Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2017
Last exams 2026
Assumptions & Key Concepts of SLT (AQA A Level Psychology): Revision Note
Exam code: 7182
Assumptions of social learning theory
Social learning theory (SLT) was proposed by Bandura (1972) as a more nuanced explanation of behaviourism
SLT takes the core principle of behaviourism - people are shaped by their environment - and refines it to include the mechanisms of how people (particularly children) learn from others
SLT posits the idea that children learn via:
observation of role models, particularly parents but also other significant people such as teachers, older siblings, celebrities
Role models tend to be older, influential figures who have high status or possess qualities the child aspires to e.g. being good at football
imitation of the behaviours observed from role models
social contexts i.e. learning is not innate but is absorbed via the child's environment such as the home, school, peer groups
Imitation, identification & modelling
The concept behind SLT:
The child observes the behaviour of a role model
If the behaviour is observed frequently the child imitates that behaviour
The imitated behaviour is performed in different contexts e.g.
a child observes domestic violence at home and goes on to imitate this sort of behaviour at school (bullying)
It is more likely that a child will imitate the behaviour of role models with whom they identify or who have similar characteristics to them e.g. same-sex parent or sibling, an attractive celebrity
Vicarious reinforcement
Reinforcement plays a role in SLT but it tends to be indirect, vicarious reinforcement rather than direct reinforcement e.g.
The child observes a specific behaviour from a role model e.g. an aggressive parent
The child sees that the aggressive parent is rewarded e.g. they have power over the other parent
The aggressive parent experiences positive direct reinforcement e.g. they got what they wanted, they feel good
The child identifies with the aggressive parent and internalises what they have just seen e.g. 'I want to feel like that'
Vicarious reinforcement has taken place
The child has observed the reward gained by the aggressive parent and is motivated to behave similarly to gain such a reward for themselves
The child may then go on to behave aggressively towards other children, particularly those who appear to be vulnerable
Vicarious reinforcement highlights the more sophisticated nature of SLT compared to behaviourism as it involves a degree of cognition
People are required to process what they have seen and imagine themselves gaining a similar reward for the specific behaviour
Mediational processes
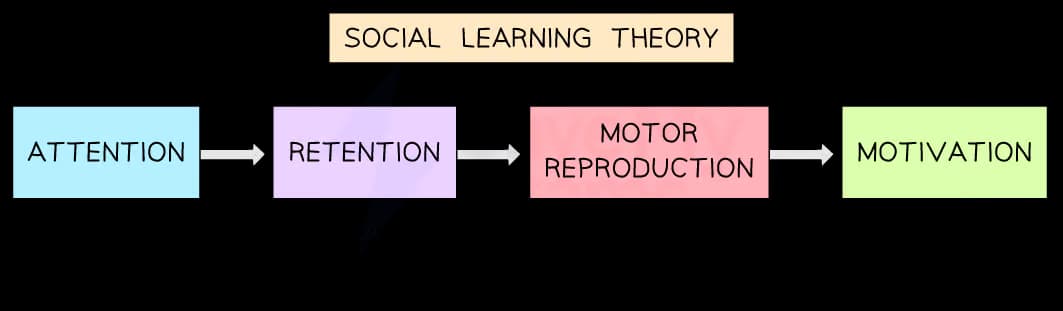
The cognitive element of SLT can be summed up via the mediational processes involved:
Attention-Retention-Reproduction-Motivation (ARRM):
Attention - noticing the behaviour, and being aware of it
Retention - remembering the behaviour and the mechanisms involved in it
Reproduction - imitating the behaviour, reproducing key features of it
Motivation - the desire to perform the behaviour, the need to be rewarded for the behaviour
Attention and retention refer to the learning of the behaviour
Reproduction and motivation refer to the performance of that behaviour
Learning and performance of the behaviour are not required to occur at the same time e.g. aggression observed in one setting may not be performed until some time later and in a different setting
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Students sometimes mistake vicarious reinforcement for direct reinforcement so do make sure that you emphasise the remote nature of vicarious reinforcement: it is the observation of other people being rewarded for a specific behaviour that triggers the motivation to imitate that behaviour in another setting.
Evaluation of assumptions & key concepts of SLT
Strengths
SLT provides a more 'rounded' explanation of how the environment shapes behaviour than that offered by behaviourism
This means that SLT is less reductionist than behaviourism
This means that SLT is also less deterministic than behaviourism as mediational processes imply that the individual has some choice over their behaviour
SLT has good application to the use of token economies in prison or health settings
The prisoner/patient is rewarded for 'good' behaviour with tokens
Observation of fellow prisoners/patients receiving rewards encourages good behaviour from others
Thus the theory has good external validity
Limitations
SLT cannot account for behaviours which are observed frequently and are not imitated e.g. a child who frequently observes domestic violence may never be violent towards anyone else
This means that SLT can offer only a limited explanation of behaviour as it does not acknowledge the role of individual differences as a factor
Research into SLT tends to consist of lab experiments
This is a limitation as SLT is an explanation of behaviour within social contexts
The controlled conditions of a lab experiment cannot hope to replicate real life thus such research lacks ecological validity

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?