Nucleic Acids (College Board AP® Biology): Study Guide
DNA & RNA
DNA and RNA are polynucleotides; they are made up of many nucleotide monomers linked together in a chain
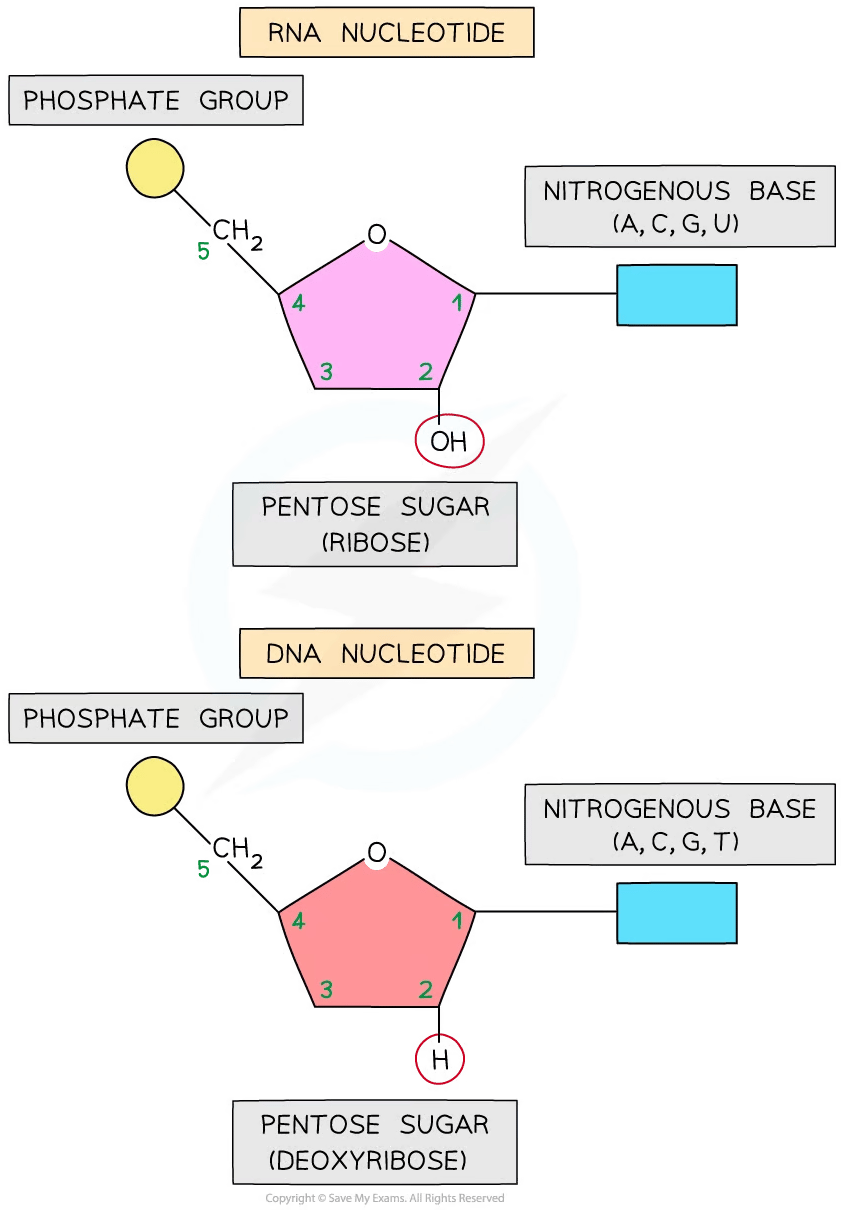
Nucleotide structure
DNA & RNA nucleotides contain three components:
a five-carbon, or pentose, sugar
DNA = deoxyribose sugar
RNA = ribose sugar
a phosphate group
a nitrogenous base
DNA = adenine, guanine, cytosine and thymine
RNA = adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil
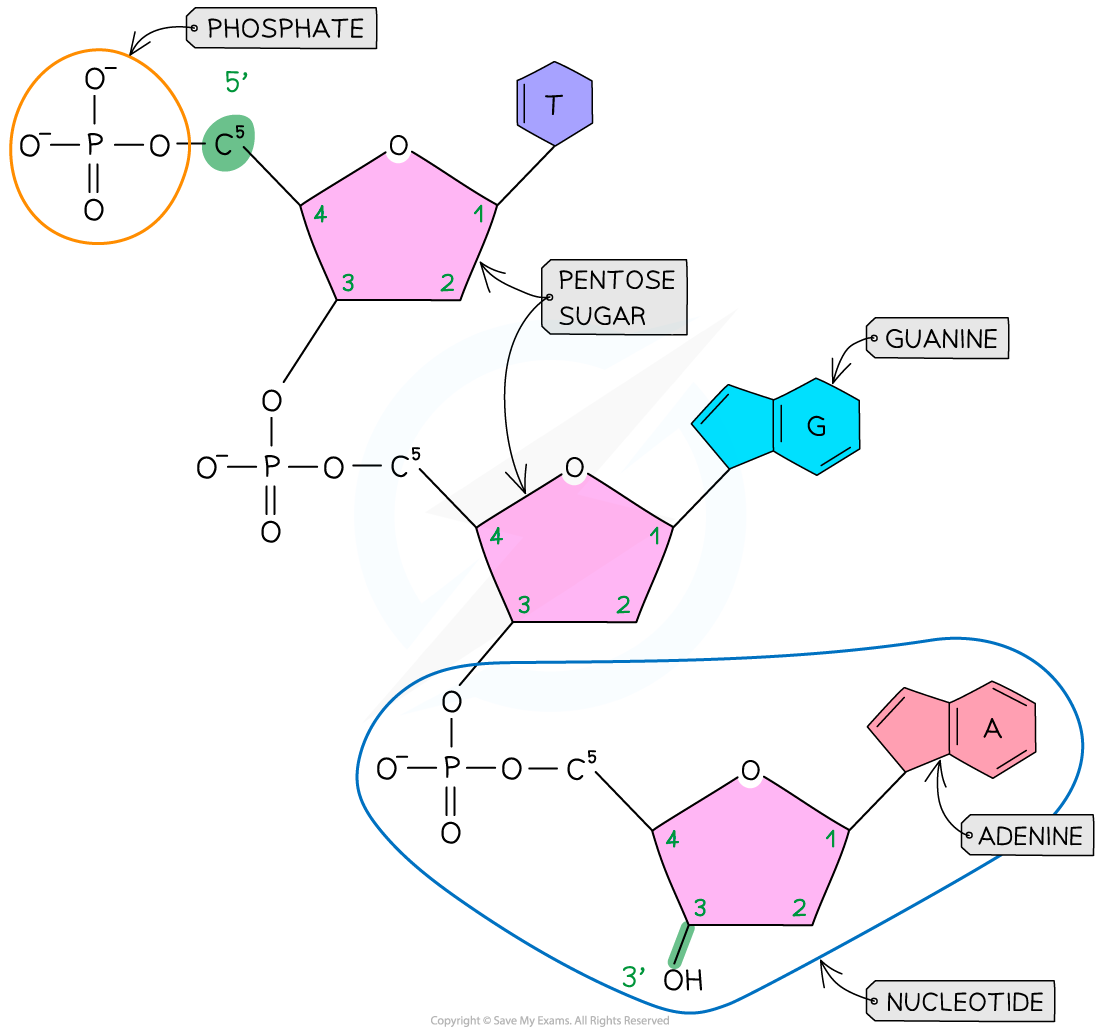
3' and 5' ends
In a polynucleotide the nucleotide monomers are arranged in a linear sequence which has two distinct ends:
the 3′ (three prime) end, which has a terminal hydroxyl (–OH) group on carbon 3 of a sugar
the 5′ (five prime) end, which has a terminal phosphate group on carbon 5 of a sugar
During nucleic acid synthesis, new nucleotides are always added to the 3′ end of the growing strand; this process forms strong covalent bonds between the nucleotides
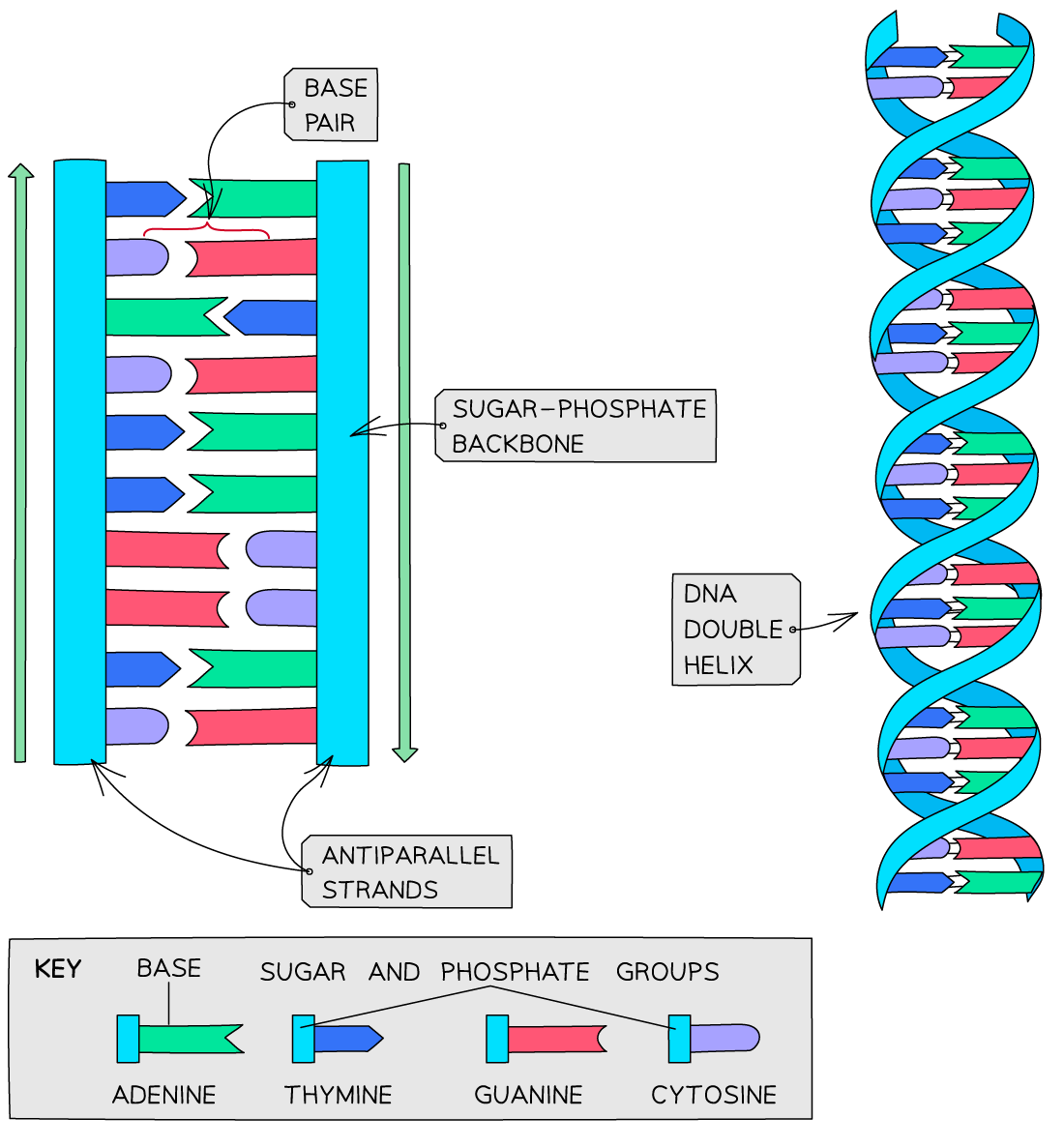
DNA structure
DNA is structured as an antiparallel double helix, with the two strands running in opposite 5′ → 3′ orientations
The nitrogenous bases within the double helix are joined by hydrogen bonds:
adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T) → A–T
cytosine (C) pairs with guanine (G) → C–G
While RNA is usually single-stranded, it can form folds which are held together by base pairing; when this occurs:
adenine (A) pairs with uracil (U) instead of thymine
cytosine (C) pairs with guanine (G) as in DNA
Comparing DNA and RNA
Structural differences between DNA and RNA include:
DNA contains the sugar deoxyribose while RNA contains the sugar ribose
DNA contains the nitrogenous base thymine (T) while RNA contains uracil (U)
DNA is typically double-stranded while RNA is typically single-stranded
Feature | DNA | RNA |
|---|---|---|
Pentose sugar | Deoxyribose | Ribose |
Nitrogenous bases | Adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), guanine (G) | Adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine (C), guanine (G) |
Base pairing | A–T, C–G | A–U, C–G |
Typical structure | Double-stranded, antiparallel double helix | Usually single-stranded |
Synthesis direction | 5′ → 3′ Nucleotides added to the 3′ end | 5′ → 3′ Nucleotides added to the 3′ end |
Bonds present in sugar-phosphate backbone | Covalent (phosphodiester) bonds | Covalent (phosphodiester) bonds |
Examiner Tips and Tricks
A common error is to describe DNA or RNA as polymers of bases; more correctly, they are polymers of nucleotides

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
