Beta Minus & Beta Plus Decay (OCR A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: H556
Beta Minus and Beta Plus Decay
Beta decay happens via the weak interaction
This is one of the four fundamental forces and it’s responsible for radioactive decays
Beta-Minus Decay
A beta-minus, β-, particle is a high energy electron emitted from the nucleus
β- decay is when a neutron turns into a proton emitting an electron and an anti-electron neutrino
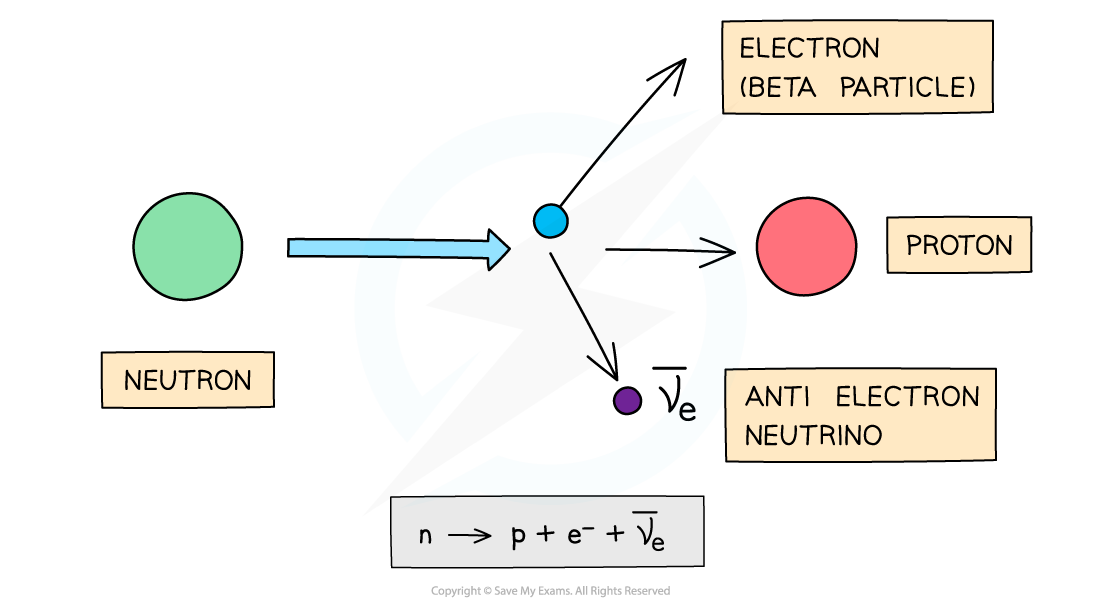
When a β- particle is emitted from a nucleus:
The number of protons increases by 1: proton number increases by 1
The total number of nucleons stays the same: nucleon number remains the same

Equation for beta minus emission
The new nucleus formed from the decay is called the “daughter” nucleus (nitrogen in the example above)
Beta-Plus Decay
A beta-plus, β+, particle is a high energy positron emitted from the nucleus
β+ decay is when a proton turns into a neutron emitting a positron (anti-electron) and an electron neutrino
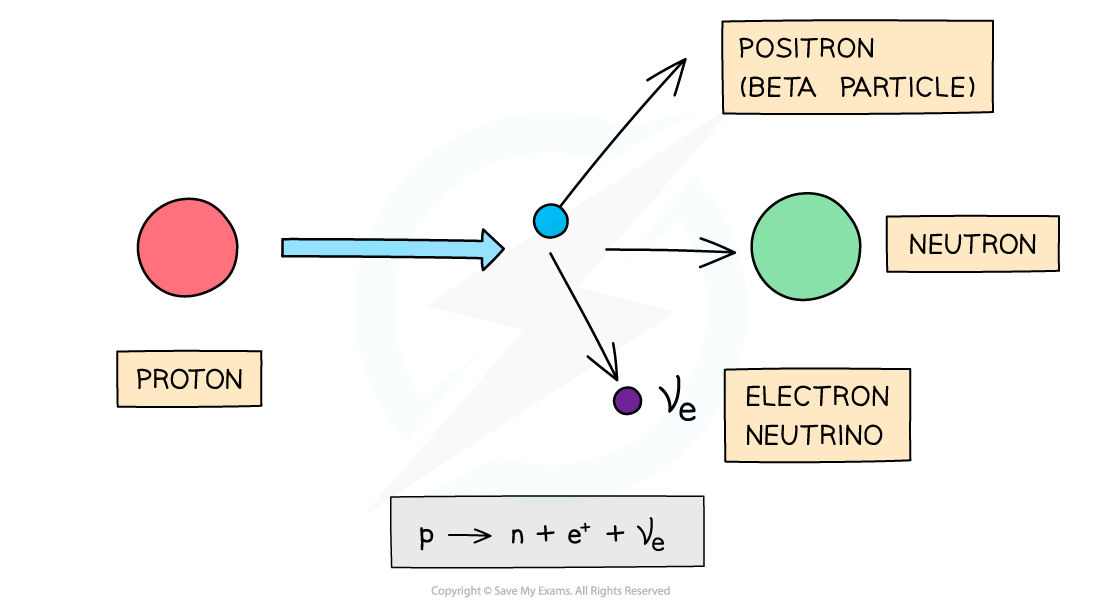
When a β+ particle is emitted from a nucleus:
The number of protons decreases by 1: proton number decreases by 1
The total number of nucleons stays the same: nucleon number remains the same

Equation for beta plus emission
Quark Model of Beta Minus Decay
Recall that β- decay is when a neutron turns into a proton emitting an electron and anti-electron neutrino
More specifically, a neutron turns into a proton because a down quark turning into an up quark

Beta minus decay is when a down quark turns into an up quark
Quark Model of Beta Plus Decay
Recall that β+ decay is when a proton turns into a neutron emitting an positron and an electron neutrino
More specifically, a proton turns into a neutron because an up quark turns into a down quark

Beta plus decay is when an up quark turns into a down quark

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
