
Stage one is drilling down and pumping oil from the reservoir at normal pressure
Roughly 15% of a reservoir's oil can be extracted during this stage
Stage two involves injecting hot water into the reservoir around the well
This water pushes the leftover oil toward the well for recovery
Stage three is when steam, carbon dioxide, or nitrogen gas are pumped into the reservoir to drive any leftover oil toward the wellhead
This is very expensive and can cost half the oil extracted
This technology sequesters carbon dioxide into the deep reservoir, reducing its greenhouse effect
Extracting coal
Coal is mostly mined from near-surface deposits using strip mining techniques
Strip-mining causes considerable environmental damage in the forms of erosion and habitat destruction
Sub-surface mining of coal is less damaging to the surface environment but is much more hazardous for the miners due to tunnel collapses and gas explosions
Mountaintop mining is a surface mining practice involving the removal of mountaintops to expose coal seams and disposing of the associated mining waste in adjacent valleys known as valley fills
This approach is especially harmful to the environment
Extracting natural gas
Extracting natural gas is done in two ways
Conventionally, by drilling
Unconventionally through hydraulic fracturing
Conventional natural gas can be reached because it is trapped under a layer of rock that can be drilled into
Usually found together with oil reservoir deposits but sometimes it forms a floating layer on top of the oil
Unconventional natural gas sits below 4,500 meters, which makes extraction very hard and sometimes economically unviable
Deep natural gas is hard to extract for different reasons
Shale is a fine-grained, layered sedimentary rock that is hard to drill into, making it a costly process
Tight gas can only be extracted by fracking and acidizing because it is trapped underground in an impermeable rock formation

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?