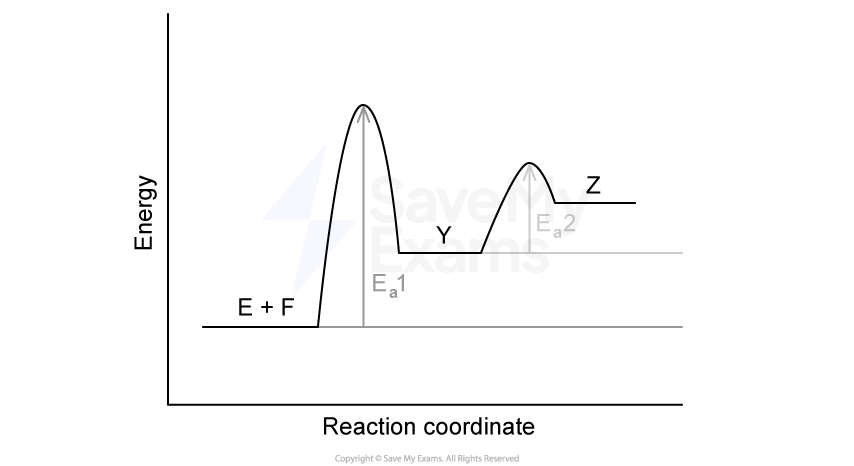
A reaction mechanism for the decomposition of dinitrogen pentoxide (N2O5) in chloroform is proposed:
Step 1: N2O5 → NO2 + NO3 (slow)
Step 2: N2O5 + NO3 → 3NO2 + O2 (fast)
Identify the rate-determining step. Justify your answer.
Write the rate law for the reaction.
Determine the overall balanced equation for the reaction.
Explain how an increase in temperature affects the rate of this reaction.
Did this page help you?