Gravitational Field Lines (OCR A Level Physics) : Revision Note
Gravitational Field Lines
The direction of a gravitational field is represented by gravitational field lines
The direction shows the direction of force
Equivalently, they show the direction of acceleration of a test mass in the field
The gravitational field lines around a point mass are radially inwards
The gravitational field lines of a uniform field, where the field strength is the same at all points, is represented by equally spaced parallel lines
For example, the fields lines on the Earth’s surface
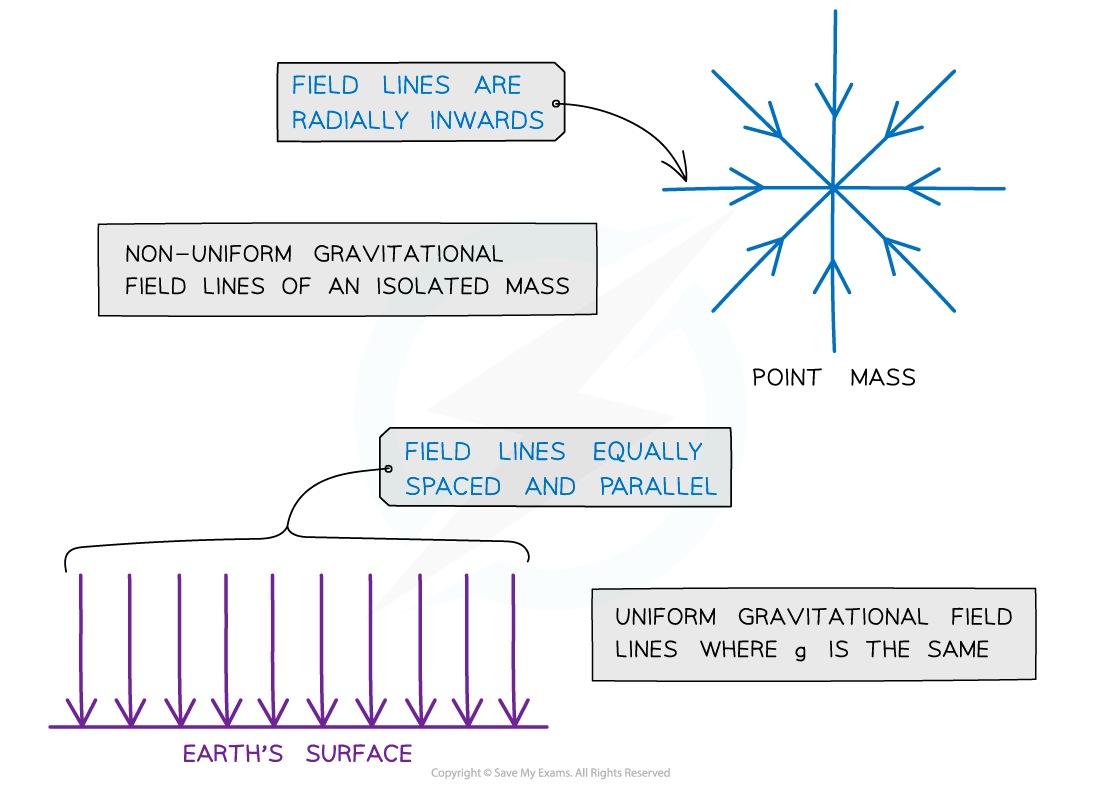
Gravitational field lines for a point mass and a uniform gravitational field
Radial fields are considered non-uniform fields
The gravitational field strength g is different depending on how far you are from the centre
Parallel field lines on the Earth’s surface are considered a uniform field
The gravitational field strength g is the same throughout
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You should be able to link gravitational field lines with vectors: the density of gravitational field lines show the magnitude of the field (i.e., the closer they are, the stronger the field), and they also indicate the field's direction.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
