Disruption to Ecosystems (College Board AP® Biology): Study Guide
Mutation & adaptation
An adaptation can be defined as:
a genetic variation that is favored by selection and that is manifested as a trait that provides an advantage to an organism in a particular environment
Adaptations arise due to mutations
Mutations occur randomly during DNA replication and not a result of specific environmental pressures
Adaptations increase an organism's fitness
Mutations that result in advantageous traits are favored by selection and so are passed on to the subsequent generations; they can become widespread within a population
This is natural selection
Heterozygous advantage
Heterozygote advantage occurs when individuals with the heterozygous genotype have a higher relative fitness than either homozygous dominant or homozygous recessive individuals
In sickle cell anemia, a mutation in the hemoglobin gene (HBB) produces abnormal hemoglobin (HbS)
HbS/HbS individuals develop sickle cell disease with severe health effects
HbA/HbA individuals are healthy but fully susceptible to malaria
HbA/HbS heterozygotes are largely symptom-free and gain resistance to malaria
This heterozygote advantage maintains the sickle cell allele in populations where malaria is common

Invasive species
Invasive species are species that move into an ecosystem where they were not previously present
Invasive species often arrive in ecosystems due to human activity, either intentionally or unintentionally
Intentional introductions: species may be traded or transported as biological controls for pests
Unintentional introductions: species may be transported unknowingly due to global transport of goods and people, e.g. in seawater present inside ships
Impact on ecosystem dynamics
Invasive species can often exploit a new niche when they arrive in their new ecosystem; this is because they may lack natural predators or competitors
This can lead to uncontrolled population growth of the invasive species and significant ecological changes
Competition: native species may be displaced or driven to extinction due to competition for resources like prey, soil nutrients, light, or space
Predation: invasive species may cause drastic declines in prey populations
Disease introduction: native species may lack immunity to diseases brought by invasive species
Biodiversity loss: a reduction in biodiversity decreases ecosystem productivity and stability
Example: kudzu
Kudzu (Pueraria montana) is a plant, native to Japan and southern China, that was was introduced to the US for ornamental purposes and soil erosion control
The plant grows extremely fast, up to 30 cm (1 foot) per day, spreading aggressively via runners
Kudzu overwhelms ecosystems, creating "kudzu graveyards" by covering and out-competing native plants

CC BY-SA 4.0, Rhododendrites, via Wikimedia Commons
Example: zebra mussels
Zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha), native to the Black Sea and Caspian Sea, spread to Europe and North America via ships
They are known for clogging waterways and water treatment systems due to high reproductive success
Zebra mussels disrupt ecosystems by competing with native species and altering aquatic environments

CC BY-SA 1.0, User Lamiot on fr.Wikipedia, via Wikimedia Commons
Human activities
Ecosystems naturally change over time due to environmental factors, but human activities can accelerate these changes
Human activities can lead to alterations in ecosystem structure, e.g. due to:
extinctions
biodiversity loss
reduced productivity
These negative effects contribute to decreased ecosystem resilience, making ecosystems more vulnerable to further environmental changes
Examples of human activities that can lead to these changes include:
environmental pollution, leading to biomagnification and eutrophication
the introduction of new diseases
habitat change, e.g. due to climate change or destruction by humans
Biomagnification
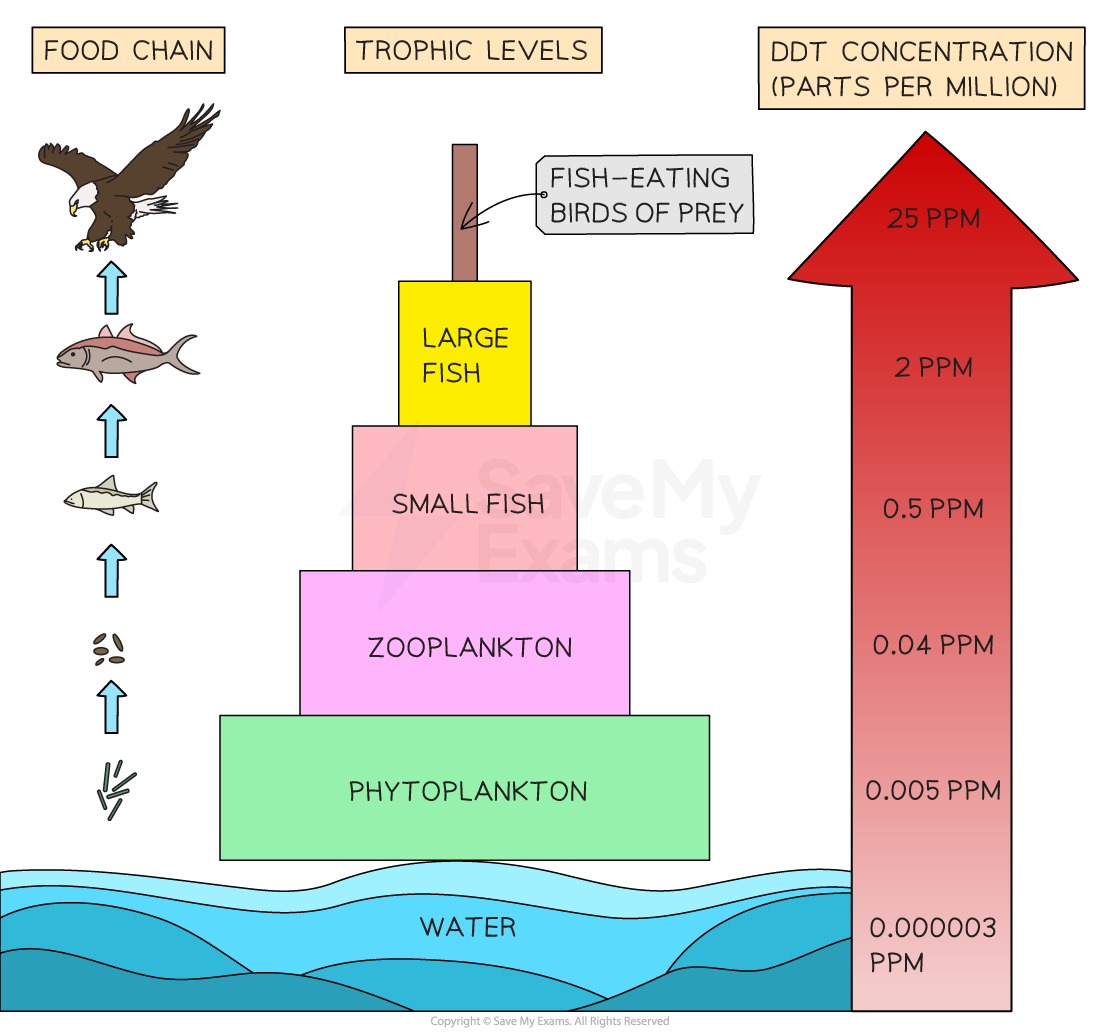
Biomagnification is the increase in concentration of persistent or non-biodegradable pollutants with ascending trophic level through a food chain
Not to be confused with bioaccumulation, which is the build-up of pollutants within an organism, or within a single trophic level
As pollutants are passed up the food chain from one trophic level to the next, they can become more concentrated due to the decrease in total biomass of organisms at higher trophic levels
The smaller organisms at the bottom of the food chain will each consume a small volume of pollutant, and then the organisms at the top of the food chain will consume many smaller organisms and receive a much larger dose of pollutant
Example: biomagnification of DDT, a persistent insecticide that enters food chains and reaches high concentrations at higher trophic levels
DDT washes away into water bodies
Plankton absorb DDT → fish accumulate it → birds of prey build up high levels
In birds, DDT caused eggshell thinning, reducing hatching success
Eutrophication
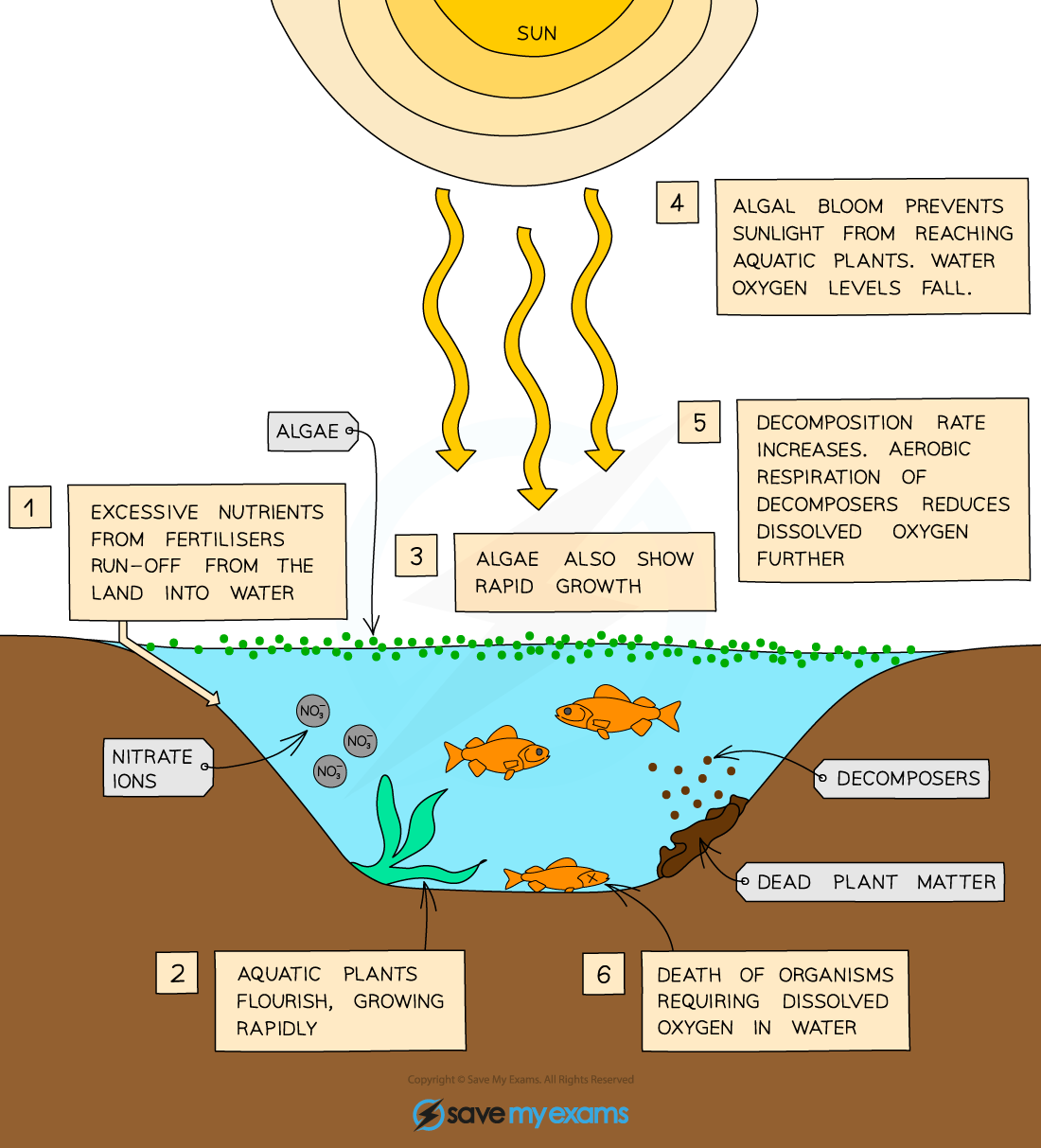
Eutrophication is the nutrient enrichment of a water body—usually by nitrates and phosphates from fertilizers
The process of eutrophication occurs as follows:
excess nitrates and phosphates from fertilizer runoff enter rivers, lakes, and coastal waters
nutrient enrichment causes rapid growth of algae that is known as an algal bloom
algal blooms block sunlight, preventing submerged plants from photosynthesizing → plants die
algae also die when nutrients are depleted
decomposers break down dead plants and algae
the aerobic respiration of decomposers uses up dissolved oxygen
oxygen levels fall, leading to the death of fish and other aquatic organisms
severe oxygen depletion creates aquatic dead zones
Introduction of new diseases
Human activities such as global travel, or the transport of organic matter, can introduce diseases to new regions, devastating native species with no natural immunity, e.g.:
Dutch elm disease: a fungal infection spread by human activity that has significantly reduced elm tree populations
potato blight: a pathogen introduced through trade, causing widespread crop failures and ecosystem disruption
Habitat change
Human activities such as fossil fuel use, urbanization, agriculture, and resource extraction destroy or fragment habitats, reducing biodiversity, e.g.:
global climate change has caused changes in weather patterns, leading to habitat loss and forcing species migrations
logging disrupts ecosystems, resulting in habitat destruction and soil degradation
urbanization converts natural landscapes into developed areas, displacing native species
mono-cropping in agriculture causes simplification of ecosystems, reducing plant and insect diversity, which impacts food chains
Geological & meteorological activity
Geological and meteorological events, such as El Niño, continental drift, and meteor impacts, create significant abiotic and biotic changes in ecosystems
In turn these may lead to shifts in habitat, species distribution, and ecosystem dynamics over time
These events are not necessarily anthropogenic, but human activity may accelerate their occurrence or effects
Example: El Niño
An El Niño climate event occurs every 2–7 years, characterized by sea temperatures rising 0.5°C or more above average in the eastern Pacific
Effects:
Warmer ocean temperatures off Peru cause thermal expansion and sea level rise
Cooler waters near Australia and Indonesia result in reduced precipitation and droughts
Changes in water temperature and precipitation affect forest and wetland ecosystems, causing vegetation die-offs, altered drainage, and soil acidification
Abiotic and biotic changes disrupt ecosystem balance, affecting species interactions
Example: continental drift
The movement of tectonic plates reshapes continents and alters ecosystem distribution over geological time
Effects:
Changes in mineral resource distribution, critical for life
Seismic events like earthquakes and volcanoes redistribute heat from the Earth’s mantle, creating abiotic changes across ecosystems
Plate movements can result in dramatic shifts in species habitats and resource availability

Example: meteor impact
Meteor impacts can cause sudden, dramatic ecosystem changes, as illustrated by the Chicxulub impact 66 million years ago
Effects:
The asteroid impact likely caused the mass extinction event that ended the age of dinosaurs
Clouds of hot dust and vapor made conditions lethal for many species
Iridium deposits near the impact site and the fossil record confirm this event
New abiotic conditions led to the evolution of new species and ecosystems

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
