The Ionic Product of Water (College Board AP® Chemistry): Study Guide
The Ionic Product of Water
The autoionization constant of water, Kw
The pH, pOH [H3O+] and [OH-] are all related to one another
An equilibrium exists in water, where a few water molecules dissociate into proton and hydroxide ions
2H2O (l) ⇌ H3O+ (aq) + OH– (aq)
OR
H2O (l) ⇌ H+ (aq) + OH– (aq)
The equilibrium expression for this is:
Kw = [H3O+] [OH–] = 1.00 x 10-14
In a neutral solution [H3O+] = [OH–]
[H3O+] can be calculated a
At 25 °C the value of Kw is 1.00 x 10-14
Since the concentration of the H3O+ and OH- ions is very small, the concentration of water is considered to be a constant
This means that the expression can be rewritten as:
Kw = [H3O+] [OH-]
Where Kw = 1.00 10-14 at 25 °C
Taking the negative log for the equilibrium will give
pKw = pH + pOH = 14
How does temperature affect Kw?
The ionisation of water is an endothermic process
2H2O (l) ⇌ H3O+ (aq) + OH- (aq)
In accordance with Le Châtelier's principle, an increase in temperature will result in the forward reaction being favoured
This causes an increase in the concentration of the hydrogen and hydroxide ions
This leads to the magnitude of Kw increasing
Therefore, the pH will decrease
Increasing the temperature, decreases the pH of water (becomes more acidic)
Decreasing the temperature, increases the pH of water (becomes more basic)
Graph to show how Kw changes with temperature
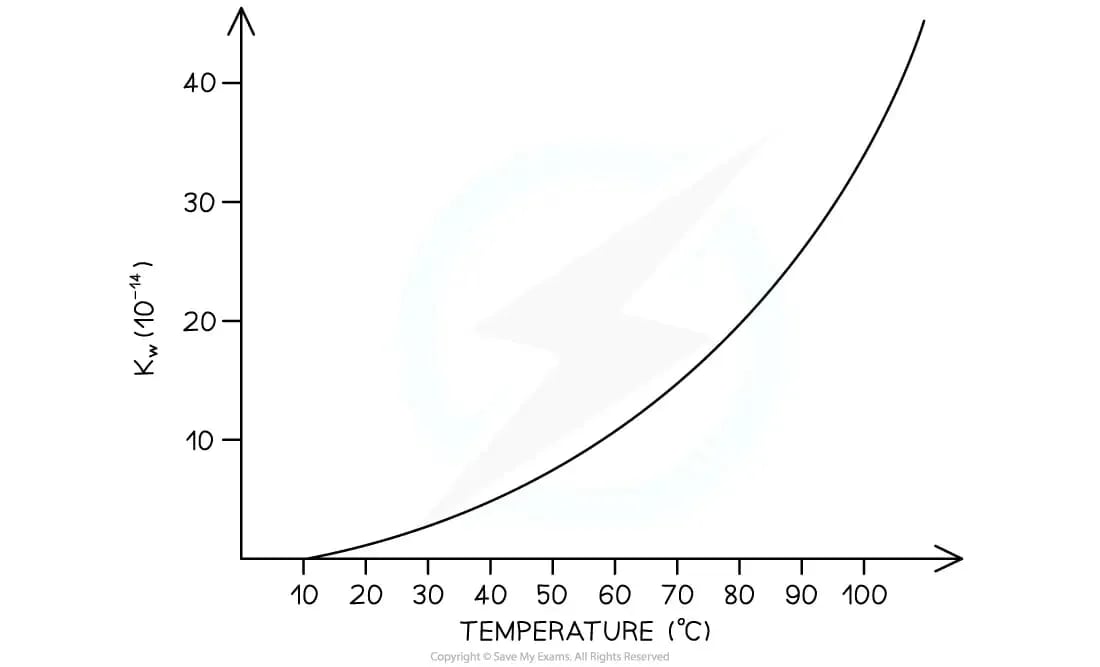
As temperature increases, Kw increases so pH decreases
Relationship between H+ (H3O+) , OH–, pH and pOH

To make a conversion, follow the arrow and equation given, so to convert OH– (aq) to pOH use pOH = -log10[OH–]
Worked Example
It is good practise to convert [between H+] (or [H3O+]), [OH–], pH and pOH.
Complete the following table giving your answers to 2 decimal places.
[H3O+] | [OH–] | pH | pOH |
|---|---|---|---|
2.40 x 10-4 |
|
|
|
| 4.60 x 10-5 |
|
|
|
| 10.36 |
|
|
|
| 3.21 |
Answer:
As shown below there are different ways to arrive at the correct answer
[H3O+] | [OH–] | pH | pOH |
|---|---|---|---|
2.40 x 10-4 |
| -log (2.40 x 10-4) = 3.62 | 14 - pH = 10.38 |
| 4.60 x 10-5 | 14 - pOH = 9.66 | -log (4.60) = 4.34 |
10-10.36 = 4.37 x 10-11 |
| 10.36 | 14 - pH = 3.64 |
| 10-3.21 = 6.17 x 10-4 | 14 - pOH = 10.79 | 3.21 |

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?