The Quark Model (OCR A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: H556
Quark Model of Hadrons
Hadrons are a group of subatomic particles that are made up of quarks
These may be either a:
Baryon (3 quarks)
Meson (quark and anti-quark pair)

Hadrons may be either a baryon or a meson
Quarks have never been discovered on their own, always in pairs or groups of three
Anti-hadrons can be either
Anti-baryons (3 anti-quarks)
Anti-meson (quark and anti-quark pair)

Anti-hadrons may be either an anti-baryon or an anti-meson
Note that all baryons or mesons have integer (whole number) charges eg. +1e, -2e etc.
This means quarks in a baryon are either all quarks or all anti-quarks. Combination of quarks and anti-quarks don’t exist in a baryon
e.g.

The anti-particle of a meson is still a quark-antiquark pair. The difference being the quark becomes the anti-quark and vice versa
Worked Example
The baryon Δ++ was discovered in a particle accelerator using accelerated positive pions on hydrogen targets. Which of the following is the quark combination of this particle?


Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remembering quark combinations is useful for the exam. However, as long as you can remember the charges for each quark, it is possible to figure out the combination by making sure the combination of quarks add up to the charge of the particle (just like in the worked example)
Quark Model of the Proton and Neutron
Protons and neutrons are not fundamental particles. They are each made up of three quarks
Protons are made up of two up quarks and a down quark
Neutrons are made up of two down quarks and an up quark

Protons and neutrons are made up of three quarks
You will be expected to remember these quark combinations for exam questions
Worked Example
Answer:
Step 1: Calculate number of protons:
The number of protons is from the proton number = 26 protons
Step 2: Calculate number of neutrons:
The number of neutrons = nucleon number - proton number = 56 - 26 = 30 neutrons
Step 3: Up quarks in a proton:
Protons are made up of uud quarks = 2 up quarks
Step 4: Up quarks in a neutron:
Neutrons are made up of udd quarks = 1 up quark
Step 5: Total number of up quarks:
26 protons x 2 up quarks = 52 up quarks
30 neutrons x 1 up quark = 30 up quarks
52 + 30 = 82 up quarks
Charges of Quarks
Types of Quark
Quarks are fundamental particles that make up other subatomic particles such as protons and neutrons
Protons and neutrons are in a category of particles called hadrons
Hadrons are defined as any particle made up of quarks
Fundamental means that quarks are not made up of any other particles. Another example is electrons
Quarks have never been observed on their own, they’re either in pairs or groups of three
There are six flavours (types) of quarks that exist:
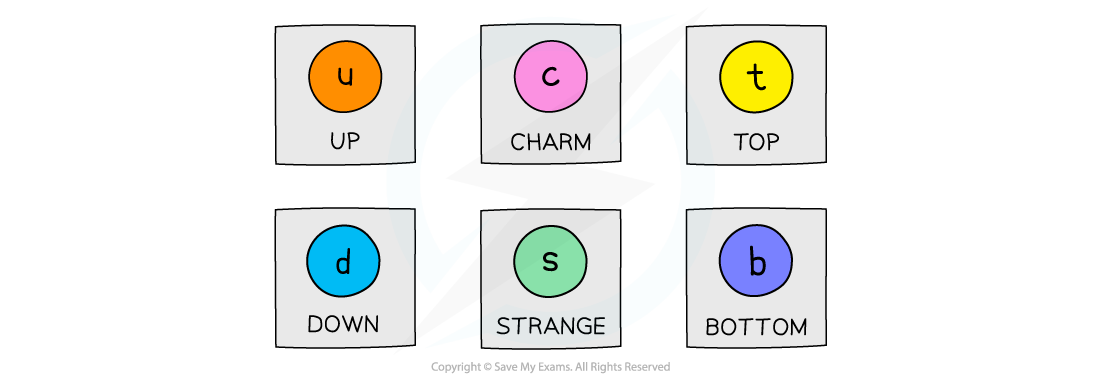
The six flavours of quarks
You only need to know about up, down and strange, as well as their antiquarks.
Charges of Quark
The charge of a hadron is determined by the sum of the charges of its quarks
Each flavour of quark has a certain relative charge:

Each flavour of quark has a charge of either +⅔e or -⅓e
You only need to know about up, down and strange, as well as their antiquarks.
For example, a proton is made up of two up quarks and a down quark. Adding up their charges gives the charge of a proton:
+⅔e + ⅔e - ⅓e = +1e
The equivalent antiparticle of the quark is the anti-quark
These are identical to quarks except with opposite relative charges

Each flavour of anti-quark has a charge of either -⅔e or +⅓e. The quark composition of anti-protons and anti-neutrons changes to anti-quarks
You only need to know about up, down and strange, as well as their antiquarks.
Worked Example
Particles are made up of a combination of three quarks or two quarks. Which quark combination would give a particle a charge of -1?
A. up, strange, strange
B. up, up, down
C. anti-up, anti-strange
D. anti-up, anti-up, anti-strange
Answer: D
Each answer option has the following quarks and charges:
A:
=
= 0
B:
=
= +1
C:
=
D:
=
We can see that the correct answer is D the combination anti-up, anti-up, anti-strange give a charge of -1
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You will be expected to remember the charge of each quark. However, instead of memorising the charges of anti-quarks too, just remember they are identical but with opposite signs.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?