The circuit diagram of an electrical circuit is shown below.
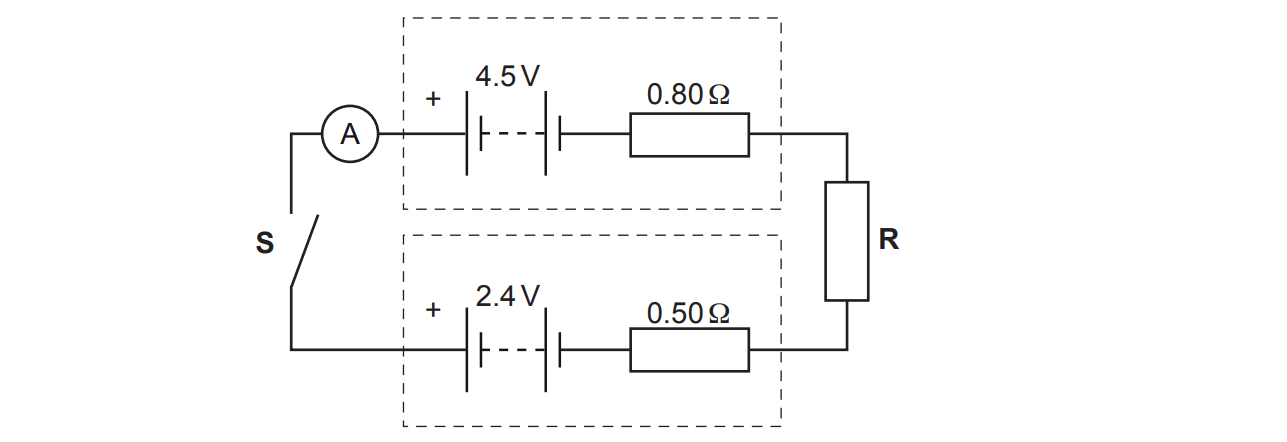
The positive terminals of the batteries are connected together.
One battery has electromotive force (e.m.f.) 4.5 V and internal resistance 0.80 Ω.
The other battery has e.m.f. 2.4 V and internal resistance 0.50 Ω.
R is a coil of insulated wire of resistance 1.2 Ω at room temperature.
The switch S is closed.
i) On the diagram, draw an arrow to show the direction of the conventional current.
[1]
ii) Calculate the current I shown by the ammeter.
I = ...................................................... A [3]
iii) The insulated wire has a diameter 4.6 × 10–4 m.
The number density of charge carriers in R is 4.2 × 1028 m–3.
Calculate the mean drift velocity v of the charge carriers in R.
v = ................................................ m s–1 [2]
iv) The current measured by the ammeter is smaller than that calculated in (ii). This is because the temperature of R increased due to heating by the current.
Without any changes to the circuit itself, state and explain what practically can be done to make the measured current the same as the calculated current.
[2]
A student is doing an experiment to determine the e.m.f. E of a cell and its internal resistance r.
The circuit diagram of the arrangement is shown below.
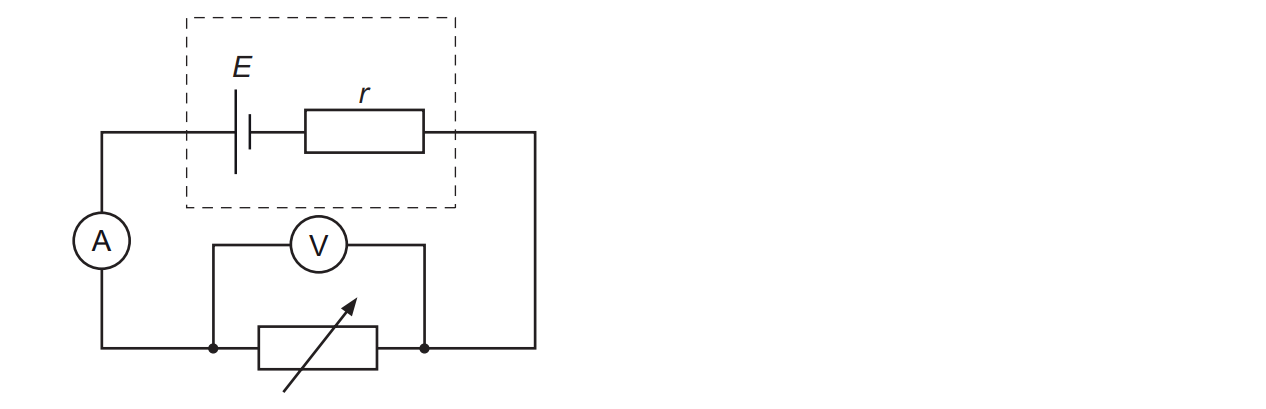
The student changes the resistance of the variable resistor. The potential difference V across the variable resistor and the current I in the circuit are measured.
The V against I graph plotted by the student is shown below.
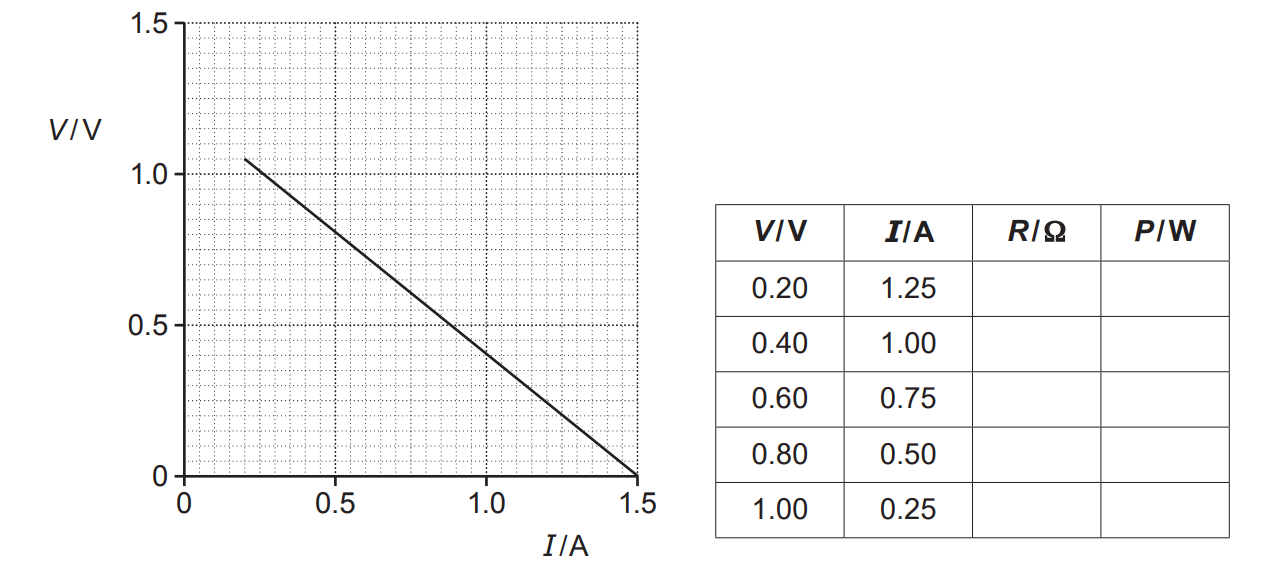
There is an incomplete table next to the graph.
R is the resistance of the variable resistor and P is the power dissipated by the variable resistor.
Use the graph to determine E and r. Explain your reasoning.
Calculate R and P to complete the table. Describe how P depends on R.
Did this page help you?




