The Piezoelectric Effect & Generating Ultrasound
- The piezoelectric effect is defined as:
The ability of particular materials to generate a potential difference (p.d.) by transferring mechanical energy to electrical energy
- This effect enables ultrasound generation and detection technology to exist in medicine

In the piezoelectric effect, an applied voltage causes a piezo-crystal to contract or expand, and vice versa
Piezoelectric Crystals
- At the heart of a piezoelectric transducer is a piezoelectric crystal
- A transducer is any device that converts energy from one form to another
- Piezoelectric crystals are materials which produce a p.d. when they are deformed
- This deformation can be by compression or stretching
- If a p.d. is applied to a piezoelectric crystal, then it deforms, and if the p.d. is reversed, then it expands
- If this is an alternating p.d. then the crystal will vibrate at the same frequency as the alternating voltage
- Crystals must be cut to a certain size in order to induce resonance
- One of the most common piezoelectric crystals is quartz, which is made from a lattice of silicon dioxide atoms
- When the lattice is distorted, the structure becomes charged creating an electric field and, as a result, an electric current
- If an electric current is applied to the crystal, then this causes the shape of the lattice to alternate which produces a sound wave
- Due to the conventional direction of electric current, it will flow from the positive to the negative region of the crystal

A molecule in a quartz crystal. When the compression and stretching alternates, an alternating e.m.f. is induced
Generating & Detecting Ultrasound
- An ultrasound transducer is made up of a piezoelectric crystal and electrodes which produce an alternating p.d.
- The crystal is heavily damped, usually with epoxy resin, to stop the crystal from vibrating too much
- This produces short pulses and increases the resolution of the ultrasound device

The structure of an ultrasound transducer
- A piezoelectric crystal can act as both a receiver or transmitter of ultrasound
- When it is receiving ultrasound, it converts the sound waves into an alternating p.d.
- When it is transmitting ultrasound, it converts an alternating p.d. into sound waves
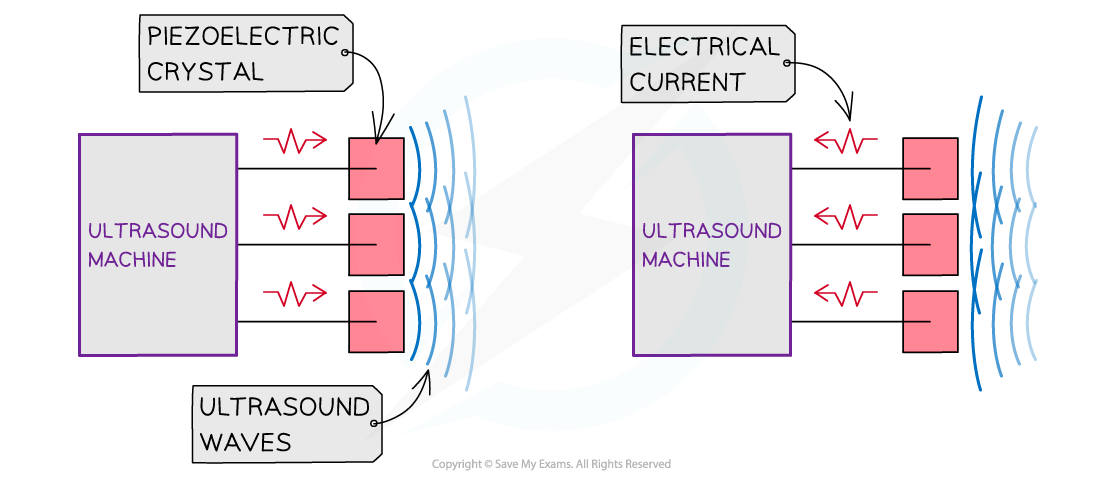
A piezoelectric crystal can act as both a receiver or transmitter of ultrasound
Worked example
Explain the principles of the generation and detection of ultrasound waves.
Generation:
-
- An alternating p.d. is applied across a piezoelectric crystal, causing it to change shape
- The alternating p.d. causes the crystal to vibrate and produce pulses of ultrasound waves
- The crystal vibrates at the frequency of the alternating p.d., so, the crystal must be cut to a specific size in order to produce resonance
Detection:
-
- The ultrasound pulse is reflected at the boundary of the tissue and returns to the transducer
- When the ultrasound wave returns, the crystal vibrates which produces an alternating p.d. across the crystal
- This received signal can then be processed and used for medical diagnosis

