Complex Carbohydrates (College Board AP® Biology): Study Guide
Structure & function in carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are biological molecules made of monomer units called monosaccharides
Complex carbohydrates form when monosaccharides join together via covalent bonds to form polysaccharide polymers
Complex carbohydrates can be either linear or branched
The type of monomer and the nature of any covalent bonds determine the properties and functions of a carbohydrate
Forming a polysaccharide
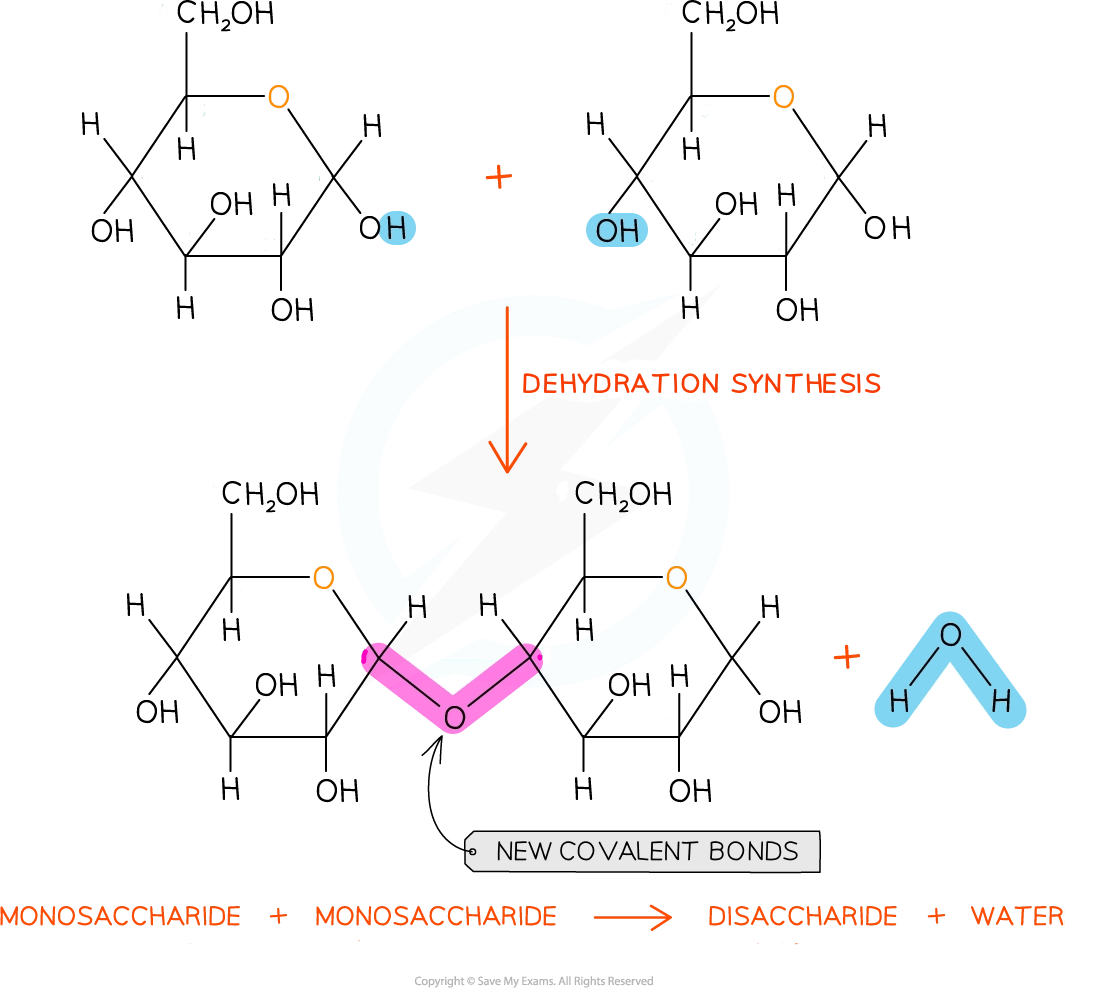
Carbohydrate monomers can join together via dehydration synthesis reactions; during this process:
a new covalent bond forms between two monomers, holding the carbohydrate together
a molecule of water is produced
This process can repeat many times to form a polysaccharide
Example: cellulose
Cellulose is a structural polysaccharide of glucose found in plant cell walls
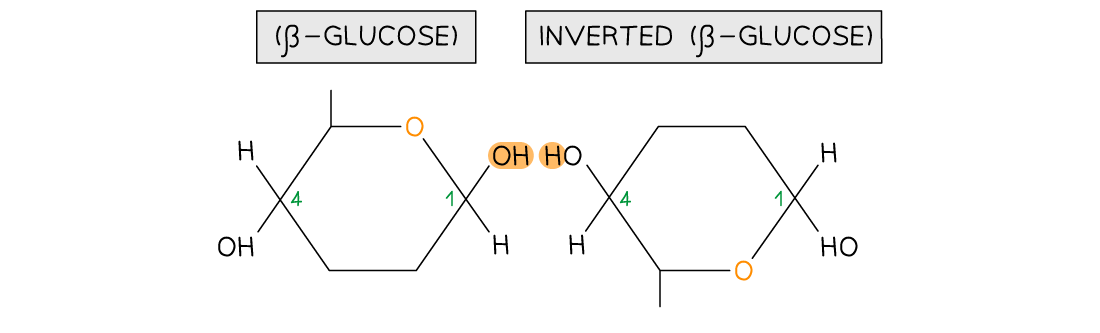
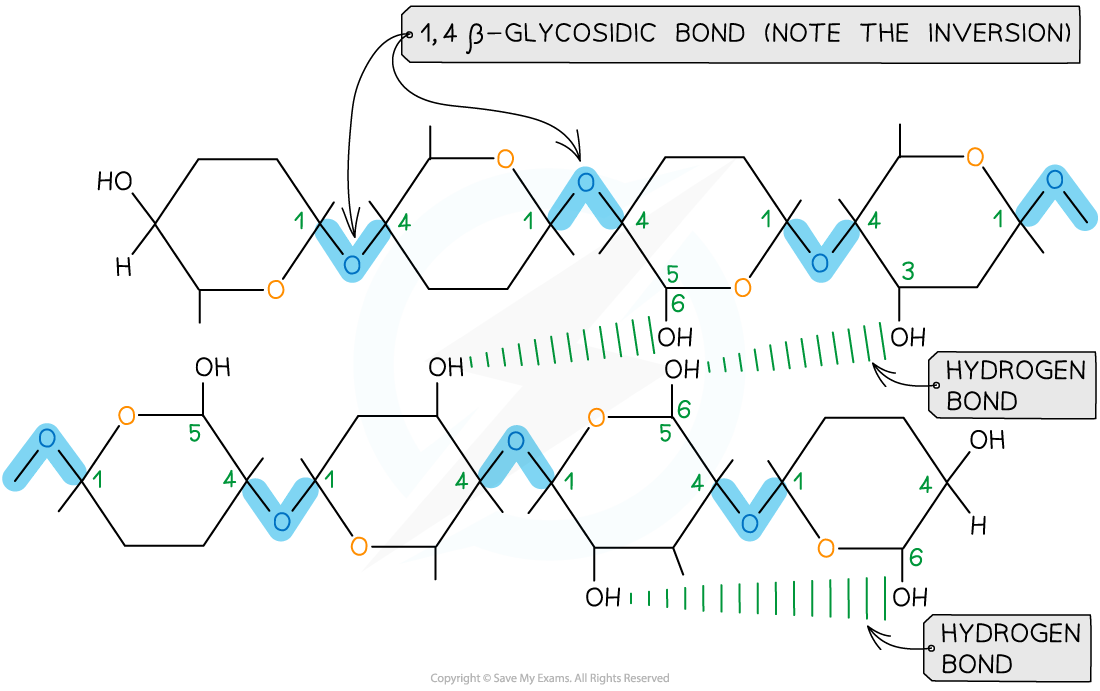
Cellulose consists of long chains of the monomer β-glucose, joined together by 1,4 glycosidic bonds
To form the 1,4 glycosidic bonds, alternate β-glucose molecules must be rotated through 180°
Due to the inversion of the β-glucose molecules, many hydrogen bonds form between cellulose chains, giving cellulose its structural strength
Example: starch and glycogen
Starch and glycogen are storage polysaccharides
Glycogen is the storage polysaccharide of animals and fungi
Starch is the storage polysaccharide of plants
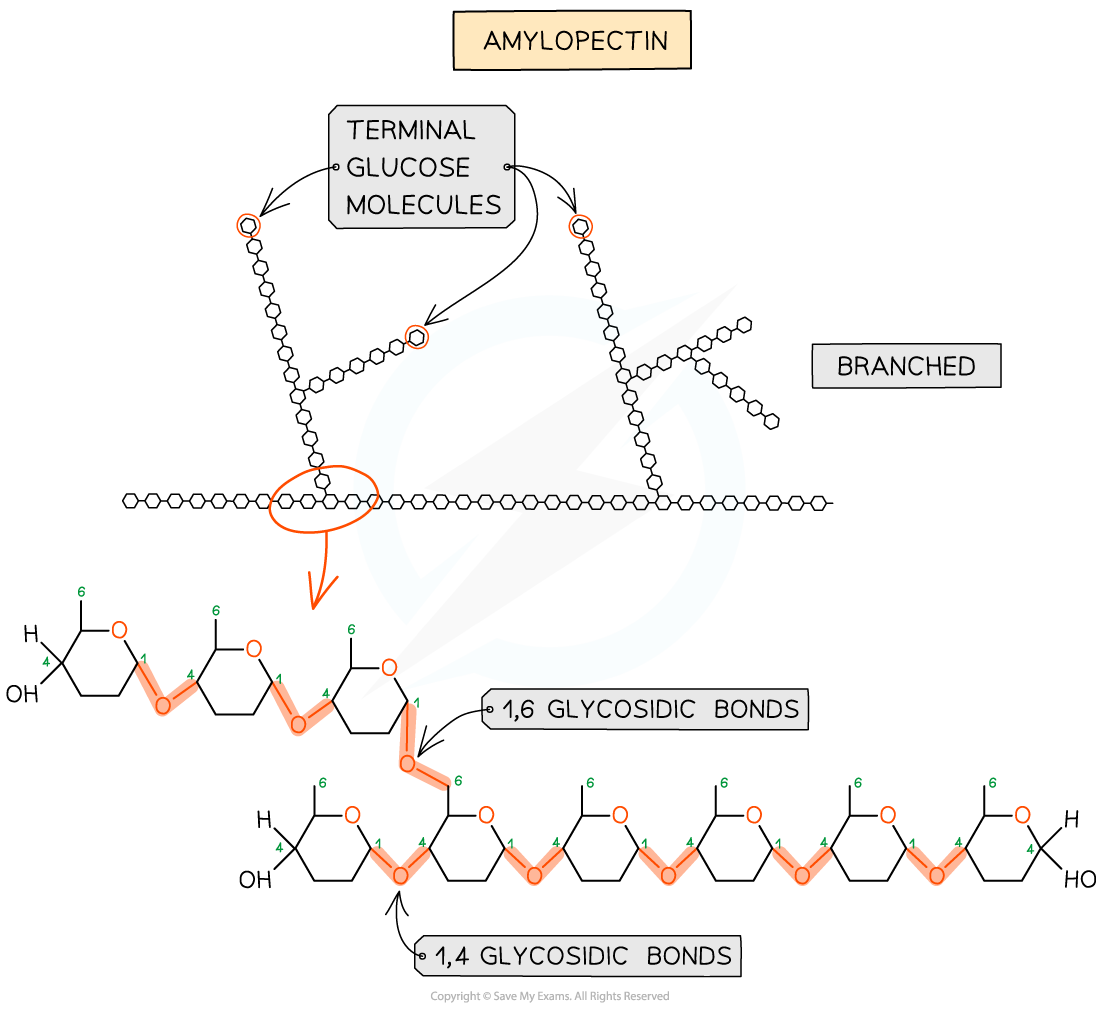
Both starch and glycogen are polymers of α-glucose , in which monosaccharides are joined by either 1,4 glycosidic bonds or 1, 6 glycosidic bonds
The presence of 1,6 glycosidic bonds means that starch and glycogen can be highly branched molecules
Both starch and glycogen:
can be compact
This means that large quantities can be stored in a small space
are insoluble
The molecules do not dissolve in cell cytoplasm, so they have no effect on the water potential of cells
exist in branched forms (glycogen is always branched while starch can be either branched or unbranched)
The branching means that there are more free ends where glucose molecules can either be added or removed
Hydrolysis and dehydration synthesis reactions can occur more rapidly, so the rate of storage or release of glucose can suit the energy demands of the cell
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember, you don't need to know the precise structures of the various sugar monomers and other carbohydrates. However, you should recognize that structure determines function, and you may see an AP question that presents different carbohydrate structures and asks you to determine their most likely functions.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
