Cells & Surface Area (College Board AP® Biology): Study Guide
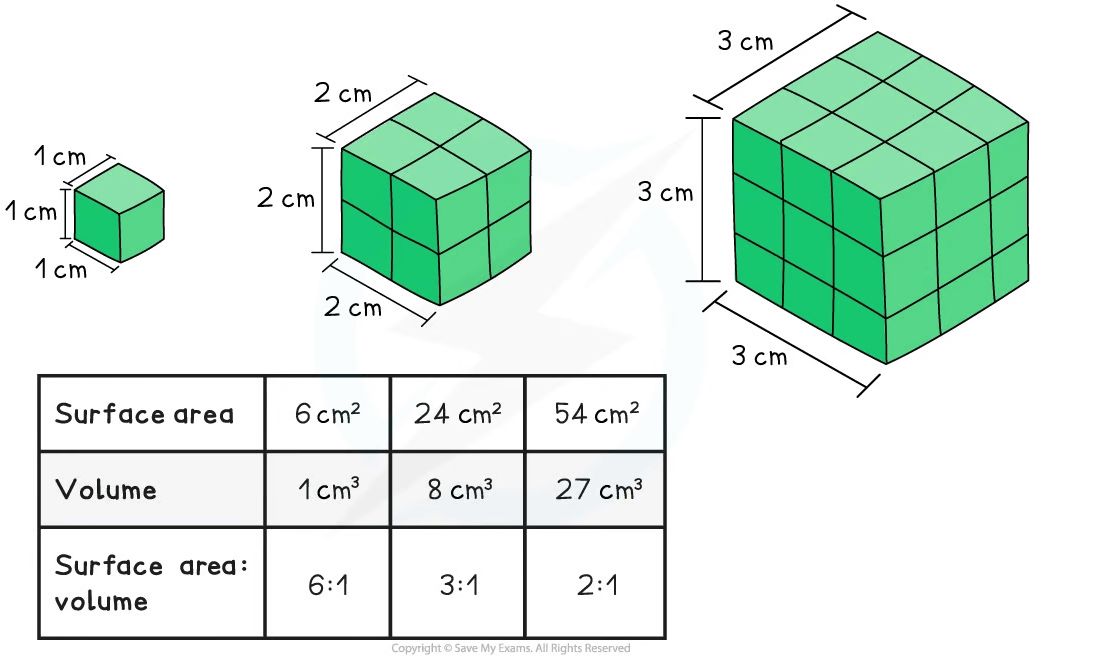
Surface area-to-volume ratio
Surface area and volume are both very important factors in the exchange of materials in organisms
Surface area refers to the total area of the organism that is exposed to the external environment
Volume refers to the total internal volume of the organism, or the total amount of space inside the organism
As the surface area and volume of an organism increase (as the size of an organism increases), the surface area : volume ratio decreases
This is because volume increases much more rapidly than surface area as size increases
Importance of surface area-to-volume ratios
Having a high surface area-to-volume ratio increases the ability of a biological system to perform the following important functions:
obtain necessary resources, e.g. oxygen, glucose, amino acids
eliminate waste products, e.g. carbon dioxide, urea
acquire or dissipate thermal energy (heat)
exchange chemicals with the surroundings, e.g. secreting or binding to hormones at the cell surface
Calculating surface area-to-volume ratios
The SA:V ratios of different biological shapes can be calculated using mathematical formulae
| Sphere | Cube | Rectangular solid | Cylinder |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 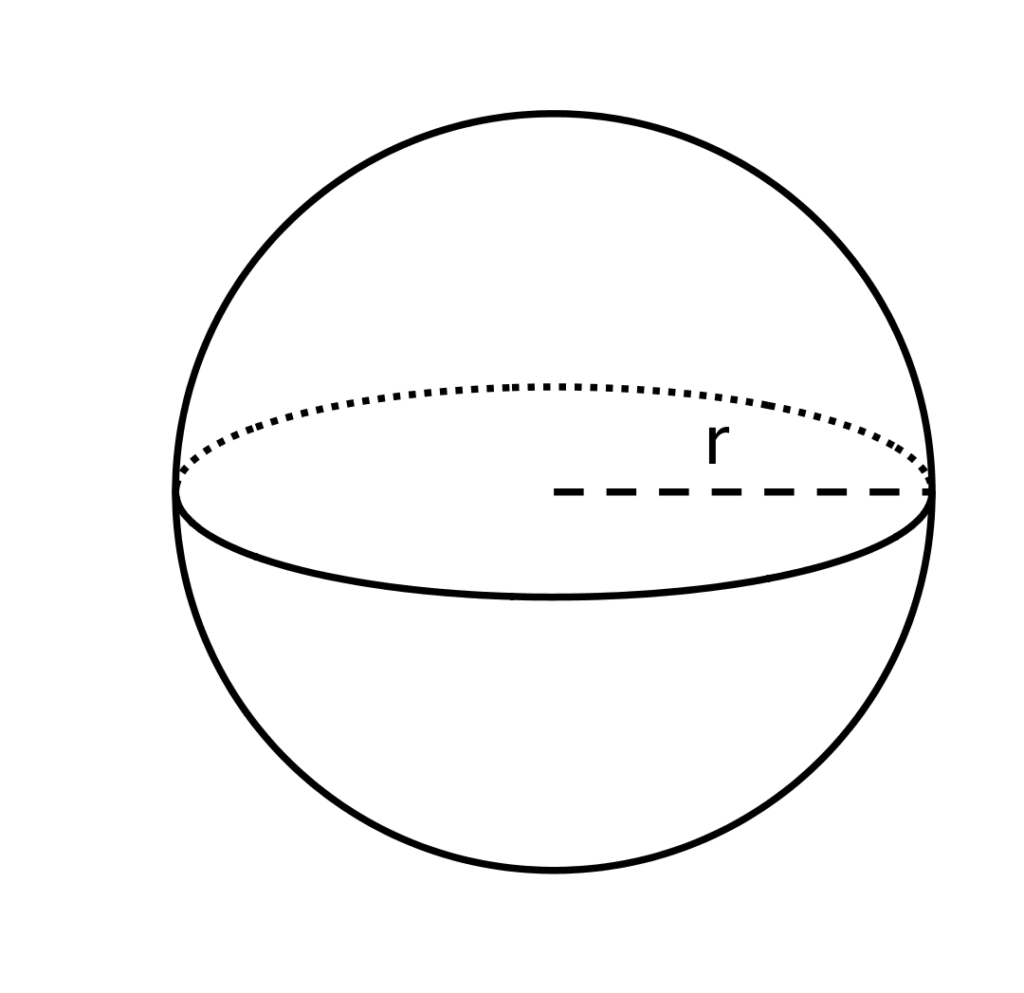 | 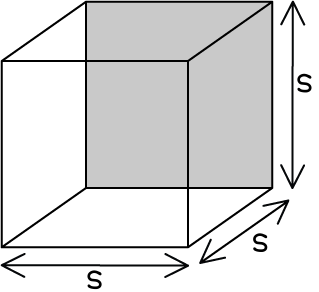 | 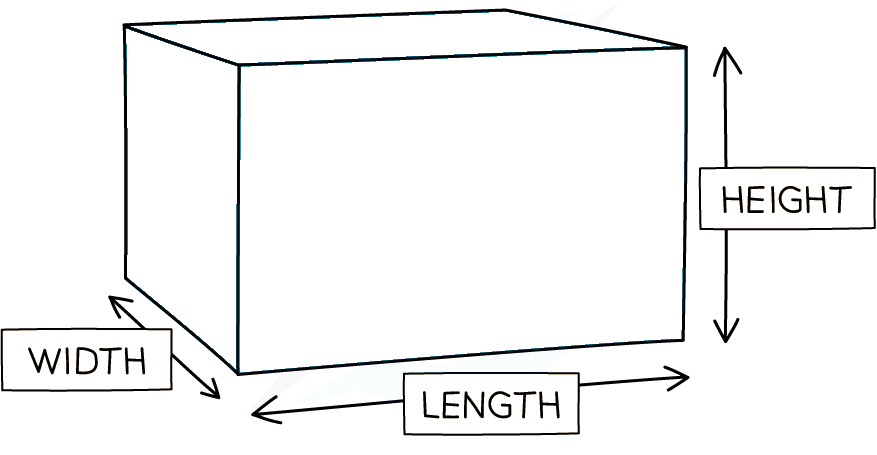 | 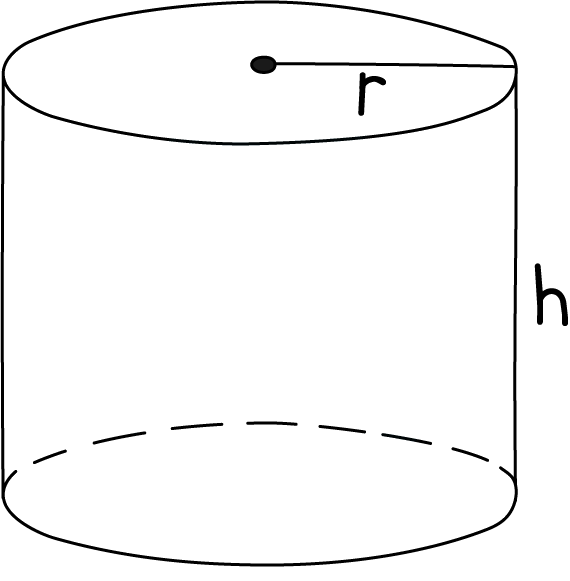 |
Surface area | | 6s2 | 2lh + 2lw + 2wh | |
Volume | s3 | l × w × h | | |
Example | If r = 1 cm V = 4/3 πr3 ∴ SA:V ratio = 4:4/3 | If s = 1 cm V = s3 = 13 =1cm3 | If l = 4cm, w = 2cm, h = 1cm, then V = 4 × 2 × 1 ∴ SA:V ratio = 28:8 | If r = 2 cm and h = 6cm, then V = π(2)2 × 6 = 24π cm2 ∴ SA : V ratio |
Worked Example
Calculate the surface area-to-volume ratios of the following microorganisms:
a bacterial cell from the species Staphylococcus aureus; these are spherical cells with a diameter of 800 nm (8 × 10-7 m)
a bacterial cell from the species Bacillus subtilis; these are rod-shaped cells which you can assume to be cylindrical. They are 5 µm long and 1 µm in diameter
Comment on your calculated answers.
Answer for Staphylococcus aureus:
Step 1: determine the radius of a cell
The diameter of a cell = 800 nm
radius = 800 ÷ 2
= 400 nm
Step 2: convert the units to µm
There are 1000 nm in a µm, so we divide by 1000
= 400 ÷ 1000
= 0.4 µm
Step 3: use the formula to calculate surface area
=
= 4 × 3.14 × 0.42
= 2.01 µm2
Step 4: use the formula to calculate volume
=
= 4/3 x 3.14 x 0.43
= 0.268 µm3
Step 5: convert to a ratio
The standard way of stating a ratio is X : 1, so we begin by converting the second number to 1
0.268 ÷ 0.268 = 1
Then we divide the first number by the same factor
2.01 ÷ 0.268 = 7.5
We can then express this as a ratio:
= 7.5:1
Answer for Bacillus subtilis
Step 1: determine the radius of a cell
The diameter of a cell = 1 µm
1 ÷ 2 = 0.5 µm
Step 2: use the formula to determine surface area
The length of a cell = 5 µm
= 2 π r h + 2 π r2
= (2π × 0.5 × 5) + (2π × 0.52)
= 15.708 + 1.571 µm2
= 17.278 µm2
Step 3: use the formula to determine volume:
= π r2 h
= π × 0.52 × 5
= 3.927 µm3
Step 4: convert to a ratio
Begin by converting the second number to 1
3.927 ÷ 3.927 = 1
Then we divide the first number by the same factor
17.278 ÷ 3.927 = 4.4
We can then express this as a ratio:
4.4:1
___________
Staphylococcus aureus has a surface area-to-volume ratio of 7.5:1
Bacillus subtilis aureus has a surface area-to-volume ratio of 4.4:1
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In an exam you are expected to be able to:
calculate the SA:V ratio of a sphere, cube, rectangular solid or cylinder, using formulae from a formula sheet
explain how the increasing size of an organism affects the SA:V ratio.
Maximizing surface area-to-volume ratio
As cells increase in size, their surface area–to–volume (SA:V) ratio decreases and their metabolic requirements increase
This means that larger cells have proportionally less surface available for exchange of substances, relative to their greater internal demand
The maximum size to which single cells can grow is restricted by this relationship
The surface area of the plasma membrane must be large enough to adequately exchange materials, so larger cells may have complex cellular structures, such as membrane folds, to enable adequate exchange of materials with the environment
Cell feature | Role | Adaptation for adequate exchange with environment |
|---|---|---|
Root hairs 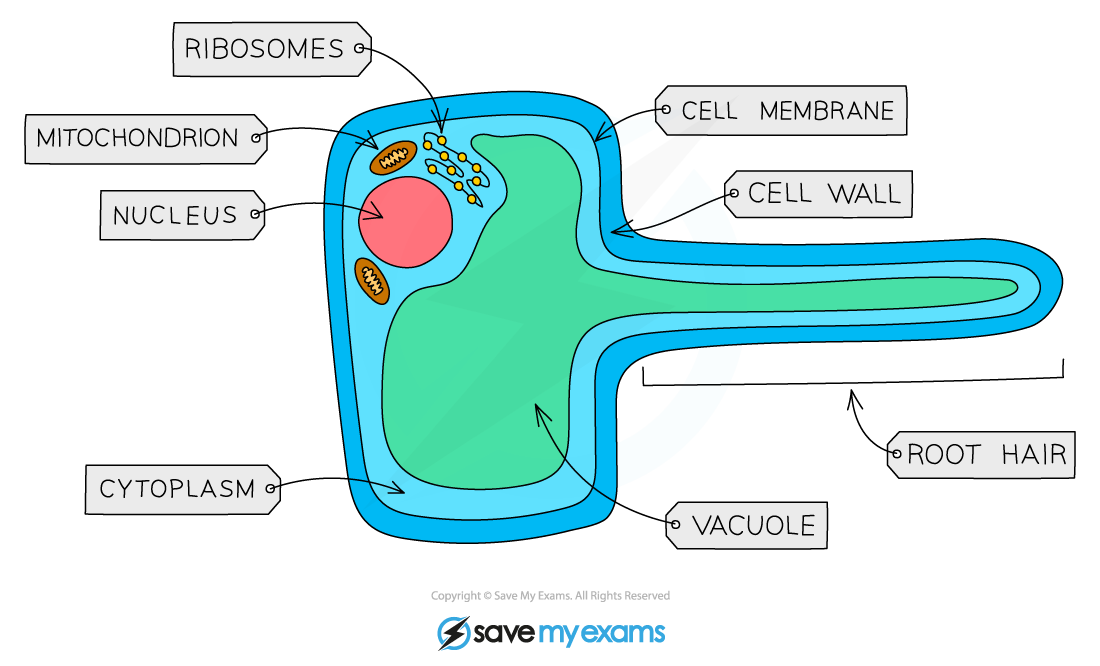 | Root hairs are single-celled extensions found on epidermis cells in plant roots They aid absorption of water and minerals from the soil | Root hairs increase the surface area of plant roots, so increasing the rate at which water and minerals can be absorbed |
Opening and closing guard cells 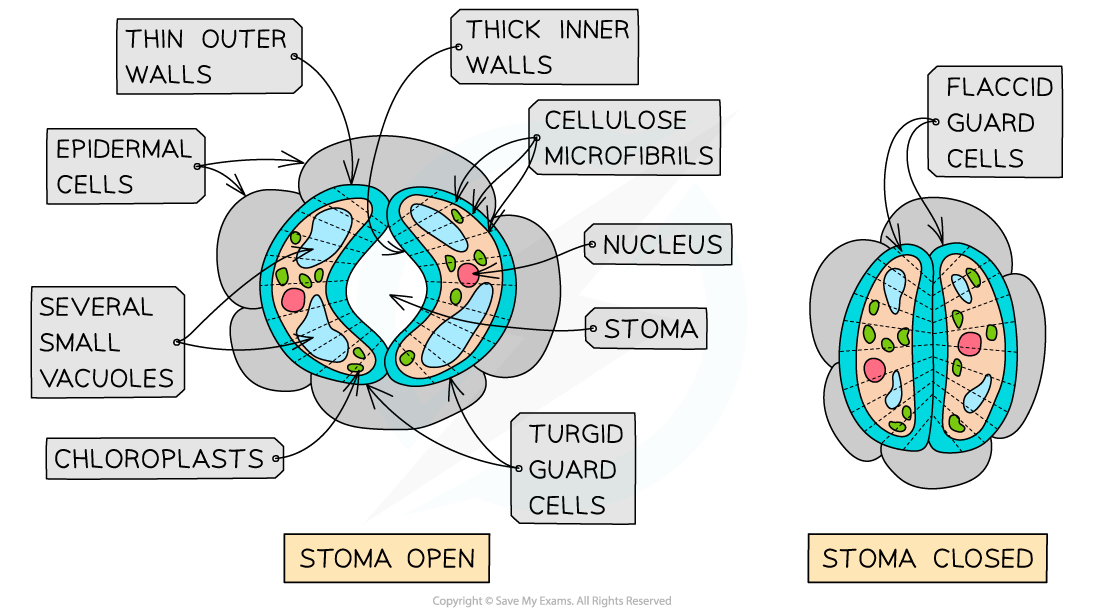 | Guard cells surround stomata on the lower surface of a leaf, where their role is to open and close the stomata This allows plants to carry out gas exchange while also controlling water loss | Guard cells can become turgid, expanding and curving outwards to allow stomata to open This allows gases to diffuse into the leaf, where they come into contact with the large surface area of the spongy mesophyll |
Microvilli on gut epithelial cells 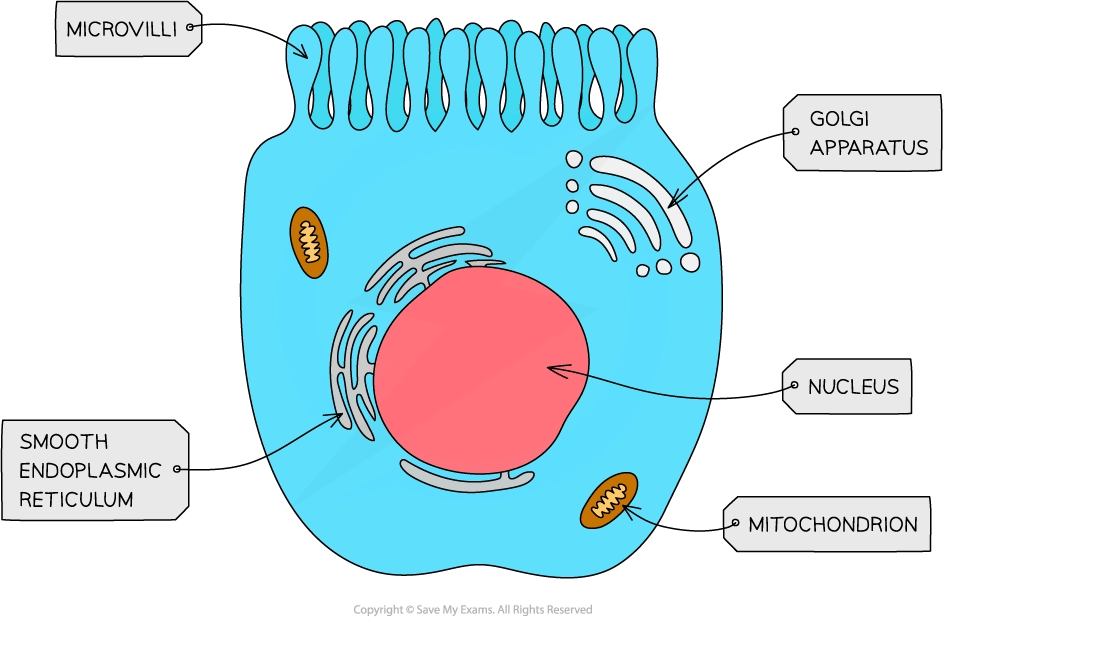 | Gut epithelial cells are located on the inside surface of the small intestine Their role is to absorb nutrients for distribution around the rest of the body | The surface area of the food-contacting surface is maximized by folded structures called microvilli |
Cilia 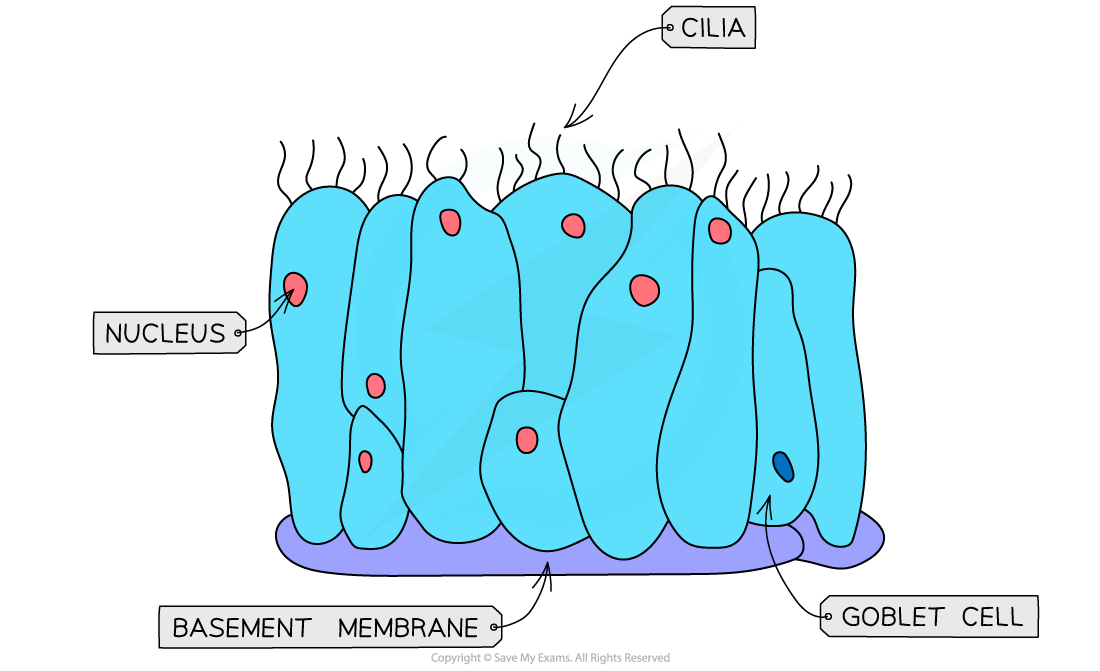 | Cilia are hair-like projections on cell surfaces that can beat to move fluid over the surface of cells, e.g. unicellular eukaryotes living in a watery environment may have many cilia | Cilia keep the fluid next to the surface of cells moving, bringing in fresh fluid; this maintains a steep concentration gradient and increases the rate of diffusion |
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Be careful not to confuse microvilli and cilia:
microvilli are formed from folded regions of the plasma membrane, and function to increase membrane surface area
cilia are hair-like structures located on the plasma membrane, and they beat to move substances past the cell surface
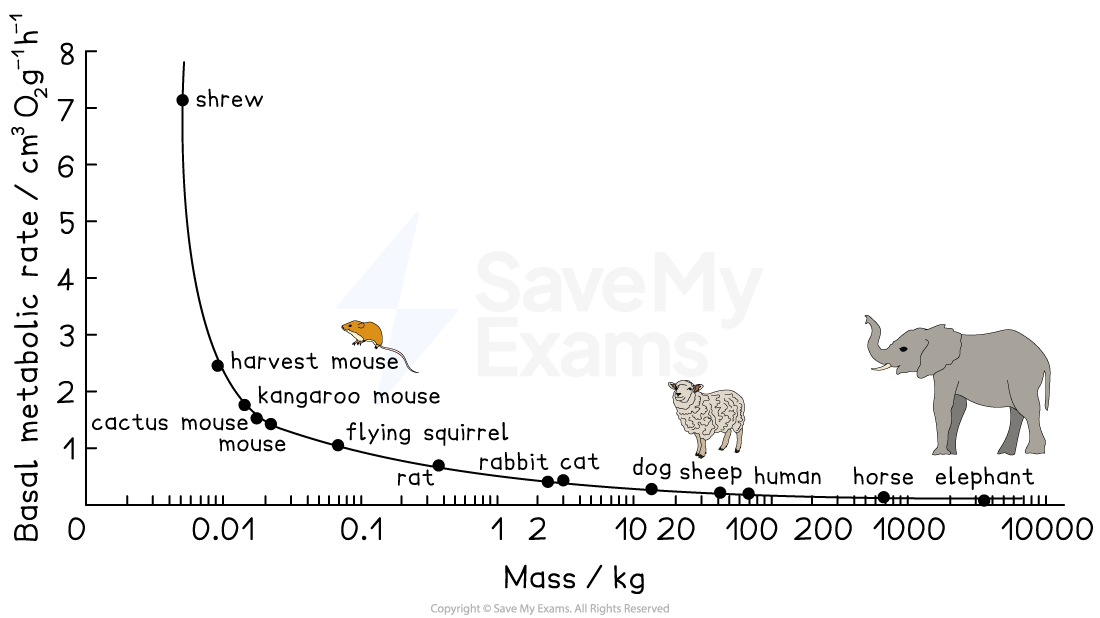
Surface area and heat exchange
The rate of heat exchange with the environment is also affected by cell size
As cell mass increases, SA:V decreases, and the rate of heat exchange with the ambient environment also decreases
Because of the relationship between SA:V and heat exchange, there is a also a relationship between metabolic rate per unit body mass and the size of multicellular organisms; this can be explained as follows:
small animals, with a higher SA:V ratio, will lose more heat to their surroundings, meaning that they need a relatively high metabolic rate to maintain body temperature
large animals, with a lower SA:V ratio, will lose less heat, meaning that they can maintain body temperature at a relatively low metabolic rate

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?