Calculating the Equilibrium Constant (College Board AP® Chemistry): Study Guide
Calculating the Equilibrium Constant
For the generic equation:
aA + bB ⇌ cC + dD
Where a, b, c, and d represent stoichiometric coefficients and A, B, C, and D represent chemical species
The equilibrium expression for Kc is:
[A] indicates the concentration of species A in mol/L
The equilibrium expression KP is:
PA indicates the partial pressure of species A in atm
Worked Example
H2 (g) + CO2 (g) ⇌ H2O (g) + CO (g)
A mixture of H2, CO2, H2O, and CO gases is combined in a 1.0 L previously evacuated, rigid sealed container. The gases are allowed to react, according to the equation above, at a constant temperature of 700°C. A graph of the concentration of each gas as a function of time is shown below.
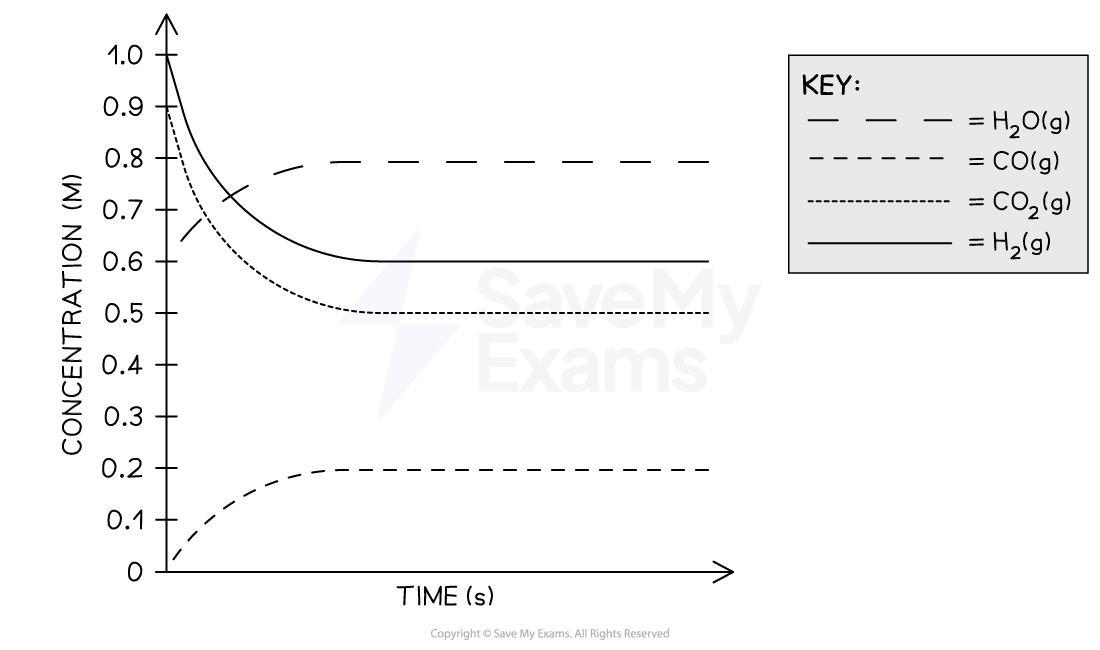
What is the value of Kc for this reaction at 700°C?
Answer:
For the generic equation
aA + bB ⇌ cC + dD
The equilibrium expression for Kc is
So, for the given reaction the equilibrium expression is
To solve for Kc we substitute the concentration of each species at equilibrium
Equilibrium is established when the concentrations of each species remain constant
From the graph, the equilibrium concentrations are
[H2O] = 0.8 M
[CO] = 0.2 M
[H2] = 0.6 M
[CO2] = 0.5 M
Substituting the concentrations into the equation for Kc
Kc = 0.5
Note that Kc is a unitless value
Worked Example
2NO2 (g) ⇌ 2NO (g) + O2 (g)
A sample of pure NO2 gas in a sealed rigid container decomposes at a constant temperature of 1000 K and a constant pressure of 6.00 atm according to the equation above. At equilibrium, the vessel is found to contain 0.200 mol of NO2, 1.700 mol of NO, and 1.100 mol of O2. Calculate the equilibrium constant for partial pressure, KP, for this reaction.
Answer:
For the generic equation
aA + bB ⇌ cC + dD
The equilibrium expression for KP is
For the given reaction the equilibrium expression is
To solve for KP we substitute the partial pressure of each species at equilibrium
Determining the total number of moles of the gas mixture
Determining the partial pressure for each gas using its mole fraction and total pressure
NO2
NO
O2
Substituting the partial pressures into the equation for KP
KP=25.4320.16
KP=159
Note that KP is a unitless value
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When writing a Kc expression, always be sure to include the brackets, as brackets around a species represent the concentration of that species. However, when writing a KP expression never use brackets as this expression involves partial pressures not concentrations.
Make sure that the values substituted into a Kc expression have the unit mol/L and values substituted into a KP expression have the unit atm.
Remember that although the values substituted into a Kc or KP expression have units, the equilibrium constant is a unitless value.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?