Centripetal Acceleration (OCR A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: H556
Centripetal Acceleration
Centripetal acceleration is defined as:
The acceleration of an object towards the centre of a circle when an object is in motion (rotating) around a circle at a constant speed
It can be defined using the radius r and linear speed v:
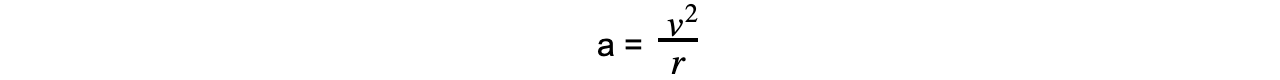
Using the equation relating angular speed ω and linear speed v:
v = r⍵
These equations can be combined to give another form of the centripetal acceleration equation:
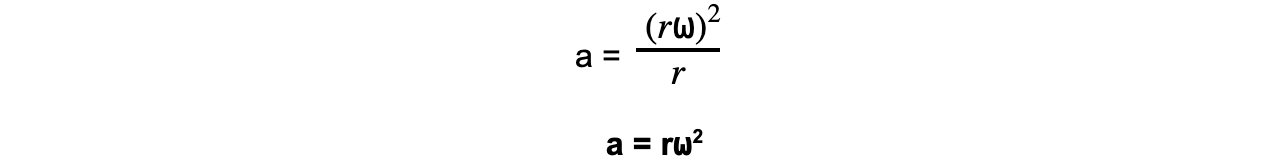
This equation shows that centripetal acceleration is equal to the radius times the square of the angular speed
Alternatively, rearrange for r:
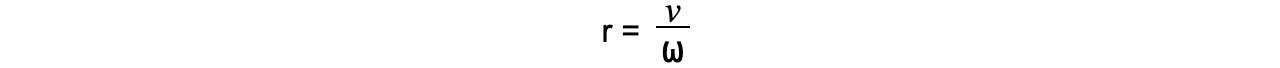
This equation can be combined with the first one to give us another form of the centripetal acceleration equation:
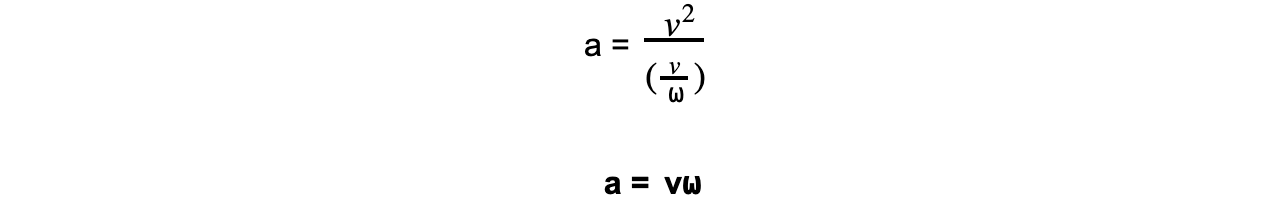
This equation shows how the centripetal acceleration relates to the linear speed and the angular speed
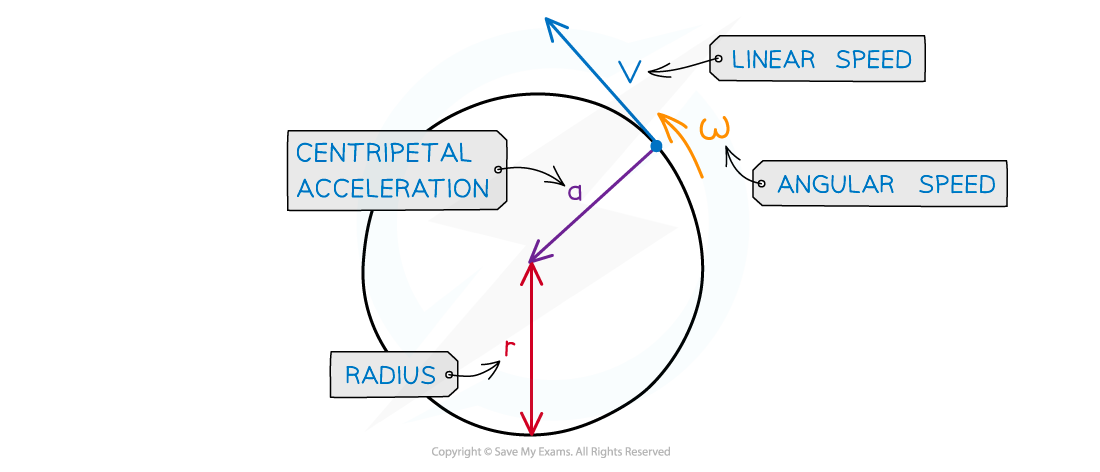
Centripetal acceleration is always directed toward the centre of the circle, and is perpendicular to the object’s velocity
Where:
a = centripetal acceleration (m s−2)
v = linear speed (m s−1)
⍵ = angular speed (rad s−1)
r = radius of the orbit (m)
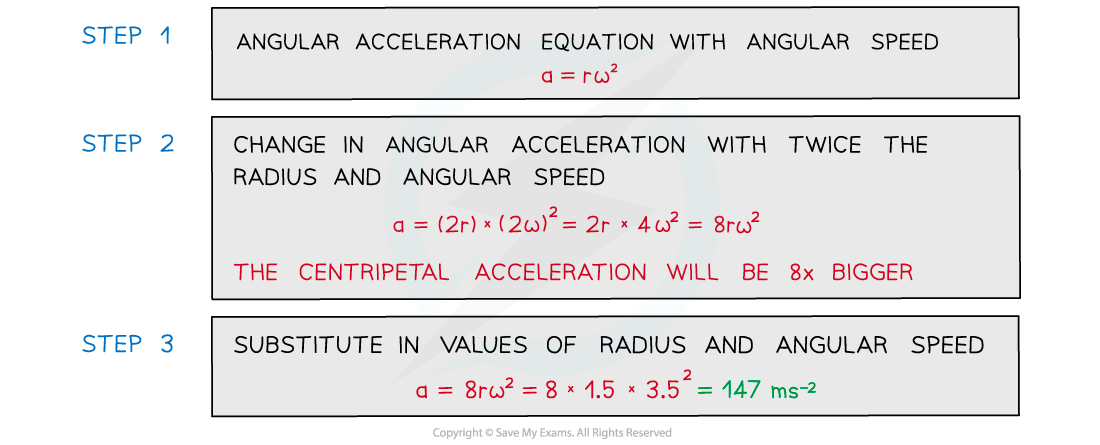
Worked Example
A ball tied to a string is rotating in a horizontal circle with a radius of 1.5 m and an angular speed of 3.5 rad s−1.
Calculate its centripetal acceleration if the radius was twice as large and angular speed was twice as fast.
Answer:

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?